Abstract
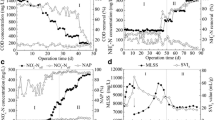
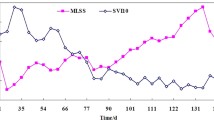
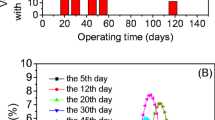
In this study, the possibility of using backwashed biofilm as seed in an aerobic granular sludge continuous-flow airlift fluidized bed (CAFB) reactor was investigated. After the addition of the inoculated backwashed biofilm, the start-up period of this reactor fed with municipal wastewater was reduced to 25 days, and aerobic granulation and stabilization were enhanced. At steady state, the chemical oxygen demand (COD) removal efficiency and nitrification efficiency were as high as 80–90 and 60 %, respectively. The CAFB was operated continuously and totally for 90 days, and its performance was much more stable when compared with system inoculated with activated sludge. Microbial distribution analyzed by fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH) showed that the nitrite-oxidizing bacteria (NOB) and ammonium-oxidizing bacteria (AOB) were compatible with heterotrophic bacteria and distributed evenly throughout the granules. Such unique population distribution might be attributed to the low COD level and abundant dissolved oxygen in the entire granule as simulated by the mathematic models. Moreover, scanning electron microscopy revealed broad holes in the granules, which might promote the mass transfer of the nutrients from the surface to the center and enable simultaneous COD removal and nitrification. In conclusion, backwashed biofilm is an alternative seed of the conventional flocculent activated sludge in the aerobic granular sludge system to enhance carbonaceous oxidization and nitrification.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adav SS, Lee D-J, Show K-Y, Tay J-H (2008a) Aerobic granular sludge: recent advances. Biotechnol Adv 26(5):411–423. doi:10.1016/j.biotechadv.2008.05.002
Adav SS, Lee D-J, Tay J-H (2008b) Extracellular polymeric substances and structural stability of aerobic granule. Water Res 42(6):1644–1650
Amann R (1995) In situ identification of micro-organisms by whole cell hybridization with rRNA-targeted nucleic acid probes. In: Akkermans AL, Elsas J, Bruijn F (eds) Molecular microbial ecology manual. Springer, Netherlands, pp 331–345. doi:10.1007/978-94-011-0351-0_23
Awwa A (1998) Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater. Washington, DC Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater 20
Carvalho G, Meyer RL, Yuan Z, Keller J (2006) Differential distribution of ammonia- and nitrite-oxidising bacteria in flocs and granules from a nitrifying/denitrifying sequencing batch reactor. Enzyme Microb Technol 39(7):1392–1398. doi:10.1016/j.enzmictec.2006.03.024
Daims H, Brühl A, Amann R, Schleifer K-H, Wagner M (1999) The domain-specific probe EUB338 is Insufficient for the detection of all bacteria: development and evaluation of a more comprehensive probe set. Syst Appl Microbiol 22(3):434–444. doi:10.1016/S0723-2020(99)80053-8
de Kreuk MK, Picioreanu C, Hosseini M, Xavier JB, van Loosdrecht MCM (2007) Kinetic model of a granular sludge SBR: influences on nutrient removal. Biotechnol Bioeng 97(4):801–815. doi:10.1002/bit.21196
Di Iaconi C, Ramadori R, Lopez A, Passino R (2004) Hydraulic shear stress calculation in a sequencing batch biofilm reactor with granular biomass. Environ Sci Technol 39(3):889–894. doi:10.1021/es0400483
Falås P, Longrée P, la Cour Jansen J, Siegrist H, Hollender J, Joss A (2013) Micropollutant removal by attached and suspended growth in a hybrid biofilm-activated sludge process. Water Res 47(13):4498–4506. doi:10.1016/j.watres.2013.05.010
Fang F, Ni B-J, Li X-Y, Sheng G-P, Yu H-Q (2009) Kinetic analysis on the two-step processes of AOB and NOB in aerobic nitrifying granules. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 83(6):1159–1169
Guo F, Zhang S-H, Yu X, Wei B (2011) Variations of both bacterial community and extracellular polymers: the inducements of increase of cell hydrophobicity from biofloc to aerobic granule sludge. Bioresour Technol 102(11):6421–6428
Habimana O, Steenkeste K, Fontaine-Aupart M-P, Bellon-Fontaine M-N, Kulakauskas S, Briandet R (2011) Diffusion of nanoparticles in biofilms is altered by bacterial cell wall hydrophobicity. Appl Environ Microbiol 77(1):367–368. doi:10.1128/aem.02163-10
Henze M (2008) Biological wastewater treatment: principles, modelling and design. IWA publishing, UK
Huang L, Yang T, Wang W, Zhang B, Sun Y (2012) Effect of Mn2 + augmentation on reinforcing aerobic sludge granulation in a sequencing batch reactor. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 93(6):2615–2623
Jang A, Yoon Y-H, Kim IS, Kim K-S, Bishop PL (2003) Characterization and evaluation of aerobic granules in sequencing batch reactor. J Biotechnol 105(1):71–82
Jiaheng Z, Su W, Jun L, Mei H, Hille A, Horn H (2011) Aerobic granulation in a modified continuous flow system. In: Bioinformatics and Biomedical EngineeringAerobic Granulation in a Modified Continuous Flow System. In: Bioinformatics and Biomedical Engineering, (iCBBE) 2011 5th International Conference on, 10–12 May 2011. pp 1–5. doi:10.1109/icbbe.2011.5781158
Jin R-C, Zheng P, Mahmood Q, Zhang L (2008) Performance of a nitrifying airlift reactor using granular sludge. Sep Purif Technol 63(3):670–675
Juang Y-C, Adav SS, Lee D-J, Tay J-H (2010) Stable aerobic granules for continuous-flow reactors: precipitating calcium and iron salts in granular interiors. Bioresour Technol 101(21):8051–8057. doi:10.1016/j.biortech.2010.05.078
Kim H-s, Schuler AJ, Gunsch CK, Pei R, Gellner J, Boltz JP, Freudenberg RG, Dodson R (2011) Comparison of conventional and integrated fixed-film activated sludge systems: attached- and suspended-growth functions and quantitative polymerase chain reaction measurements. Water Environ Res 83(7):627–635. doi:10.2175/106143010X12851009156448
Li Y, Liu Y (2005) Diffusion of substrate and oxygen in aerobic granule. Biochem Eng J 27(1):45–52. doi:10.1016/j.bej.2005.06.012
Li Y, Liu Y, Shen L, Chen F (2008) DO diffusion profile in aerobic granule and its microbiological implications. Enzyme Microb Technol 43(4):349–354
Li A-j, Zhang T, X-y L (2010) Fate of aerobic bacterial granules with fungal contamination under different organic loading conditions. Chemosphere 78(5):500–509
Liu Y (2006) A simple thermodynamic approach for derivation of a general Monod equation for microbial growth. Biochem Eng J 31(1):102–105
Liu Y (2012) Wastewater purification: aerobic granulation in sequencing batch reactors. CRC
Liu Y, Liu Q-S (2006) Causes and control of filamentous growth in aerobic granular sludge sequencing batch reactors. Biotechnol Adv 24(1):115–127. doi:10.1016/j.biotechadv.2005.08.001
Liu Y, Yang S-F, Tay J-H (2004) Improved stability of aerobic granules by selecting slow-growing nitrifying bacteria. J Biotechnol 108(2):161–169
Liu H, Li Y, Yang C, Pu W, He L, Bo F (2012) Stable aerobic granules in continuous-flow bioreactor with self-forming dynamic membrane. Bioresour Technol 121:111–118
Mahendran B, Lishman L, Liss SN (2012) Structural, physicochemical and microbial properties of flocs and biofilms in integrated fixed-film activated sludge (IFFAS) systems. Water Res 46(16):5085–5101
Melo L (2005) Biofilm physical structure, internal diffusivity and tortuosity. Water Sci Technol 52(7):77–84
Mobarry BK, Wagner M, Urbain V, Rittmann BE, Stahl DA (1996) Phylogenetic probes for analyzing abundance and spatial organization of nitrifying bacteria. Appl Environ Microbiol 62(6):2156–2162
Morales N, Figueroa M, Mosquera-Corral A, Campos JL, Méndez R (2012) Aerobic granular-type biomass development in a continuous stirred tank reactor. Sep Purif Technol 89:199–205. doi:10.1016/j.seppur.2012.01.024
Mosquera-Corral A, de Kreuk MK, Heijnen JJ, van Loosdrecht MCM (2005) Effects of oxygen concentration on N-removal in an aerobic granular sludge reactor. Water Res 39(12):2676–2686. doi:10.1016/j.watres.2005.04.065
Ni B-J, Yu H-Q, Sun Y-J (2008) Modeling simultaneous autotrophic and heterotrophic growth in aerobic granules. Water Res 42(6):1583–1594
Ruiz G, Jeison D, Chamy R (2003) Nitrification with high nitrite accumulation for the treatment of wastewater with high ammonia concentration. Water Res 37(6):1371–1377. doi:10.1016/S0043-1354(02)00475-X
Schramm A, de Beer D, van den Heuvel JC, Ottengraf S, Amann R (1999) Microscale distribution of populations and activities of Nitrosospira and Nitrospira spp. along a macroscale gradient in a nitrifying bioreactor: quantification by in situ hybridization and the use of microsensors. Appl Environ Microbiol 65(8):3690–3696
Schramm A, De Beer D, Gieseke A, Amann R (2000) Microenvironments and distribution of nitrifying bacteria in a membrane-bound biofilm. Environ Microbiol 2(6):680–686. doi:10.1046/j.1462-2920.2000.00150.x
Shi X-Y, Yu H-Q, Sun Y-J, Huang X (2009) Characteristics of aerobic granules rich in autotrophic ammonium-oxidizing bacteria in a sequencing batch reactor. Chem Eng J 147(2–3):102–109. doi:10.1016/j.cej.2008.06.037
Song Y, Ishii S, Rathnayake L, Ito T, Satoh H, Okabe S (2013) Development and characterization of the partial nitrification aerobic granules in a sequencing batch airlift reactor. Bioresour Technol 139:285–291
van den Akker B, Beard H, Kaeding U, Giglio S, Short MD (2010) Exploring the relationship between viscous bulking and ammonia-oxidiser abundance in activated sludge: a comparison of conventional and IFAS systems. Water Res 44(9):2919–2929. doi:10.1016/j.watres.2010.02.016
Verawaty M, Pijuan M, Yuan Z, Bond PL (2012) Determining the mechanisms for aerobic granulation from mixed seed of floccular and crushed granules in activated sludge wastewater treatment. Water Res 46(3):761–771. doi:10.1016/j.watres.2011.11.054
Wan J, Bessière Y, Spérandio M (2009) Alternating anoxic feast/aerobic famine condition for improving granular sludge formation in sequencing batch airlift reactor at reduced aeration rate. Water Res 43(20):5097–5108
Wang XH, Zhang HM, Yang FL, Xia LP, Gao MM (2007) Improved stability and performance of aerobic granules under stepwise increased selection pressure. Enzyme Microb Technol 41(3):205–211. doi:10.1016/j.enzmictec.2007.01.005
Wei D, Xue X, Chen S, Zhang Y, Yan L, Wei Q, Du B (2013) Enhanced aerobic granulation and nitrogen removal by the addition of zeolite powder in a sequencing batch reactor. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 97(20):9235–9243. doi:10.1007/s00253-012-4625-8
Winkler MK, Kleerebezem R, Strous M, Chandran K, Loosdrecht MCM (2013) Factors influencing the density of aerobic granular sludge. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 97(16):7459–7468. doi:10.1007/s00253-012-4459-4
Wu L, Peng C, Peng Y, Li L, Wang S, Ma Y (2012) Effect of wastewater COD/N ratio on aerobic nitrifying sludge granulation and microbial population shift. J Environ Sci 24(2):234–241. doi:10.1016/S1001-0742(11)60719-5
Xu G, Xu X, Yang F, Liu S (2011) Selective inhibition of nitrite oxidation by chlorate dosing in aerobic granules. J Hazard Mater 185(1):249–254
Zhou J, Wei S, Li J, He M, Hille A, Horn H (2011) Aerobic granulation in a modified continuous flow system. In: Bioinformatics and BiomZedical Engineering, (iCBBE) 2011 5th International Conference on, 2011. IEEE, pp 1–5
Zhou D, Dong S, Gao L, Liu M, Niu S (2013a) Distribution characteristics of extracellular polymeric substances and cells of aerobic granules cultivated in a continuous-flow airlift reactor. J Chem Technol Biotechnol 88(5):942–947. doi:10.1002/jctb.3927
Zhou D, Liu M, Wang J, Dong S, Cui N, Gao L (2013b) Granulation of activated sludge in a continuous flow airlift reactor by strong drag force. Biotechnol Bioproc Eng 18(2):289–299
Acknowledgment
The authors are grateful to the financial support from the Natural Sciences Foundation of China (50908097).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(PDF 267 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, Y., Zhou, D., Xu, Z. et al. Enhanced aerobic granulation, stabilization, and nitrification in a continuous-flow bioreactor by inoculating biofilms. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 98, 5737–5745 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-014-5637-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-014-5637-3