Abstract
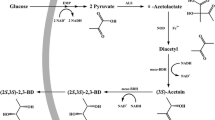
The Escherichia coli XL1-blue strain was metabolically engineered to synthesize poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxyvalerate) [P(3HB-co-3HV)] through 2-ketobutyrate, which is generated via citramalate pathway, as a precursor for propionyl-CoA. Two different metabolic pathways were examined for the synthesis of propionyl-CoA from 2-ketobutyrate. The first pathway is composed of the Dickeya dadantii 3937 2-ketobutyrate oxidase or the E. coli pyruvate oxidase mutant (PoxB L253F V380A) for the conversion of 2-ketobutyrate into propionate and the Ralstonia eutropha propionyl-CoA synthetase (PrpE) or the E. coli acetyl-CoA:acetoacetyl-CoA transferase for further conversion of propionate into propionyl-CoA. The second pathway employs pyruvate formate lyase encoded by the E. coli tdcE gene or the Clostridium difficile pflB gene for the direct conversion of 2-ketobutyrate into propionyl-CoA. As the direct conversion of 2-ketobutyrate into propionyl-CoA could not support the efficient production of P(3HB-co-3HV) from glucose, the first metabolic pathway was further examined. When the recombinant E. coli XL1-blue strain equipped with citramalate pathway expressing the E. coli poxB L253F V380A gene and R. eutropha prpE gene together with the R. eutropha PHA biosynthesis genes was cultured in a chemically defined medium containing 20 g/L of glucose as a sole carbon source, P(3HB-co-2.3 mol% 3HV) was produced up to the polymer content of 61.7 wt.%. Moreover, the 3HV monomer fraction in P(3HB-co-3HV) could be increased up to 5.5 mol% by additional deletion of the prpC and scpC genes, which are responsible for the metabolism of propionyl-CoA in host strains.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aldor I, Keasling JD (2001) Metabolic engineering of poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxyvalerate) composition in recombinant Salmonella enterica serovar typhimurium. Biotechnol Bioeng 76(2):108–114
Aldor IS, Kim SW, Prather KL, Keasling JD (2002) Metabolic engineering of a novel propionate-independent pathway for the production of poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxyvalerate) in recombinant Salmonella enterica serovar typhimurium. Appl Environ Microbiol 68(8):3848–3854
Atsumi S, Liao JC (2008) Directed evolution of Methanococcus jannaschii citramalate synthase for biosynthesis of 1-propanol and 1-butanol by Escherichia coli. Appl Environ Microbiol 74(24):7802–7808
Atsumi S, Hanai T, Lioa JC (2008) Non-fermentative pathways for synthesis of branched-chain higher alcohols as biofuels. Nature 451:86–89
Berezina N (2012) Enhancing the 3-hydroxyvalerate component in bioplastic PHBV production by Cupriavidus necator. Biotechnol J 7(2):304–309
Braunegg G, Sonnleitner B, Lafferty R (1978) A rapid gas chromatographic method for the determination of poly-β-hydroxybutyric acid in microbial biomass. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 6(1):29–37
Chang YY, Cronan JE (2000) Conversion of Escherichia coli pyruvate oxidase to an ‘alpha-ketobutyrate oxidase’. Biochem J 352:717–724
Chen Q, Wang Q, Wei G, Liang Q, Qi Q (2011) Production in Escherichia coli of poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxyvalerate) with differing monomer compositions from unrelated carbon sources. Appl Environ Microbiol 77(14):4886–4893
Choi GG, Kim MW, Kim JY, Rhee YH (2003) Production of poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxyvalerate) with high molar fractions of 3-hydroxyvalerate by a threonine-overproducing mutant of Alcaligenes sp. SH-69. Biotechnol Lett 25(9):665–670
Choi YJ, Park JH, Kim TY, Lee SY (2012) Metabolic engineering of Escherichia coli for the production of 1-propanol. Metab Eng 14(5):477–486
Datsenko KA, Wanner BL (2000) One-step inactivation of chromosomal genes in Escherichia coli K-12 using PCR products. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 97(12):6640–6645
Hesslinger C, Fairhurst SA, Sawers G (1998) Novel keto acid formate-lyase and propionate kinase enzymes are components of an anaerobic pathway in Escherichia coli that degrades L-threonine to propionate. Mol Microbiol 27(2):477–492
Jacquel N, Lo CW, Wei YH, Wu HS, Wang SS (2008) Isolation and purification of bacterial poly (3-hydroxyalkanoates). Biochem Eng J 39(1):15–27
Jenkins LS, Nunn WD (1987) Genetic and molecular characterization of the genes involved in short-chain fatty acid degradation in Escherichia coli: the ato system. J Bacteriol 169(1):42–52
Jung YK, Kim TY, Park SJ, Lee SY (2010) Metabolic engineering of Escherichia coli for the production of polylactic acid and its copolymers. Biotechnol Bioeng 105(1):161–171
Khanna S, Srivastava AK (2007) Production of poly(3-hydroxybutyric-co-3-hydroxyvaleric acid) having a high hydroxyvalerate content with valeric acid feeding. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 34(6):457–461
Lee SY (1996) Bacterial polyhydroxyalkanoates. Biotechnol Bioeng 49(1):1–14
Lee JW, Na D, Park JM, Lee J, Choi S, Lee SY (2012) Systems metabolic engineering of microorganisms for natural and non-natural chemicals. Nat Chem Biol 8(6):536–546
Liu XW, Wang HH, Chen JY, Li XT, Chen GQ (2009) Biosynthesis of poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxyvalerate) by recombinant Escherichia coli harboring propionyl-CoA synthase gene (prpE) or propionate permease gene (prpP). Biochem Eng J 43(1):72–77
Madison LL, Huisman GW (1999) Metabolic engineering of poly(3-hydroxyalkanoates): from DNA to plastic. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 63(1):21–53
Mainguet SE, Liao JC (2010) Bioengineering of microorganisms for C3 to C5 alcohols production. Biotechnol J 5(12):1297–1308
Marcheschi RJ, Gronenberg LS, Liao JC (2013) Protein engineering for metabolic engineering current and next-generation tools. Biotechnol J 8(5):545–555
Na D, Yoo SM, Chung H, Park H, Park JH, Lee SY (2013) Metabolic engineering of Escherichia coli using synthetic small regulatory RNAs. Nat Biotechnol 31(2):170–174
Park SJ, Choi JI, Lee SY (2005) Engineering of Escherichia coli fatty acid metabolism for the production of polyhydroxyalkanoates. Enzym Microb Technol 36(4):579–588
Park SJ, Lee SY, Kim TW, Jung YK, Yang TH (2012a) Biosynthesis of lactate-containing polyesters by metabolically engineered bacteria. Biotechnol J 7(2):199–212
Park SJ, Lee TW, Lim SC, Kim TW, Lee H, Kim MK, Lee SH, Song BK, Lee SY (2012b) Biosynthesis of polyhydroxyalkanoates containing 2-hydroxybutyrate from unrelated carbon source by metabolically engineered Escherichia coli. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 93(1):273–283
Park SJ, Kang KH, Lee H, Park AR, Yang JE, Oh YH, Song BK, Jegal J, Lee SH, Lee SY (2013) Propionyl-CoA dependent biosynthesis of 2-hydroxybutyrate containing polyhydroxyalkanoates in metabolically engineered Escherichia coli. J Biotechnol 165(2):93–98
Peralta-Yahya PP, Keasling JD (2010) Advanced biofuel production in microbes. Biotechnol J 5(2):147–162
Rehm BHA (2010) Bacterial polymers: biosynthesis, modifications and applications. Nat Rev Microbiol 8(8):578–592
Reinecke F, Steinbüchel A (2009) Ralstonia eutropha strain H16 as model organism for PHA metabolism and for biotechnological production of technically interesting biopolymers. J Mol Microbiol Biotechnol 16(1–2):91–108
Sambrook J, Russell DW (2001) Molecular cloning: a laboratory manual, vol 3. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, Cold Spring Harbor
Steinbüchel A, Valentin HE (1995) Diversity of bacterial polyhydroxyalkanoic acids. FEMS Microbiol Lett 128(3):219–228
Tseng HC, Harwell CL, Martin CH, Prather KL (2010) Biosynthesis of chiral 3-hydroxyvalerate from single propionate-unrelated carbon sources in metabolically engineered E. coli. Microb Cell Factories 9:96
Valentin HE, Mitsky TA, Mahadeo DA, Tran M, Gruys KJ (2000) Application of a propionyl coenzyme A synthetase for poly(3-hydroxypropionate-co-3-hydroxybutyrate) accumulation in recombinant Escherichia coli. Appl Environ Microbiol 66(12):5253–5258
Wong MS, Causey TB, Mantzaris N, Bennett GN, San KY (2008) Engineering poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxyvalerate) copolymer composition in E. coli. Biotechnol Bioeng 99(4):919–928
Yang TH, Kim TW, Kang HO, Lee SH, Lee EJ, Lim SC, Oh SO, Song AJ, Park SJ, Lee SY (2010) Biosynthesis of polylactic acid and its copolymers using evolved propionate CoA transferase and PHA synthase. Biotechnol Bioeng 105(1):150–160
Yang YH, Brigham CJ, Song E, Jeon JM, Rha CK, Sinskey AJ (2012) Biosynthesis of poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxyvalerate) containing a predominant amount of 3-hydroxyvalerate by engineered Escherichia coli expressing propionate-CoA transferase. J Appl Microbiol 113(4):815–823
Yoo SM, Na D, Lee SY (2013) Design and use of synthetic regulatory small RNAs to control gene expression in Escherichia coli. Nat Protoc 8(9):1694–1707
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Technology Development Program to Solve Climate Changes (Systems Metabolic Engineering for Biorefineries) from the Ministry of Science, ICT, and Future Planning through the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF-2012-C1AAA001-2012M1A2A2026556).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Jung Eun Yang and Yong Jun Choi equally contributed to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, J.E., Choi, Y.J., Lee, S.J. et al. Metabolic engineering of Escherichia coli for biosynthesis of poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxyvalerate) from glucose. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 98, 95–104 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-013-5285-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-013-5285-z