Abstract
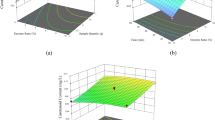
Agro-industrial by-products are a sustainable source of natural additives that can replace the synthetic ones in the food industry. Grape pomace is an abundant by-product that contains about 70% of the grape’s polyphenols. Polyphenols are natural antioxidants with multiple health-promoting properties. They are secondary plant metabolites with a wide range of solubilities. Here, a novel extraction process of these compounds was developed using enzymes that specifically liberates target polyphenols in the appropriate hydroalcoholic mixture. Tannase, cellulase, and pectinase retained 22, 60, and 52% of their activity, respectively, in ethanol 30% v/v. Therefore, extractions were tested in ethanol concentrations between 0 and 30% v/v. Some of these enzymes presented synergistic effects in the extraction of specific polyphenols. Maximum yield of gallic acid was obtained using tannase and pectinase enzymes in ethanol 10% v/v (49.56 ± 0.01 mg L−1 h−1); in the case of p-coumaric acid, by cellulase and pectinase treatment in ethanol 30% v/v (7.72 ± 0.26 mg L−1 h−1), and in the case of trans-resveratrol, by pectinase treatment in ethanol 30% v/v (0.98 ± 0.04 mg L−1 h−1). Also, the effect of enzymes and solvent polarity was analysed for the extraction of malvidin-3-O-glucoside, syringic acid, and quercetin. Previous studies were mainly focused on the maximization of total polyphenols extraction yields, being the polyphenolic profile the consequence but not the driving force of the optimization. In the present study, the basis of a platform for a precise extraction of the desire polyphenols is provided.
Key points
• Enzymes can be used up to ethanol 30% v/v.
• The specific enzymes’ action determines the polyphenolic profile of the extracts.
• The yields obtained of target polyphenols are competitive.
Graphical Abstract






Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets generated during and/or analysed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Ainsworth EA, Gillespie KM (2007) Estimation of total phenolic content and other oxidation substrates in plant tissues using Folin-Ciocalteu reagent. Nat Protoc 2:875–877. https://doi.org/10.1038/nprot.2007.102
Antoniolli A, Fontana AR, Piccoli P, Bottini R (2015) Characterization of polyphenols and evaluation of antioxidant capacity in grape pomace of the cv. Malbec Food Chem 178:172–178. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2015.01.082
Averilla JN, Oh J, Wu Z, Liu K, Jang CH, Kim HJ, Kim J, Kim J (2019) Improved extraction of resveratrol and antioxidants from grape peel using heat and enzymatic treatments. J Sci Food Agric 99:4043–4053. https://doi.org/10.1002/jsfa.9632
Badhani B, Sharma N, Kakkar R (2015) Gallic acid: a versatile antioxidant with promising therapeutic and industrial applications. RSC Adv 5:27540–27557. https://doi.org/10.1039/C5RA01911G
Beres C, Costa GNS, Cabezudo I, da Silva-James NK, Teles ASC, Cruz APG, Mellinger-Silva C, Tonon RV, Cabral LMC, Freitas SP (2017) Towards integral utilization of grape pomace from winemaking process: a review. Waste Manag 68:581–594. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2017.07.017
Borja GM, Rodriguez A, Campbell K, Borodina I, Chen Y, Nielsen J (2019) Metabolic engineering and transcriptomic analysis of Saccharomyces cerevisiae producing p-coumaric acid from xylose. Microb Cell Fact 18:191. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12934-019-1244-4
Brazinha C, Cadima M, Crespo JG (2014) Optimization of extraction of bioactive compounds from different types of grape pomace produced at wineries and distilleries. J Food Sci 79:E1142–E1149. https://doi.org/10.1111/1750-3841.12476
Chamorro S, Viveros A, Alvarez I, Vega E, Brenes A (2012) Changes in polyphenol and polysaccharide content of grape seed extract and grape pomace after enzymatic treatment. Food Chem 133:308–314. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2012.01.031
Devesa-Rey R, Vecino X, Varela-Alende JL, Barral MT, Cruz JM, Moldes AB (2011) Valorization of winery waste vs. the costs of not recycling. Waste Manag 31:2327–2335. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2011.06.001
Dwyer K, Hosseinian F, Rod M (2014) The market potential of grape waste alternatives. J Food Res 3:91. https://doi.org/10.5539/jfr.v3n2p91
Fernández-Fernández AM, Iriondo-DeHond A, Dellacassa E, Medrano-Fernandez A, del Castillo MD (2019) Assessment of antioxidant, antidiabetic, antiobesity, and anti-inflammatory properties of a Tannat winemaking by-product. Eur Food Res Technol 245:1539–1551. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00217-019-03252-w
Ferri M, Rondini G, Calabretta MM, Michelini E, Vallini V, Fava F, Roda A, Minnucci G, Tassoni A (2017) White grape pomace extracts, obtained by a sequential enzymatic plus ethanol-based extraction, exert antioxidant, anti-tyrosinase and anti-inflammatory activities. N Biotechnol 39:51–58. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nbt.2017.07.002
Fontana AR, Antoniolli A, Bottini R (2013) Grape pomace as a sustainable source of bioactive compounds: extraction, characterization, and biotechnological applications of phenolics. J Agric Food Chem 61:8987–9003. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf402586f
Ignat I, Volf I, Popa VI (2011) A critical review of methods for characterisation of polyphenolic compounds in fruits and vegetables. Food Chem 126:1821–1835. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2010.12.026
Kammerer D, Claus A, Schieber A, Carle R (2005) A novel process for the recovery of polyphenols from grape (Vitis vinifera) pomace. J Food Sci 70:C157–C163. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2621.2005.tb07077.x
Kanpiengjai A, Khanongnuch C, Lumyong S, Haltrich D, Nguyen T-H, Kittibunchakul S (2020) Co-production of gallic acid and a novel cell-associated tannase by a pigment-producing yeast, Sporidiobolus ruineniae A45.2. Microb Cell Fact 19:95. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12934-020-01353-w
Kuo C-H, Chen B-Y, Liu Y-C, Chen J-H, Shieh C-J (2016) Production of resveratrol by piceid deglycosylation using cellulase. Catalysts 6:32. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal6030032
Marco M-G, Rodríguez LV, Ramos EL, Renovato J (2009) A novel tannase from the xerophilic fungus Aspergillus niger GH1. J Microbiol Biotechnol 19:987–996. https://doi.org/10.4014/jmb.0811.615
Martins IM, Roberto BS, Blumberg JB, Chen C-YO, Macedo GA (2016) Enzymatic biotransformation of polyphenolics increases antioxidant activity of red and white grape pomace. Food Res Int 89:533–539. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodres.2016.09.009
Meini M-R, Cabezudo I, Boschetti CE, Romanini D (2019) Recovery of phenolic antioxidants from Syrah grape pomace through the optimization of an enzymatic extraction process. Food Chem 283:257–264. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2019.01.037
Meini M-R, Cabezudo I, Galetto CS, Romanini D (2021) Production of grape pomace extracts with enhanced antioxidant and prebiotic activities through solid-state fermentation by Aspergillus niger and Aspergillus oryzae. Food Biosci 42:101168. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fbio.2021.101168
Milke L, Aschenbrenner J, Marienhagen J, Kallscheuer N (2018) Production of plant-derived polyphenols in microorganisms: current state and perspectives. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 102:1575–1585. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-018-8747-5
Miller GL (1959) Use of dinitrosalicylic acid reagent for determination of reducing sugar. Anal Chem 31:426–428. https://doi.org/10.1021/ac60147a030
Monteiro LMO, Pereira MG, Vici AC, Heinen PR, Buckeridge MS, de Polizeli M, LT de M, (2019) Efficient hydrolysis of wine and grape juice anthocyanins by Malbranchea pulchella β-glucosidase immobilized on MANAE-agarose and ConA-Sepharose supports. Int J Biol Macromol 136:1133–1141. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2019.06.106
Moro KIB, Bender ABB, da Silva LP, Penna NG (2021) Green extraction methods and microencapsulation technologies of phenolic compounds from grape pomace: a review. Food Bioprocess Technol 14:1407–1431. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11947-021-02665-4
Nguyen HQ, Quyen DT (2012) Purification and properties of an endoglucanase from Aspergillus oryzae VTCC-F045. Austr J Basic Appl Sci 4:6217–6222
Pandey KB, Rizvi SI (2009) Plant polyphenols as dietary antioxidants in human health and disease. Oxid Med Cell Longev 2:270–278. https://doi.org/10.4161/oxim.2.5.9498
Pham TH, Quyen DT, Nghiem NM (2012) Purification and properties of an endoglucanase from Aspergillus niger VTCC-F021. Turk J Biol 36:694–701
Pinelo M, Arnous A, Meyer AS (2006) Upgrading of grape skins: significance of plant cell-wall structural components and extraction techniques for phenol release. Trends Food Sci Technol 17:579–590. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tifs.2006.05.003
Pino-García R del, Porrelli A, Rus-Fernández P, Segura-Carretero A, Curiel JA (2020) Identification, purification and characterization of a novel glycosidase (BgLm1) from Leuconostoc mesenteroides. LWT 122:108829. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lwt.2019.108829
Puri M, Sharma D, Barrow CJ (2012) Enzyme-assisted extraction of bioactives from plants. Trends Biotechnol 30:37–44. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tibtech.2011.06.014
Re R, Pellegrini N, Proteggente A, Pannala A, Yang M, Rice-Evans C (1999) Antioxidant activity applying an improved ABTS radical cation decolorization assay. Free Radic Biol Med 26:1231–1237. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0891-5849(98)00315-3
Reynolds A, Knox A, Di Profio F (2018) Evaluation of macerating pectinase enzyme activity under various temperature, pH and ethanol regimes. Beverages 4:10. https://doi.org/10.3390/beverages4010010
Robbins RJ (2003) Phenolic acids in foods: an overview of analytical methodology. J Agric Food Chem 51:2866–2887. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf026182t
Sharma S, Bhat TK, Dawra RK (2000) A spectrophotometric method for assay of tannase using Rhodanine. Anal Biochem 279:85–89. https://doi.org/10.1006/abio.1999.4405
Sirohi R, Tarafdar A, Singh S, Negi T, Gaur VK, Gnansounou E, Bharathiraja B (2020) Green processing and biotechnological potential of grape pomace: current trends and opportunities for sustainable biorefinery. Bioresour Technol 314:123771. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2020.123771
Sri Harsha PSC, Gardana C, Simonetti P, Spigno G, Lavelli V (2013) Characterization of phenolics, in vitro reducing capacity and anti-glycation activity of red grape skins recovered from winemaking by-products. Bioresour Technol 140:263–268. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2013.04.092
Ueda JM, Pedrosa MC, Heleno SA, Carocho M, Ferreira ICFR, Barros L (2022) Food additives from fruit and vegetable by-products and bio-residues: a comprehensive review focused on sustainability. Sustainability 14:5212. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14095212
Unterkofler J, Muhlack RA, Jeffery DW (2020) Processes and purposes of extraction of grape components during winemaking: current state and perspectives. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 104:4737–4755. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-020-10558-3
van Schie MMCH, Spöring J-D, Bocola M, Domínguez de María P, Rother D (2021) Applied biocatalysis beyond just buffers – from aqueous to unconventional media. Options and Guidelines Green Chem 23:3191–3206. https://doi.org/10.1039/D1GC00561H
Wang C, Liu X, Zhang M, Shao H, Zhang M, Wang X, Wang Q, Bao Z, Fan X, Li H (2019) Efficient enzyme-assisted extraction and conversion of polydatin to resveratrol from Polygonum cuspidatum using thermostable cellulase and immobilized β-glucosidase. Front Microbiol 10:445. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2019.00445
Xavier Machado T de O, Portugal IBM, Padilha CV da S, Ferreira Padilha F, dos Santos Lima M (2021) New trends in the use of enzymes for the recovery of polyphenols in grape byproducts. J Food Biochem 45. https://doi.org/10.1111/jfbc.13712
Xu F, Sun R-C, Sun J-X, Liu C-F, He B-H, Fan J-S (2005) Determination of cell wall ferulic and p-coumaric acids in sugarcane bagasse. Anal Chim Acta 552:207–217. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2005.07.037
Yuan S-F, Yi X, Johnston TG, Alper HS (2020) De novo resveratrol production through modular engineering of an Escherichia coli–Saccharomyces cerevisiae co-culture. Microb Cell Fact 19:143. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12934-020-01401-5
Zhang G, Hu M, He L, Fu P, Wang L, Zhou J (2013) Optimization of microwave-assisted enzymatic extraction of polyphenols from waste peanut shells and evaluation of its antioxidant and antibacterial activities in vitro. Food Bioprod Process 91:158–168. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fbp.2012.09.003
Zhou J, Liang M, Lin Y, Pang H, Wei Y, Huang R, Du L (2022) Application of β-glucosidase in a biphasic system for the efficient conversion of polydatin to resveratrol. Molecules 27:1514. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27051514
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank BordeRío Bodega & Viñedos, Argentina, for supplying the grape pomace and Kikkoman, Japan, for supplying a free sample of tannase preparation. This work was supported by grants from Agencia Nacional de Promoción Científica y Tecnológica, Argentina [PICT 2020 SERIE A-00445], Consejo Nacional de Investigaciones Científicas y Técnicas (CONICET), Argentina [PIP 11220200103120], Agencia Santafesina de Ciencia Tecnología e Innovación [DTT-2021-065], and Universidad Nacional de Rosario [ViTec 2021, 0020190100061/111UR]. MRM and DR are staff members of CONICET, and DMP is recipient of a doctoral fellowship from CONICET.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization: MRM, DMP, DR. Methodology: MRM, DMP. Formal analysis and investigation: DMP. Writing—original draft preparation: DMP. Writing—review and editing: MRM. Funding acquisition: MRM, DR. Resources: MRM, DR. Supervision: MRM, DR.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human or animals performed by any of the authors.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Piazza, D.M., Romanini, D. & Meini, MR. High-efficiency novel extraction process of target polyphenols using enzymes in hydroalcoholic media. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 107, 1205–1216 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-023-12386-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-023-12386-7