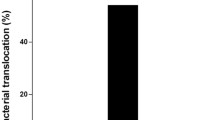Abstract
This work investigated the effect of the intragastric administration of five lactic acid bacteria from healthy people on acute liver failure in rats. Sprague–Dawley rats were given intragastric supplements of Lactobacillus salivarius LI01, Lactobacillus salivarius LI02, Lactobacillus paracasei LI03, Lactobacillus plantarum LI04, or Pediococcus pentosaceus LI05 for 8 days. Acute liver injury was induced on the eighth day by intraperitoneal injection of 1.1 g/kg body weight d-galactosamine (d-GalN). After 24 h, samples were collected to determine the level of liver enzymes, liver function, histology of the terminal ileum and liver, serum levels of inflammatory cytokines, bacterial translocation, and composition of the gut microbiome. The results indicated that pretreatment with L. salivarius LI01 or P. pentosaceus LI05 significantly reduced elevated alanine aminotransferase and aspartate aminotransferase levels, prevented the increase in total bilirubin, reduced the histological abnormalities of both the liver and the terminal ileum, decreased bacterial translocation, increased the serum level of interleukin 10 and/or interferon-γ, and resulted in a cecal microbiome that differed from that of the liver injury control. Pretreatment with L. plantarum LI04 or L. salivarius LI02 demonstrated no significant effects during this process, and pretreatment with L. paracasei LI03 aggravated liver injury. To the best of our knowledge, the effects of the three species—L. paracasei, L. salivarius, and P. pentosaceus—on d-GalN-induced liver injury have not been previously studied. The excellent characteristics of L. salivarius LI01 and P. pentosaceus LI05 enable them to serve as potential probiotics in the prevention or treatment of acute liver failure.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adawi D, Kasravi FB, Molin G, Jeppsson B (1997) Effect of Lactobacillus supplementation with and without arginine on liver damage and bacterial translocation in an acute liver injury model in the rat. Hepatology 25:642–647
Adawi D, Molin G, Jeppsson B (1998) Inhibition of nitric oxide production and the effects of arginine and Lactobacillus administration in an acute liver injury model. Ann Surg 228:748–755
Adawi D, Ahrne S, Molin G (2001) Effects of different probiotic strains of Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium on bacterial translocation and liver injury in an acute liver injury model. Int J Food Microbiol 70:213–220
Bengmark S (2009) Bio-ecological control of chronic liver disease and encephalopathy. Metab Brain Dis 24:223–236
Bernal W, Auzinger G, Dhawan A, Wendon J (2010) Acute liver failure. Lancet 376:190–201
Capozzi V, Russo P, Duenas MT, Lopez P, Spano G (2012) Lactic acid bacteria producing B-group vitamins: a great potential for functional cereals products. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 96:1383–1394
Deutschman CS, Cereda M, Ochroch EA, Raj NR (2006) Sepsis-induced cholestasis, steatosis, hepatocellular injury, and impaired hepatocellular regeneration are enhanced in interleukin-6 −/− mice. Crit Care Med 34:2613–2620
Du WB, Li LJ, Huang JR, Yang Q, Liu XL, Li J, Chen YM, Cao HC, Xu W, Fu SZ, Chen YG (2005) Effects of artificial liver support system on patients with acute or chronic liver failure. Transplant Proc 37:4359–4364
Festi D, Vestito A, Mazzella G, Roda E, Colecchia A (2006) Management of hepatic encephalopathy: focus on antibiotic therapy. Digestion 73(Suppl 1):94–101
Haro C, Zelaya H, Lazarte S, Alvarez S, Aguero G (2009) Lactobacillus casei: influence on the innate immune response and haemostatic alterations in a liver-injury model. Can J Microbiol 55:648–656
Hynonen U, Palva A (2013) Lactobacillus surface layer proteins: structure, function and applications. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 97:5225–5243
Johansson ME, Gustafsson JK, Holmen-Larsson J, Jabbar KS, Xia L, Xu H, Ghishan FK, Carvalho FA, Gewirtz AT, Sjovall H, Hansson GC (2013) Bacteria penetrate the normally impenetrable inner colon mucus layer in both murine colitis models and patients with ulcerative colitis. Gut 63:281–291
Joossens M, Huys G, Cnockaert M, De Preter V, Verbeke K, Rutgeerts P, Vandamme P, Vermeire S (2011) Dysbiosis of the faecal microbiota in patients with Crohn’s disease and their unaffected relatives. Gut 60:631–637
Kasravi FB, Adawi D, Molin G, Bengmark S, Jeppsson B (1997) Effect of oral supplementation of Lactobacilli on bacterial translocation in acute liver injury induced by D-galactosamine. J Hepatol 26:417–424
Kirpich IA, McClain CJ (2012) Probiotics in the treatment of the liver diseases. J Am Coll Nutr 31:14–23
Lu H, He J, Wu Z, Xu W, Zhang H, Ye P, Yang J, Zhen S, Li L (2013) Assessment of microbiome variation during the perioperative period in liver transplant patients: a retrospective analysis. Microb Ecol 65:781–791
Ma S, Dai Y (2011) Principal component analysis based methods in bioinformatics studies. Brief Bioinform 12:714–722
McGee RG, Bakens A, Wiley K, Riordan SM, Webster AC (2011) Probiotics for patients with hepatic encephalopathy. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 11, CD008716. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD008716
Messaoudi S, Manai M, Kergourlay G, Prevost H, Connil N, Chobert JM, Dousset X (2013) Lactobacillus salivarius: bacteriocin and probiotic activity. Food Microbiol 36:296–304
Muyzer G, de Waal EC, Uitterlinden AG (1993) Profiling of complex microbial populations by denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis analysis of polymerase chain reaction-amplified genes coding for 16S rRNA. Appl Environ Microbiol 59:695–700
O’Grady J (2012) Liver transplantation for acute liver failure. Best Pract Res Clin Gastroenterol 26:27–33
Osman N, Adawi D, Ahrne S, Jeppsson B, Molin G (2007) Endotoxin- and D-galactosamine-induced liver injury improved by the administration of Lactobacillus, Bifidobacterium and blueberry. Dig Liver Dis 39:849–856
Schnabl B (2013) Linking intestinal homeostasis and liver disease. Curr Opin Gastroenterol 29:264–270
Tamura K, Peterson D, Peterson N, Stecher G, Nei M, Kumar S (2011) MEGA5: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis using maximum likelihood, evolutionary distance, and maximum parsimony methods. Mol Biol Evol 28:2731–2739
Tranah TH, Vijay GK, Ryan JM, Shawcross DL (2013) Systemic inflammation and ammonia in hepatic encephalopathy. Metab Brain Dis 28:1–5
Tsai YT, Cheng PC, Pan TM (2012) The immunomodulatory effects of lactic acid bacteria for improving immune functions and benefits. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 96:853–862
Tunon MJ, Alvarez M, Culebras JM, Gonzalez-Gallego J (2009) An overview of animal models for investigating the pathogenesis and therapeutic strategies in acute hepatic failure. World J Gastroenterol 15:3086–3098
Vanhoutte T, Huys G, Brandt E, Swings J (2004) Temporal stability analysis of the microbiota in human feces by denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis using universal and group-specific 16S rRNA gene primers. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 48:437–446
Wang Y, Li Y, Xie J, Zhang Y, Wang J, Sun X, Zhang H (2013) Protective effects of probiotic Lactobacillus casei Zhang against endotoxin- and d-galactosamine-induced liver injury in rats via anti-oxidative and anti-inflammatory capacities. Int Immunopharmacol 15:30–37
Wlodzimirow KA, Eslami S, Abu-Hanna A, Nieuwoudt M, Chamuleau RA (2012) Systematic review: acute liver failure—one disease, more than 40 definitions. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 35:1245–1256
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by the National Basic Research Program of China (973 program) (No. 2013CB531401), the Key Program of the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 81330011), and the Scientific Research Fund of the Department of Education of Zhejiang Province (Y200805384).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Long-Xian Lv, Xin-Jun Hu, and Gui-Rong Qian contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lv, LX., Hu, XJ., Qian, GR. et al. Administration of Lactobacillus salivarius LI01 or Pediococcus pentosaceus LI05 improves acute liver injury induced by d-galactosamine in rats. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 98, 5619–5632 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-014-5638-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-014-5638-2