Abstract
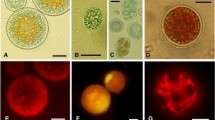
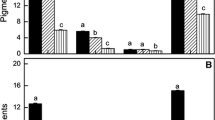
The green unicellular alga, Haematococcus pluvialis has two antioxidative mechanisms against environmental oxidative stress: antioxidative enzymes in vegetative cells and the antioxidative ketocarotenoid, astaxanthin, in cyst cells. We added a reagent that generates superoxide anion radicals (O2 −), methyl viologen, to mature and immature cysts of H. pluvialis. Tolerance to methyl viologen was higher in mature than in immature cysts. Mature (astaxanthin-rich) cysts showed high antioxidant activity against O2 − in permeabilized cells, but not in astaxanthin-free cell extracts, while immature (astaxanthin-poor) cysts had very low antioxidant activities against O2 − in both. The results suggested that astaxanthin accumulated in the cyst cells functions as an antioxidant against excessive oxidative stress. The same levels of antioxidant activities against O2 − in both permeabilized cells and cell extracts from vegetative cells suggested the presence of antioxidative enzymes (superoxide dismutase).
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 13 January 1997 / Received revision: 26 February 1997 / Accepted: 27 March 1997
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kobayashi, M., Kakizono, T., Nishio, N. et al. Antioxidant role of astaxanthin in the green alga Haematococcus pluvialis . Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 48, 351–356 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1007/s002530051061
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s002530051061