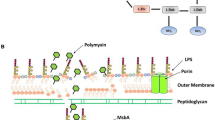
Abstract
Polymyxins are cationic antimicrobial peptides used as the last-line therapy to treat multidrug-resistant Gram-negative bacterial infections. The bactericidal activity of polymyxins against Gram-negative bacteria relies on the electrostatic interaction between the positively charged polymyxins and the negatively charged lipid A of lipopolysaccharide (LPS). Given that Gram-positive bacteria lack an LPS-containing outer membrane, it is generally acknowledged that polymyxins are less active against Gram-positive bacteria. However, Gram-positive bacteria produce negatively charged teichoic acids, which may act as the target of polymyxins. More and more studies suggest that polymyxins have potential as a treatment for Gram-positive bacterial infection. This mini-review discusses recent advances in the mechanism of the antibacterial activity and resistance of polymyxins in Gram-positive bacteria.
Key Points | |
• Teichoic acids play a key role in the action of polymyxins on Gram-positive bacteria. | |
• Polymyxin kills Gram-positive bacteria by disrupting cell surface and oxidative damage. | |
• Modification of teichoic acids and phospholipids contributes to polymyxin resistance in Gram-positive bacteria. | |
• Polymyxins have potential as a treatment for Gram-positive bacterial infection. |





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arendt W, Hebecker S, Jäger S, Nimtz M, Moser J (2012) Resistance phenotypes mediated by aminoacyl-phosphatidylglycerol synthases. J Bacteriol 194:1401–1416
Bax HI, de Steenwinkel JE, ten Kate MT, van der Meijden A, Verbon A, Bakker-Woudenberg IA (2015) Colistin as a potentiator of anti-TB drug activity against Mycobacterium tuberculosis. J Antimicrob Chemother 70:2828–2837
Blair JM, Webber MA, Baylay AJ, Ogbolu DO, Piddock LJ (2015) Molecular mechanisms of antibiotic resistance. Nat Rev Microbiol 13:42–51
Brochmann RP, Toft A, Ciofu O, Briales A, Kolpen M, Hempel C, Bjarnsholt T, Høiby N, Jensen PØ (2014) Bactericidal effect of colistin on planktonic Pseudomonas aeruginosa is independent of hydroxyl radical formation. Int J Antimicrob Agents 43:140–147
Brown S, Santa Maria Jr JP, Walker S (2013) Wall teichoic acids of gram-positive bacteria. Annu Rev Microbiol 67:313–336
Capra EJ, Laub MT (2012) Evolution of two-component signal transduction systems. Annu Rev Microbiol 66:325–347
Cheung AL, Bayer AS, Yeaman MR, Xiong YQ, Waring AJ, Memmi G, Donegan N, Chaili S, Yang SJ (2014) Site-specific mutation of the sensor kinase GraS in Staphylococcus aureus alters the adaptive response to distinct cationic antimicrobial peptides. Infect Immun 82:5336–5345
Collins LV, Kristian SA, Weidenmaier C, Faigle M, Van Kessel KPM, Van Strijp JAG, Götz F, Neumeister B, Peschel A (2002) Staphylococcus aureus strains lacking D-alanine modifications of teichoic acids are highly susceptible to human neutrophil killing and are virulence attenuated in mice. J Infect Dis 186:214–219
D'Costa VM, Mukhtar TA, Patel T, Koteva K, Waglechner N, Hughes DW, Wright GD, De Pascale G (2012) Inactivation of the lipopeptide antibiotic daptomycin by hydrolytic mechanisms. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 56:757–764
Debabov DV, Heaton MP, Zhang Q, Stewart KD, Lambalot RH, Neuhaus FC (1996) The D-Alanyl carrier protein in Lactobacillus casei: cloning, sequencing, and expression of dltC. J Bacteriol 178:3869–3876
Deris ZZ, Akter J, Sivanesan S, Roberts KD, Thompson PE, Nation RL, Li J, Velkov T (2014) A secondary mode of action of polymyxins against Gram-negative bacteria involves the inhibition of NADH-quinone oxidoreductase activity. J Antibiot 67:147–151
Dwyer DJ, Kohanski MA, Collins JJ (2009) Role of reactive oxygen species in antibiotic action and resistance. Curr Opin Microbiol 12:482–489
Ernst CM, Peschel A (2011) Broad-spectrum antimicrobial peptide resistance by MprF-mediated aminoacylation and flipping of phospholipids. Mol Microbiol 80:290–299
Ernst CM, Peschel A (2019) MprF-mediated daptomycin resistance. Int J Med Microbiol 309:359–363
Ernst CM, Staubitz P, Mishra NN, Yang SJ, Hornig G, Kalbacher H, Bayer AS, Kraus D, Peschel A (2009) The bacterial defensin resistance protein MprF consists of separable domains for lipid lysinylation and antimicrobial peptide repulsion. PLoS Pathog 5:e1000660
Ernst CM, Kuhn S, Slavetinsky CJ, Krismer B, Heilbronner S, Gekeler C, Kraus D, Wagner S, Peschel A (2015) The lipid-modifying multiple peptide resistance factor is an oligomer consisting of distinct interacting synthase and flippase subunits. MBio 6:e02340–14
Ernst CM, Slavetinsky CJ, Kuhn S, Hauser JN, Nega M, Mishra NN, Gekeler C, Bayer AS, Peschel A (2018) Gain-of-function mutations in the phospholipid flippase MprF confer specific daptomycin resistance. MBio 9:e01659–18
Evans ME, Feola DJ, Rapp RP (1999) Polymyxin B sulfate and colistin: old antibiotics for emerging multiresistant Gram-negative bacteria. Ann Pharmacother 33:960–967
Falagas ME, Kasiakou SK, Saravolatz LD (2005) Colistin: the revival of polymyxins for the management of multidrug-resistant Gram-negative bacterial infections. Clin Infect Dis 40:1333–1341
Falord M, Karimova G, Hiron A, Msadek T (2012) GraXSR proteins interact with the VraFG ABC transporter to form a five-component system required for cationic antimicrobial peptide sensing and resistance in Staphylococcus aureus. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 56:1047–1058
Fische W (1994) Lipoteichoic acid and lipids in the membrane of Staphylococcus aureus. Med Microbiol Immunol 183:61–76
Grau-Campistany A, Manresa Á, Pujol M, Rabanal F, Cajal Y (2016) Tryptophan-containing lipopeptide antibiotics derived from polymyxin B with activity against Gram positive and Gram negative bacteria. BBA-Biomembranes 1858:333–343
Guina T, Yi EC, Wang H, Hackett M, Miller SI (2000) A PhoP-regulated outer membrane protease of Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium promotes resistance to alpha-helical antimicrobial peptides. J Bacteriol 182:4077–4086
Heaton MP, Neuhaus FC (1994) Role of the D-alanyl carrier protein in the biosynthesis of D-alanyl-lipoteichoic acid. J Bacteriol 176:681–690
Hyyryläinen HL, Vitikainen M, Thwaite J, Wu H, Sarvas M, Harwood CR, Kontinen VP, Stephenson K (2000) D-Alanine substitution of teichoic acids as a modulator of protein folding and stability at the cytoplasmic membrane/cell wall interface of Bacillus subtilis. J Biol Chem 275:26696–26703
Ito M, Aida T, Koyama Y (1966) Studies on the bacterial formation of a peptide antibiotic, colistin. Part I. On the enyzmatic inactivation of colistin by Bacillus colistinus. Agric Biol Chem 30:1112–1118
Ito-Kagawa M, Koyama Y (1980) Selective cleavage of a peptide antibiotic, colistin by colistinase. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 33:1551–1555
Jeannot K, Bolard A, Plesiat P (2017) Resistance to polymyxins in Gram-negative organisms. Int J Antimicrob Agents 49:526–535
Joo HS, Fu CI, Otto M (2016) Bacterial strategies of resistance to antimicrobial peptides. Philos T R Soc B: Biol Sci 371:20150292
Kamar R, Réjasse A, Jéhanno I, Attieh Z, Courtin P, Chapot-Chartier MP, Nielsen-Leroux C, Lereclus D, EL Chamy L, Kallassy M, Sanchis-Borja V (2017) DltX of Bacillus thuringiensis is essential for D-alanylation of teichoic acids and resistance to antimicrobial response in insects. Front Microbiol 8:1437
Khattar ZA, Rejasse A, Destoumieux-Garzon D, Escoubas JM, Sanchis V, Lereclus D, Givaudan A, Kallassy M, Nielsen-Leroux C, Gaudriault S (2009) The dlt operon of Bacillus cereus is required for resistance to cationic antimicrobial peptides and for virulence in insects. J Bacteriol 191:7063–7073
Klein S, Lorenzo C, Hoffmann S, Walther JM, Storbeck S, Piekarski T, Tindall BJ, Wray V, Nimtz M, Moser J (2009) Adaptation of Pseudomonas aeruginosa to various conditions includes tRNA-dependent formation of alanyl-phosphatidylglycerol. Mol Microbiol 71(3):551–565
Kohanski MA, Dwyer DJ, Hayete B, Lawrence CA, Collins JJ (2007) A common mechanism of cellular death induced by bactericidal antibiotics. Cell 130:797–810
Kovács M, Halfmann A, Fedtke I, Heintz M, Peschel A, Vollmer W, Hakenbeck R, Brückner R (2006) A functional dlt operon, encoding proteins required for incorporation of D-alanine in teichoic acids in gram-positive bacteria, confers resistance to cationic antimicrobial peptides in Streptococcus pneumoniae. J Bacteriol 188:5797–5805
Krell T, Lacal J, Busch A, Silva-Jiménez H, Guazzaroni ME, Ramos JL (2010) Bacterial sensor kinases: diversity in the recognition of environmental signals. Annu Rev Microbiol 64:539–559
Kristian SA, Dürr M, Van Strijp JA, Neumeister B, Peschel A (2003) MprF-mediated lysinylation of phospholipids in Staphylococcus aureus leads to protection against oxygen-independent neutrophil killing. Infect Immun 71:546–549
Kristian SA, Datta V, Weidenmaier C, Kansal R, Fedtke I, Peschel A, Gallo RL, Nizet V (2005) D-Alanylation of teichoic acids promotes group A Streptococcus antimicrobial peptide resistance, neutrophil survival, and epithelial cell invasion. J Bacteriol 187:6719–6725
Kwa A, Kasiakou SK, Tam VH, Falagas ME (2007) Polymyxin B: similarities to and differences from colistin (polymyxin E). Expert Rev Anti-Infect Ther 5:811–821
Landman D, Georgescu C, Martin DA, Quale J (2008) Polymyxins revisited. Clin Microbiol Rev 21:449–465
LaPorte DC, Rosenthal KS, Storm DR (1977) Inhibition of Escherichia coli growth and respiration by polymyxin B covalently attached to agarose beads. Biochemistry 16:1642–1648
Li J, Nation RL, Turnidge JD, Milne RW, Coulthard K, Rayner CR, Paterson DL (2006) Colistin: the re-emerging antibiotic for multidrug-resistant Gram-negative bacterial infections. Lancet Infect Dis 6:589–601
Li M, Cha DJ, Lai Y, Villaruz AE, Sturdevant DE, Otto M (2007a) The antimicrobial peptide-sensing system aps of Staphylococcus aureus. Mol Microbiol 66:1136–1147
Li M, Lai Y, Villaruz AE, Cha DJ, Sturdevant DE, Otto M (2007b) Gram-positive three-component antimicrobial peptide-sensing system. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 104:9469–9474
Li YX, Zhong Z, Hou P, Zhang WP, Qian PY (2018) Resistance to nonribosomal peptide antibiotics mediated by D-stereospecific peptidases. Nat Chem Biol 14:381–387
Mascher T (2006) Intramembrane-sensing histidine kinases: a new family of cell envelope stress sensors in Firmicutes bacteria. FEMS Microbiol Lett 264:133–144
McBride SM, Sonenshein AL (2011) The dlt operon confers resistance to cationic antimicrobial peptides in Clostridium difficile. Microbiology 157:1457–1465
Meeske AJ, Sham LT, Kimsey H, Koo BM, Gross CA, Bernhardt TG, Rudner DZ (2015) MurJ and a novel lipid II flippase are required for cell wall biogenesis in Bacillus subtilis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 112:6437–6442
Mogi T, Murase Y, Mori M, Shiomi K, Ōmura S, Paranagama MP, Kita K (2009) Polymyxin B identified as an inhibitor of alternative NADH dehydrogenase and malate: quinone oxidoreductase from the Gram-positive bacterium Mycobacterium smegmatis. J Biochem 146:491–499
Muzamal U, Gomez D, Kapadia F, Golemi-Kotra D (2014) Diversity of two-component systems: insights into the signal transduction mechanism by the Staphylococcus aureus two-component system GraSR. F1000Research 3:252
Neuhaus FC, Baddiley J (2003) A continuum of anionic charge: structures and functions of D-alanyl-teichoic acids in Gram-positive bacteria. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 67:686–723
Neuhaus FC, Heaton MP, Debabov DV, Zhang Q (1996) The dlt operon in the biosynthesis of D-alanyl-lipoteichoic acid in Lactobacillus casei. Microb Drug Resist 2:77–84
Nilsson M, Rybtke M, Givskov M, Høiby N, Twetman S, Tolker-Nielsen T (2016) The dlt genes play a role in antimicrobial tolerance of Streptococcus mutans biofilms. Int J Antimicrob Agents 48:298–304
Oku Y, Kurokawa K, Ichihashi N, Sekimizu K (2004) Characterization of the Staphylococcus aureus mprF gene, involved in lysinylation of phosphatidylglycerol. Microbiology 150:45–51
Olaitan AO, Morand S, Rolain JM (2014) Mechanisms of polymyxin resistance: acquired and intrinsic resistance in bacteria. Front Microbiol 5:643
Otto M (2009) Bacterial sensing of antimicrobial peptides. In: Collin M, Schuch R (eds) Bacterial sensing and signaling. Karger, Basel, pp 136–149
Percy MG, Gründling A (2014) Lipoteichoic acid synthesis and function in gram-positive bacteria. Annu Rev Microbiol 68:81–100
Perego M, Glaser P, Minutello A, Strauch MA, Leopold K, Fischer W (1995) Incorporation of D-alanine into lipoteichoic acid and wall teichoic acid in Bacillus subtilis. Identification of genes and regulation. J Biol Chem 270:15598–15606
Peschel A, Otto M, Jack RW, Kalbacher H, Jung G, Götz F (1999) Inactivation of the dlt operon in Staphylococcus aureus confers sensitivity to defensins, protegrins, and other antimicrobial peptides. J Biol Chem 274:8405–8410
Peschel A, Vuong C, Otto M, Götz F (2000) The D-alanine residues of Staphylococcus aureus teichoic acids alter the susceptibility to vancomycin and the activity of autolytic enzymes. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 44:2845–2847
Peschel A, Jack RW, Otto M, Collins LV, Staubitz P, Nicholson G, Kalbacher H, Nieuwenhuizen WF, Jung G, Tarkowski A, van Kessel KPM, van Strijp JAG (2001) Staphylococcus aureus resistance to human defensins and evasion of neutrophil killing via the novel virulence factor MprF is based on modification of membrane lipids with l-lysine. J Exp Med 193:1067–1076
Poirel L, Jayol A, Nordmann P (2017) Polymyxins: antibacterial activity, susceptibility testing, and resistance mechanisms encoded by plasmids or chromosomes. Clin Microbiol Rev 30:557–596
Rabanal F, Grau-Campistany A, Vila-Farrés X, Gonzalez-Linares J, Borràs M, Vila J, Manresa A, Cajal Y (2015) A bioinspired peptide scaffold with high antibiotic activity and low in vivo toxicity. Sci Rep 5:10558
Reichmann NT, Cassona CP, Gründling A (2013) Revised mechanism of D-alanine incorporation into cell wall polymers in Gram-positive bacteria. Microbiology 159:1868–1877
Reith J, Mayer C (2011) Peptidoglycan turnover and recycling in Gram-positive bacteria. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 92:1–11
Roy H, Ibba M (2008) RNA-dependent lipid remodeling by bacterial multiple peptide resistance factors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 105:4667–4672
Roy H, Ibba M (2009) Broad range amino acid specificity of RNA-dependent lipid remodeling by multiple peptide resistance factors. J Biol Chem 284:29677–29683
Rudilla H, Pérez-Guillén I, Rabanal F, Sierra JM, Vinuesa T, Viñas M (2018) Novel synthetic polymyxins kill Gram-positive bacteria. J Antimicrob Chemother 73:3385–3390
Saar-Dover R, Bitler A, Nezer R, Shmuel-Galia L, Firon A, Shimoni E, Trieu-Cuot P, Shai Y (2012) D-Alanylation of lipoteichoic acids confers resistance to cationic peptides in Group B Streptococcus by increasing the cell wall density. PLoS Pathog 8:e1002891
Sampson TR, Liu X, Schroeder MR, Kraft CS, Burd EM, Weiss DS (2012) Rapid killing of Acinetobacter baumannii by polymyxins is mediated by a hydroxyl radical death pathway. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 56:5642–5649
Si W, Wang L, Usongo V, Zhao X (2018) Colistin induces S. aureus susceptibility to bacitracin. Front Microbiol 9:2805
Sohlenkamp C, Galindo-Lagunas KA, Guan Z, Vinuesa P, Robinson S, Thomas-Oates J, Raetz CRH, Geiger O (2007) The lipid lysyl-phosphatidylglycerol is present in membranes of Rhizobium tropici CIAT899 and confers increased resistance to polymyxin B under acidic growth conditions. Mol Plant Microbe In 20:1421–1430
Staubitz P, Neumann H, Schneider T, Wiedemann I, Peschel A (2004) MprF-mediated biosynthesis of lysylphosphatidylglycerol, an important determinant in staphylococcal defensin resistance. FEMS Microbiol Lett 231:67–71
Steinbuch KB, Fridman M (2016) Mechanisms of resistance to membrane-disrupting antibiotics in Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria. MedChemComm 7:86–102
Stock AM, Robinson VL, Goudreau PN (2000) Two-component signal transduction. Annu Rev Biochem 69:183–215
Stumpe S, Schmid R, Stephens DL, Georgiou G, Bakker EP (1998) Identification of OmpT as the protease that hydrolyzes the antimicrobial peptide protamine before it enters growing cells of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol 180:4002–4006
Suzuki T, Hayashi K, Fujikawa K (1963) Studies on the chemical structure of colistin. III Enzymatic hydrolysis of colistin. A J Biochem 54:412–418
Tochikubo K, Yasuda Y, Kozuka S (1986) Decreased particulate NADH oxidase activity in Bacillus subtilis spores after polymyxin B treatment. Microbiology 132:277–287
Trimble MJ, Mlynárčik P, Kolář M, Hancock RE (2016) Polymyxin: alternative mechanisms of action and resistance. CSH Perspect Med 6:a025288
Velkov T, Thompson PE, Nation RL, Li J (2010) Structure-activity relationships of polymyxin antibiotics. J Med Chem 53:1898–1916
Wecke J, Perego M, Fischer W (1996) D-alanine deprivation of Bacillus subtilis teichoic acids is without effect on cell growth and morphology but affects the autolytic activity. Microb Drug Resist 2:123–129
Wecke J, Madela K, Fischer W (1997) The absence of D-alanine from lipoteichoic acid and wall teichoic acid alters surface charge, enhances autolysis and increases susceptibility to methicillin in Bacillus subtilis. Microbiology 143:2953–2960
Wood BM, Santa Maria JP, Matano LM, Vickery CR, Walker S (2018) A partial reconstitution implicates DltD in catalyzing lipoteichoic acid D-alanylation. J Biol Chem 293:17985–17996
Woods EC, Nawrocki KL, Suárez JM, McBride SM (2016) The Clostridium difficile Dlt pathway is controlled by the extracytoplasmic function sigma factor σV in response to lysozyme. Infect Immun 84:1902–1916
Woyczikowska B, Paśś L, Girdwoyń M, Raczyńska-Bojanowska K (1973) Proteolytic degradation of polymyxins by the enzymes of Bacillus polymyxa. Acta Biochim Pol 20:285–296
Wydau-Dematteis S, Louis M, Zahr N, Lai-Kuen R, Saubaméa B, Butel MJ, Pons JL (2015) The functional dlt operon of Clostridium butyricum controls the D-alanylation of cell wall components and influences cell septation and vancomycin-induced lysis. Anaerobe 35:105–114
Xiong YQ, Mukhopadhyay K, Yeaman MR, Adler-Moore J, Bayer AS (2005) Functional interrelationships between cell membrane and cell wall in antimicrobial peptide-mediated killing of Staphylococcus aureus. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 49:3114–3121
Yang SJ, Bayer AS, Mishra NN, Meehl M, Ledala N, Yeaman MR, Xiong YQ, Cheung AL (2012) The Staphylococcus aureus two-component regulatory system, GraRS, senses and confers resistance to selected cationic antimicrobial peptides. Infect Immun 80:74–81
Yin J, Wang G, Cheng D, Fu J, Qiu J, Yu Z (2019) Inactivation of polymyxin by hydrolytic mechanism. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 63:e02378–e02318
Yu Z, Qin W, Lin J, Fang S, Qiu J (2015) Antibacterial mechanisms of polymyxin and bacterial resistance. Biomed Res Int 2015:679109
Yu Z, Zhu Y, Qin W, Yin J, Qiu J (2017) Oxidative stress induced by polymyxin E is involved in rapid killing of Paenibacillus polymyxa. Biomed Res Int 2017:5437139
Yu Z, Zhu Y, Fu J, Qiu J, Yin J (2019a) Enhanced NADH metabolism involves colistin-induced killing of Bacillus subtilis and Paenibacillus polymyxa. Molecules 24:387
Yu Z, Zhang L, Qin W, Yin J, Qiu J (2019b) Exogenous catalase stimulates the polymyxin E-induced rapid killing of Paenibacillus polymyxa. Int J Pept Res Ther 25:161–168
Author contribution statement
YJ and YZ conceived and designed the review. CD, FJ, and LY collected the data. YJ, MQ, LQ, and YZ wrote the manuscript. All authors read and approved the manuscript.
Funding
This research was supported by the grants from Zhejiang Provincial Natural Science Foundation of China (LY20C010003), National Natural Science Foundation of China (31670114), and the National Key R&D Program of China (2017YFC1600100).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yin, J., Meng, Q., Cheng, D. et al. Mechanisms of bactericidal action and resistance of polymyxins for Gram-positive bacteria. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 104, 3771–3780 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-020-10525-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-020-10525-y