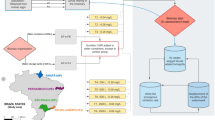
Abstract
Entomopathogenic fungi can achieve important innovative outcomes for integrated mosquito control especially of Aedes aegypti, the key vector of arboviruses to humans in the tropics and subtropics. This study sought to design and to develop a simple dissemination device to attract and to infect gravid A. aegypti adults with a granular formulation of the ascomycete Metarhizium humberi IP 46, and to validate this device in the laboratory as well as in semi-field and field conditions. Hydrogel (polyacrylamide potassium polyacrylate) was confirmed to be a suitable substitute for water used in the device that attracted gravid females under field conditions. Females laid eggs on black polyethylene terephthalate carpet fixed in the device that also proved to be a suitable substrate for a granular formulation of fungal microsclerotia and/or conidia. The plastic device (29.5 cm high) was divided into a lower closed compartment with a water reservoir and an upper, laterally open but covered compartment with continuously hydrated gel and the fungal formulation attached to the carpet. The uppermost compartment permitted free circulation of mosquito adults. The device attracted both male and female A. aegypti. The fungal formulations of IP 46 propagules tested in the device were effective against adults in laboratory, semi-field, and field settings. Findings in the laboratory, semi-field, and especially in field conditions strengthen the value and utility of this innovative device for focal applications of a mycoinsecticide against this important mosquito vector.
Key points
• Low-cost and simple disseminating device for focal control of Aedes aegypti.
• Granulized Metarhizium humberi IP 46 and hydrogel yield extended control.
• Findings in field tests strengthen benefit of the device for focal application.
Graphical abstract






Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Data available on request.
References
Albeny-Simões D, Murrell EG, Elliot SL, Andrade MR, Lima E, Juliano AS, Vilela EF (2014) Attracted to the enemy: Aedes aegypti prefers oviposition sites with predator-killed conspecifics. Oecologia 175:481–492. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00442-014-2910-1
Albernaz DAS, Tai MHH, Luz C (2009) Enhanced ovicidal activity of an oil formulation of the fungus Metarhizium anisopliae on the mosquito Aedes aegypti. Med Vet Entomol 23:141–147. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2915.2008.00792.x
Arbaoui AA, Chua TH (2014) Bacteria as a source of oviposition attractant for Aedes aegypti mosquitoes. Trop Biomed 31:134–142
Barrera R, MacKay AJ, Amador M (2013) A novel autocidal ovitrap for the surveillance and control of Aedes aegypti. J Am Mosquito Contr 29:293–296. https://doi.org/10.2987/13-6345R.1
Brady OJ, Hay SI (2020) The global expansion of Dengue: how Aedes aegypti mosquitoes enabled the first pandemic arbovirus. Annu Rev Entomol 65:191–208. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-ento-011019-024918
Buckner EA, Williams KF, Marsicano AL, Latham MD, Lesser CR (2017) Evaluating the vector control potential of the In2care mosquito trap against Aedes aegypti and Aedes albopictus under semifield conditions in Manatee County, Florida. J Am Mosqu Control Assoc 33:193–199. https://doi.org/10.2987/17-6642R.1
Consoli RAGB, Oliveira RL (1994) Principais mosquitos de importância sanitária no Brasil. Editora Fiocruz, Rio de Janeiro, 228. https://doi.org/10.7476/9788575412909
Donatti JE, Gomes AC (2007) Adultrap: Descrição de armadilha para adulto de Aedes aegypti (Diptera, Culicidae). Rev Bras Entomol 51:255–256. https://doi.org/10.1590/S0085-56262007000200019
Fay RW, Eliason DAA (1966) Preferred oviposition sites as a surveillance method for Aedes aegypti. Mosq News 26:531–535
Fernandes ÉKK, Marreto RN, Luz C, Catão AML, Paixão FRS, Santos TR, Mascarin GM (2017) Composição e processo de preparação multiparticulada de natureza sólida contendo microescleródios de Metarhizium anisopliae para controle de artrópodes-praga de importância na saúde humana, veterinária e na agropecuária e seus usos. Patent applied in Brazil BR1020170040615
Freitas RM, Codeço CT, Oliveira RL (2007) Daily survival rates and dispersal of Aedes aegypti females in Rio de Janeiro, Brazil. Am J Trop Med Hyg 76:659–665. https://doi.org/10.4269/ajtmh.2007.76.659
García-Munguía AM, Garza-Hernández JA, Rebollar-Tellez EA, Rodríguez-Pérez MA, Reyes-Villanueva F (2011) Transmission of Beauveria bassiana from male to female Aedes aegypti mosquitoes. Parasit Vectors 24. https://doi.org/10.1186/1756-3305-4-24
Harrington LC, Scott TW, Lerdthusnee K, Coleman RC, Costero A, Clark GG, Jones JJ, Kitthawee S, Kittayapong P, Sithiprasasna R, Edman JD (2005) Dispersal of the dengue vector Aedes aegypti within and between rural communities. Am J Trop Med Hyg 72:209–220. https://doi.org/10.4269/ajtmh.2005.72.209
Jackson MA, Jaronski ST (2009) Production of microsclerotia of the fungal entomopathogen Metarhizium anisopliae and their potential for use as a biocontrol agent for soil-inhabiting insects. Mycol Res 113:842–850. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mycres.2009.03.004
Kumawat R, Singh KV, Bansal SK, Singh H (2014) Use of different coloured ovitraps in the surveillance of Aedes mosquitoes in an arid-urban area of western Rajasthan, India. J Vector Borne Dis 51:320–326
Leles RN, López LCC, García JJ, Fernandes EKK, Luz C (2013) A simple method for the detection of Leptolegnia chapmanii from infected Aedes aegypti larvae. Can J Microbiol 59:425–429. https://doi.org/10.1139/cjm-2012-0703
Lima WP, Neto FC, Macoris MLG, Zuccari DAPC, Dibo MR (2009) Estabelecimento de metodologia para alimentação de Aedes aegypti (Diptera-Culicidae) em camundongos swiss e avaliação da toxicidade e do efeito residual do óleo essencial de Tagetes minuta L. (Asteraceae) em populações de Aedes aegypti. Rev Soc Bras Med 42:638–641. https://doi.org/10.1590/S0037-86822009000600005
Liu YL, Zhai XZ, Oluwafemi AR, Zhang HY (2014) Influence of substrate color on oviposition behavior, egg hatchability, and substance of egg origin in the mosquito Anopheles sinensis (Wiedemann) (Diptera: Culicidae). Neotrop Entomol 43:483–487. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13744-014-0236-7
Lobo LS, Rodrigues J, Luz C (2016) Effectiveness of Metarhizium anisopliae formulations against dengue vectors under laboratory and field conditions. Biocontr Sci Technol 26:386–401. https://doi.org/10.1080/09583157.2015.1123220
Lovett B, Bilgo E, Millogo SA, Ouattarra AK, Sare I, Gnambani EJ, Dabire RK, Diabate A, St Leger RJ (2019) Transgenic Metarhizium rapidly kills mosquitoes in a malaria-endemic region of Burkina Faso. Science 364:894–897. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.aaw8737
Luz C, Rocha LFN, Montalva C, Souza DA, Botelho ABRZ, Lopes RB, Faria M, Delalibera IJ (2019) Metarhizium humberi sp. nov. (Hypocreales: Clavicipitaceae), a new member of the PARB clade in the Metarhizium anisopliae complex from Latin America. J Invertebr Pathol 166:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jip.2019.107216
Madeira NG, Macharelli CA, Carvalho LR (2002) Variation of the oviposition preferences of Aedes aegypti in function of substratum and humidity. Mem Inst Oswaldo Cruz 97:415–420. https://doi.org/10.1590/S007402762002000300025
Mascarin GM, Kobori NN, Vital RCJ, Jackson MA, Quintela ED (2014) Production of microsclerotia by Brazilian strains of Metarhizium spp. using submerged liquid culture fermentation. World J Microb Biot 30:1583–1590. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-013-1581-0
Mnyone LL, Kirby MJ, Lwetoijera DW, Mpingwa MW, Knols BGJ, Takken W, Russell TL (2009) Infection of the malaria mosquito, Anopheles gambiae, with two species of entomopathogenic fungi: effects of concentration, co-formulation, exposure time and persistence. Malar J 8:309. https://doi.org/10.1186/1475-2875-8-309
Navarro-Silva MA, Marques FA, Duque JEL (2009) Review of semiochemicals that mediate the oviposition of mosquitoes: a possible sustainable tool for the control and monitoring of Culicidae. Rev Bras Entomol 53:1–6. https://doi.org/10.1590/S0085-56262009000100002
Paula AR, Brito ES, Pereira CR, Carrera MP, Samuels RI (2008) Susceptibility of adult Aedes aegypti (Diptera: Culicidae) to infection by Metarhizium anisopliae and Beauveria bassiana: prospects for Dengue vector control. Biocontr Sci Technol 8:1017–1025. https://doi.org/10.1080/09583150802509199
Ponnusamy L, Schal C, Wesson DM, Arellano C, Apperson CS (2015) Oviposition responses of Aedes mosquitoes to bacterial isolates from attractive bamboo infusions. Parasit Vectors 8:486. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13071-015-1068-y
Reiter P, Amador MA, Colon N (1991) Enhancement of the CDC ovitrap with hay infusions for daily monitoring of Aedes aegypti populations. J Am Mosquito Contr 7:52–55
Reyes-Villanueva F, Garza-Hernandez JA, Garcia-Munguia AM, Tamez-Guerra P, Howard AFV, Rodriguez-Perez MA (2011) Dissemination of Metarhizium anisopliae of low and high virulence by mating behavior in Aedes aegypti. Parasit Vectors 4:171. https://doi.org/10.1186/1756-3305-4-171
Rocha LFN, Inglis PW, Humber RA, Kipnis A, Luz C (2013) Occurrence of Metarhizium spp. in Central Brazilian soils. J Basic Microbiol 52:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1002/jobm.201100482
Rocha LFN, Sousa NA, Rodrigues J, Catão AML, Marques CS, Fernandes ÉKK, Luz C (2015) Efficacy of Tolypocladium cylindrosporum against Aedes aegypti eggs, larvae and adults. J Appl Microbiol 119:1412–1419. https://doi.org/10.1111/jam.12945
Rodrigues J, Borges PR, Fernandes ÉKK, Luz C (2019) Activity of additives and their effect in formulations of Metarhizium anisopliae s.l. IP 46 against Aedes aegypti adults and on post mortem conidiogenesis. Acta Trop 193:192–198. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actatropica.2019.03.002
Rodrigues J, Catão AML, Santos AS, Paixão FRS, Santos TR, Martinez JM, Marreto RN, Mascarin GM, Fernandes ÉKK, Luz C (2021) Relative humidity impacts development and activity against Aedes aegypti adults by granular formulations of Metarhizium humberi microsclerotia. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 105:2725–2736. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-021-11157-6
Roiz D, Wilson AL, Scott TW, Fonseca DM, Jourdain F, Müller P, Velayudhan R, Corbel V (2018) Integrated Aedes management for the control of Aedes-borne diseases. PLoS Negl Trop Dis 12(12):e0006845. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pntd.0006845
Rueda LM (2004) Pictorial keys for the identification of mosquitoes (Diptera: Culicidae) associated with Dengue Virus transmission. Zootaxa 589:1–60. https://doi.org/10.11646/zootaxa.589.1
Russell ABM, Kay BH, Shipton, (2001) Survival of Aedes aegypti (Diptera: Culicidae) eggs in surface and subterranean breeding sites during the northern Queensland dry season. J Med Entomol 38:441–445. https://doi.org/10.1603/0022-2585-38.3.441
Salazar F, Angeles J, Sy AK, Inobaya MT, Aguila A, Toner T, Bangs MJ, Thomsen E, Pau RE (2019) Efficacy of the In2Care® auto-dissemination device for reducing dengue transmission: study protocol for a parallel, two-armed cluster randomised trial in the Philippines. Trials 20:269. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13063-019-3376-6
Santos AH, Tai MHH, Rocha LFN, Silva HHG, Luz C (2009) Dependence of Metarhizium anisopliae on high humidity for ovicidal activity on Aedes aegypti. Biol Control 50:37–42. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biocontrol.2009.01.018
Santos TR, Paixão FRS, Catão AML, Muniz ER, Silva CSR, Taveira SF, Luz C, Mascarin GM, Fernandes ÉKK, Marreto RN (2021) Inorganic pellets containing microsclerotia of Metarhizium anisopliae: a new technological platform for the biological control of the cattle tick Rhipicephalus microplus. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 105:5001–5012. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-021-11372-1
Scholte E-J, Knols BG, Takken W (2004) Autodissemination of the entomopathogenic fungus Metarhizium anisopliae amongst adults of the malaria vector Anopheles gambiae s.s. Malar J 3:45. https://doi.org/10.1186/1475-2875-3-45
Scholte E-J, Knols BGJ, Takken W (2006) Infection of the malaria mosquito Anopheles gambiae with the entomopathogenic fungus Metarhizium anisopliae reduces blood feeding and fecundity. J Invertebr Pathol 91:43–49. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jip.2005.10.006
Silva LE, Paula AR, Ribeiro A, Butt TM, Silva CP, Samuels RI (2018) A new method of deploying entomopathogenic fungi to control adult Aedes aegypti mosquitoes. J Appl Entomol 142:59–66. https://doi.org/10.1111/jen.12402
Silva RO, Silva HHG, Luz C (2004) Effect of Metarhizium anisopliae isolated from soil samples of the Central Brazilian cerrado against Aedes aegypti larvae under laboratory conditions. Rev Pat Trop 33:207–213. https://doi.org/10.5216/rpt.v33i2.3446
Snetselaar J, Andriessen R, Suer RA, Osinga AJ, Knols BGJ, Farenhorst M (2014) Development and evaluation of a novel contamination device that targets multiple life-stages of Aedes aegypti. Parasit Vectors 7:200. https://doi.org/10.1186/1756-3305-7-200
Swan T, Lounibos LP, Nishimura N (2018) Comparative oviposition site selection in containers by Aedes aegypti and Aedes albopictus (Diptera: Culicidae) from Florida. J Med Entomol 20:1–6. https://doi.org/10.1093/jme/tjy034
Throne JE, Weaker DK, Chew V, Baker JE (1995) Probit analysis of correlated data: multiple observations over time at one concentration. J Econ Entomol 88:1510–1512. https://doi.org/10.1093/jee/88.5.1510
Ver Hoef JM, Boveng PL (2007) Quasi-Poisson vs. negative binomial regression: How should we model overdispersed count data? Ecology 88:2766–2772. https://doi.org/10.1890/07-0043.1
Weaver S, Scott C, Charlier C, Vasilakis N, Lecuit M (2018) Zika, chikungunya, and other emerging vector-borne viral diseases. Ann Rev Med 69:395–408. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-med-050715-105122
Wong J, Stoddard ST, Astete H, Morrison AC, Scott TW (2011) Oviposition site selection by the Dengue vector Aedes aegypti and its implications for Dengue control. PLoS Neglect Trop D 5:e1015. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pntd.0001015
Acknowledgements
Authors thank the staff of Public Health Departments in Terezópolis and Goiânia in particular Célia Maria Ferreira Santos for their support during field tests and Bruno Lorham de Souza for technical assistance at IPTSP.
Funding
This study was supported by the National Council for Scientific and Technological Development, CNPq, Coordination of the Improvement of Higher Education, CAPES/MEC, CNPq/MCTI and Brazilian Ministry of Health, Decit/SCTIE/MS (440506/2016) and scholarships to JMM and JR (both CAPES). We also thank CNPq for the grants PQ 306319/2018–7 to ÉKKF and PQ 311672/2016–7 to CL.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
CL, JMM, JR, RNM, GMM, ÉKKF, and RAH conceived the research. JMM, JR, and CL designed the experiments. JMM, JR, and CL performed the experiments. CL, JR, JMM, and RAH wrote the paper. All authors read and approved the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
JMM, JR, ÉKKF, and CL declare patent application at INPI (Instituto Nacional de Propriedade Industrial, Brazil) about the device in progress.
Ethical approval
All applicable international, national, and/or institutional guidelines for the care and use of animals were followed.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
The original version of this article was revised. The overlapping image of Figures 3 and 4 is now corrected.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Martinez, J.M., Rodrigues, J., Marreto, R.N. et al. Efficacy of focal applications of a mycoinsecticide to control Aedes aegypti in Central Brazil. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 105, 8703–8714 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-021-11644-w
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-021-11644-w