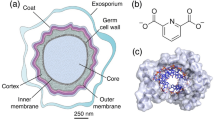
Abstract
Due to their contribution to gastrointestinal and pulmonary disease, their ability to produce various deadly exotoxins, and their resistance to extreme temperature, pressure, radiation, and common chemical disinfecting agents, bacterial endospores of the Firmicutes phylum are a major concern for public and environmental health. In addition, the hardy and dormant nature of endospores renders them a particularly significant threat to the integrity of robotic extraterrestrial life-detection investigations. To prevent the contamination of critical surfaces with seemingly ubiquitous bacterial endospores, clean rooms maintained at exceedingly stringent cleanliness levels (i.e., fewer than 100,000 airborne particles per ft3) are used for surgical procedures, pharmaceutical processing and packaging, and fabrication and assembly of medical devices and spacecraft components. However, numerous spore-forming bacterial species have been reported to withstand typical clean room bioreduction strategies (e.g., UV lights, maintained humidity, paucity of available nutrients), which highlights the need for rapid and reliable molecular methods for detecting, enumerating, and monitoring the incidence of viable endospores. Robust means of evaluating and tracking spore burden not only provide much needed information pertaining to endospore ecophysiology in different environmental niches but also empower decontamination and bioreduction strategies aimed at sustaining the reliability and integrity of clean room environments. An overview of recent molecular advances in detecting and enumerating viable endospores, as well as the expanding phylogenetic diversity of pathogenic and clean room-associated spore-forming bacteria, ensues.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amann R, Fuchs BM (2008) Single-cell identification in microbial communities by improved fluorescence in situ hybridization techniques. Nat Rev Microbiol 6:339–348
Amann RI, Ludwig W, Schleifer KH (1995) Phylogenetic identification and in situ detection of individual microbial cells without cultivation. Microbiol Rev 59:143–169
Anderson J, Reynolds C, Ringelberg D, Edwards J, Foley K (2008) Differentiation of live-viable versus dead bacterial endospores by calibrated hyperspectral reflectance microscopy. J Microsc 232:130–136
Aureli P, Fenicia L, Pasolini B, Gianfranceschi M, McCroskey LM, Hatheway CL (1986) Two cases of type E infant botulism caused by neurotoxigenic Clostridium butyricum in Italy. J Infect Dis 154:207–211
Baeumner AJ, Leonard B, McElwee J, Montagna RA (2004) A rapid biosensor for viable B. anthracis spores. Anal Bioanal Chem 380:15–23
Barer MR, Harwood CR (1999) Bacterial viability and culturability. Adv Microb Physiol 41:93–137
Bert F, Ouahes O, Lambert-Zechovsky N (1995) Brain abscess due to Bacillus macerans following a penetrating periorbital injury. J Clin Microbiol 33:1950–1953
Birch L, Dawson CE, Cornett JH, Keer JT (2001) A comparison of nucleic acid amplification techniques for the assessment of bacterial viability. Lett Appl Microbiol 33:296–301
Black EP, Koziol-Dube K, Guan D, Wei J, Setlow B, Cortezzo DE, Hoover DG, Setlow P (2005) Factors influencing the germination of Bacillus subtilis spores via the activation of nutrient receptors by high pressure. Appl Environ Microbiol 71:5879–5887
Black EP, Wei J, Atluri S, Cortezzo DE, Koziol-Dube K, Hoover DG, Setlow P (2007) Analysis of factors influencing the rate of germination of spores of Bacillus subtilis by very high pressure. J Appl Microbiol 102:65–76
Blodgett RJ (2005) Serial dilution with a confirmation step. Food Microbiol 22:547–552
Boulos L, Prevost M, Barbeau B, Coallier J, Desjardins R (1999) LIVE/DEAD BacLight: application of a new rapid staining method for direct enumeration of viable and total bacteria in drinking water. J Microbiol Methods 37:77–86
Brescia CC, Griffin SM, Ware MW, Varughese EA, Egorov AI, Villegas EN (2009) Cryptosporidium propidium monoazide-PCR, a molecular biology-based technique for genotyping of viable Cryptosporidium oocysts. Appl Environ Microbiol 75:6856–6863
Cao-Hoang L, Marechal PA, Le-Thanh M, Gervais P, Wache Y (2008) Fluorescent probes to evaluate the physiological state and activity of microbial biocatalysis: a guide for prokaryotic and eukaryotic investigation. Biotechnol J 3:890–903
Cenciarini-Borde C, Courtois S, La Scola B (2009) Nucleic acids as viability markers for bacteria detection using molecular tools. Future Microbiol 4:45–65
Curtis LT (2008) Prevention of hospital-acquired infections: review of non-pharmacological interventions. J Hosp Infect 69:204–219
Davies HA, Borriello SP (1990) Detection of capsule in strains of Clostridium difficile of varying virulence and toxigenicity. Microb Pathog 9:141–146
de Graaf DC, Alippi AM, Brown M, Evans JD, Feldlaufer M, Gregorc A, Hornitzky M, Pernal SF, Schuch DMT, Titera D, Tomkies V, Ritter W (2006) Diagnosis of American foulbrood in honey bees: a synthesis and proposed analytical protocols. Lett Appl Microbiol 43:583–590
Demos SG, Lieber CA, Lin B, Ramsamooj R (2005) Imaging of tissue microstructures using a multimodal microscope design. IEEE J Sel Top Quantum Electron 11:752–758
Denéve C, Janoir C, Poilane I, Fantinato C, Collignon A (2009) New trends in Clostridium difficile virulence and pathogenesis. Int J Antimicrob Agents 33:S24–S28
Diaper JP, Tither K, Edwards C (1992) Rapid assessment of bacterial viability by flow cytometry. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 38:268–272
Drancourt M, Berger P, Raoult D (2004) Systematic 16S rRNA gene sequencing of atypical clinical isolates identified 27 new bacterial species associated with humans. J Clin Microbiol 42:2197–2202
Driks A (1999) Bacillus subtilis spore coat. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 63:1–20
Ezzell JW, Welkos SL (1999) The capsule of Bacillus anthracis, a review. J Appl Microbiol 87:250
Forsgren E (2010) European foulbrood in honeybees. J Invertebr Pathol 103:S5–S9
Fujinami Y, Kataoka M, Matsushita K, Sekigushi H, Ito T, Tsuge K, Seto Y (2004) Sensitive detection of bacteria and spores using a portable bioluminescence ATP measurement assay system distinguishing from white powder materials. J Health Sci 50:126–132
Ghelardi E, Celandroni F, Salvetti S, Fiscarelli E, Senesi S (2007) Bacillus thuringiensis pulmonary infection: critical role for bacterial membrane-damaging toxins and host neutrophils. Microbiol Infect 9:591–598
Gioia J, Yerrapragada S, Qin X, Xiang H, Igboeli OC, Muzny D (2007) Paradoxical DNA repair and peroxide resistance gene conservation in Bacillus pumilus SAFR-032. PLoS One 2:e928
Goodacre R, Timmins EM, Burton R, Kaderbhai N, Woodward AM, Kell DB, Rooney PJ (1998) Rapid identification of urinary tract infection bacteria using hyperspectral whole-organism fingerprinting and artificial neural networks. Microbiology 144:1157–1170
Grochulski P, Masson L, Borisova S, Pusztai-Carey M, Schwartz J, Brousseau R, Cygler M (1995) Bacillus thuringiensis CrylA(a) insecticidal toxin: crystal structure and channel formation. J Mol Biol 254:447–469
Harvey SM, Sturgeon J, Dassey DE (2002) Botulism due to Clostridium baratii type F toxin. J Clin Microbiol 40:2260–2262
Hatheway CL (1990) Toxigenic clostridia. Clin Microbiol Rev 3:66–98
Henriques AO, Moran CPJ (2007) Structure, assembly and function of the spore surface layers. Annu Rev Microbiol 61:555–588
Horneck G, Klaus DM, Mancinelli RL (2010) Space microbiology. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 74:121–156
ISO (2003) Cleanrooms and associated controlled environments—biocontamination control–Part 1: General principles and methods, ISO 14698-1: 2003. International Organization for Standardization, Geneva, Switzerland.
Kane SR, Létant SE, Murphy GA, Alfaro TM, Krauter PW, Mahnke R, Legler TC, Raber E (2009) Rapid, high-throughput, culture-based PCR methods to analyze samples for viable spores of Bacillus anthracis and its surrogates. J Microbiol Methods 76:278–284
Kaneko K, Hayashidani H, Takahashi K, Shiraki Y, Limawongpranee S, Ogawa M (1999) Bacterial contamination in the environment of food factories processing ready-to-eat fresh vegetables. J Food Protect 62:800–804
Karner M, Furhman JA (1997) Determination of active marine bacterioplankton: a comparison of universal 16S rRNA probes, autoradiography, and nucleioid staining. Appl Environ Microbiol 63:1208–1213
Kempf MJ, Chen F, Kern R, Venkateswaran K (2005) Recurrent isolation of hydrogenperoxide-resistant spores of Bacillus pumilus from a spacecraft assembly facility. Astrobiology 5:391–405
Kim KK, Lee KC, Yu H, Ryoo S, Park Y, Lee JS (2010) Paenibacillus sputi sp. nov., isolated from the sputum of a patient with pulmonary disease. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 60:2371–2376
King TC, Sirdeskmukh R, Schlessinger D (1986) Nucleolytic processing of ribonucleic acid transcripts in procaryotes. Microbiol Rev 50:428–451
Ko KS, Kim YS, Lee MY, Shin SY, Jung DS, Peck KR, Song JH (2008) Paenibacillus konsidensis sp. nov., isolated from a patient. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 58:2164–2168
Kobayasi H, Oethinger M, Tuohy MJ, Hall GS, Bauer TW (2009) Improving clinical significance of PCR: use of propidium monoazide to distinguish viable from dead Staphylococcus aureus and Staphylococcus epidermidis. J Orthop Res 27:1243–1247
Kodaka H, Fukuda K, Mizuochi S, Horigome K (1996) Adenosine triphosphate content of microorganisms related with food spoilage. Jpn J Food Microbiol 13:29–34
Kotiranta A, Lounatmaa K, Haapasalo M (2000) Epidemiology and pathogenesis of Bacillus cereus infections. Microbiol Infect 2(2):189–198
La Duc MT, Kern R, Venkateswaran K (2004) Microbial monitoring of spacecraft and associated environments. Microb Ecol 47:150–158
La Duc MT, Dekas A, Osman S, Moissl C, Newcombe D, Venkateswaran K (2007) Isolation and characterization of bacteria capable of tolerating the extreme conditions of clean room environments. Appl Environ Microbiol 73:2600–2611
Laflamme C, Lavigne S, Ho J, Duchaine C (2004) Assessment of bacterial endospore viability with fluorescent dyes. J Appl Microbiol 96:684–692
Laflamme C, Ho J, Veillette M, deLatremoille MC, Verrault D, Meriaux A, Duchaine C (2005a) Flow cytometry analysis of germinating Bacillus spores, using membrane potential dye. Arch Microbiol 183:107–112
Laflamme C, Verrault D, Lavigne S, Trudel L, Ho J, Duchaine C (2005b) Autofluorescence as a viability marker for detection of bacterial spores. Front Biosci 10:1647–1653
Laflamme C, Verrault D, Ho J, Duchaine C (2006) Flow cytometry sorting protocol of Bacillus spore using ultraviolet laser and autofluorescence as main sorting criterion. J Fluoresc 16:733–737
Laflamme C, Gendron L, Turgeon N, Filion G, Ho J, Duchaine C (2009) Rapid detection of germinating Bacillus cereus cells using fluorescent in situ hybridization. J Rapid Methods Autom Microbiol 17:80–102
Lee J, Deininger RA (2004) A rapid screening method for the detection of viable spores in powder using bioluminescence. Luminescence 19:209–211
Létant SE, Kane SR, Murphy GA, Alfaro TM, Hodges LR, Rose LJ, Raber E (2010) Most-probable-number rapid viability PCR method to detect viable spores of Bacillus anthracis in swab samples. J Microbiol Methods 81:200–246
Létant SE, Murphy GA, Alfaro TM, Avila JR, Kane SR, Raber E, Bunt TM, Shah SR (2011) Rapid-viability PCR method for detection of live, virulent Bacillus anthracis in environmental samples. Appl Environ Microbiol 77:6570–6578
Levinson HS, Hyatt MT (1966) Sequence of events during Bacillus megaterium spore germination. J Bacteriol 91:1811–1818
Link L, Sawyer J, Venkateswaran K, Nicholson W (2004) Extreme spore UV resistance of Bacillus pumilus isolates obtained from an ultraclean spacecraft assembly facility. Microb Ecol 47:159–163
Logan NA (2012) Bacillus and relatives in foodborne illness. J Appl Microbiol 112:417–429
López-Amorós R, Castel S, Comas-Riu J, Vives-Rego J (1997) Assessment of E. coli and Salmonella viability and starvation by confocal laser microscopy and flow cytometry using rhodamine 123, DiBAC4(3), propidium iodide, and CTC. Cytometry 29:298–305
Magge A, Setlow B, Cowan AE, Setlow P (2009) Analysis of dye binding by and membrane potential in spores of Bacillus species. J Appl Microbiol 106:814–824
Mangram AJ, Horan TC, Pearson ML, Silver LC, Jarvis WR (1999) Guideline for prevention of surgical site infection. Am J Infect Control 27:97–134
Mathys A, Chapman B, Bull M, Heinz V, Knorr D (2007) Flow cytometric assessment of Bacillus spore response to high pressure and heat. Innovative Food Sci Emerg Technol 8:519–527
McClane BA (2007) Clostridium perfringens. In: Doyle MP, Beuchat LR (eds) Food microbiology: fundamentals and frontiers, 3rd edn. ASM, Washington, DC, pp 423–444
Mock M, Fouet A (2001) Anthrax. Annu Rev Microbiol 55:647–671
Mohapatra BR, La Duc MT (2012a) Evaluation of fluorescence in situ hybridization to detect encapsulated Bacillus pumilus SAFR-032 spores released from poly(methylmethacrylate). Microbiol Immunol 56:40–47
Mohapatra BR, La Duc MT (2012b) Rapid detection of viable Bacillus pumilus SAFR-032 encapsulated spores using novel propidium monoazide-linked fluorescence in situ hybridization. J Microbiol Methods 50:15–19
Moir A (2006) How do spores germinate? J Appl Microbiol 101:526–530
Monis PT, Giglio S (2006) Nucleic acid amplification-based techniques for pathogen detection and identification. Infect Genet Evol 6:2–12
Mothershed EA, Whitney AM, Bates JR, Costanzo SD (2006) Nucleic acid-based methods for the detection of bacterial pathogens: present and future considerations for the clinical laboratory. Clin Chim Acta 363:206–220
Nagarkar PP, Ravetkar SD, Watve MG (2001) Oligophilic bacteria as tools to monitor aseptic pharmaceutical production units. Appl Environ Microbiol 67:1371–1374
Nakamura LK (1990) Bacillus thiaminolyticus sp. nov., nom. rev. Int J Syst Bacteriol 40:242–246
NASA (1980) Handbook for the microbial examination of space hardware, NHB 6022, 1980. National Aeronautics and Space Administration, Washington, DC, 20546
Nebe-von Caron G, Stephens P, Badley RA (1998) Assessment of bacterial viability status by flow cytometry and single cell sorting. J Appl Microbiol 84:988–998
Newcombe DA, Schuerger AC, Benardini JN, Dickinson D, Tanner R, Venkateswaran K (2005) Survival of spacecraft-associated microorganisms under simulated Martian UV irradiation. Appl Environ Microbiol 71:8147–8156
Newsome T, Li BJ, Zou N, Lo SC (2004) Presence of bacterial phage-like DNA sequences in commercial Taq DNA polymerase reagents. J Clin Microbiol 42:2264–2267
Nocker A, Sossa-Fernandez P, Burr MD, Camper AK (2007) Use of propidium monoazide for live/dead distinction in microbial ecology. Appl Environ Microbiol 73:5111–5117
Nocker A, Mazza A, Masson L, Camper AK, Brousseau R (2009) Selective detection of live bacteria combining propidium monoazide sample treatment with microarray technology. J Microbiol Methods 76:253–261
Nocker A, Richter-Heitmann T, Montijn R, Schuren F, Kort R (2010) Discrimination between live and dead cells in bacterial communities from environmental samples analyzed by 454 pyrosequencing. Int Microbiol 13:59–65
Noskin GA, Suriano T, Collins S, Sesler S, Peterson LR (2001) Paenibacillus macerans pseudobacteremia resulting from contaminated blood culture bottles in a neonatal intensive care unit. Am J Infect Control 29:126–129
Oliver JD (2005) The viable but nonculturable state in bacteria. J Microbiol 43:93–100
Ouyang J, Pei Z, Lutwick L, Dalal S, Yang L, Cassai N, Sandhu K, Hanna B, Wieczorek RL, Bluth M, Pincus MR (2008) Paenibacillus thiaminolyticus: a new cause of human infection, inducing bacteremia in a patient on hemodialysis. Ann Clin Lab Sci 38:393–400
Pacheco FLC, Pinto TDA (2010) The bacterial diversity of pharmaceutical cleanrooms analyzed by the fatty acid methyl ester technique. PDA J Pharm Sci Technol 64:156–166
Paredes-Sabja D, Setlow P, Sarker MR (2011) Germination of spores of Bacillales and Clostridiales species: mechanisms and proteins involved. Trends Microbiol 19:85–94
Parshionikar S, Laseke I, Fout GS (2010) Use of propidium monoazide in reverse transcriptase PCR to distinguish between infectious and noninfectious enteric viruses in water samples. Appl Environ Microbiol 76:4318–4326
Poxton IR, McCoubrey J, Blair G (2001) The pathogenicity of Clostridium difficile. Clin Microbiol Infect 7:421–427
Rawsthorne H, Dock CN, Jaykus LA (2009) PCR-based method using propidium monoazide to distinguish viable from nonviable Bacillus subtilis spores. Appl Environ Microbiol 75:2936–2939
Rieg S, Bauer TM, Peyerl-Hoffmann G, Held J, Ritter W, Wagner D, Kern WV, Serr A (2010) Paenibacillus larvae bacteremia in injection drug users. Emerg Infect Dis 16:487–489
Rippere K, Tran M, Yousten A, Hilu K, Klein M (1998) Bacillus popilliae and Bacillus lentimorbus, bacteria causing milky disease in Japanese beetles and related scarab larvae. Int J Syst Bacteriol 48:395–402
Rodriguez GG, Phipps D, Ishiguro K, Ridgway HF (1992) Use of a fluorescent redox probe for direct visualization of actively respiring bacteria. Appl Environ Microbiol 58:1801–1808
Rogers GB, Stressmann FA, Koller G, Daniels T, Carroll MP, Bruce KD (2008) Assessing the diagnostic importance of nonviable bacterial cells in respiratory infections. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis 62:133–141
Roux V, Fenner L, Raoult D (2008) Paenibacillus provencensis sp. nov., isolated from human cerebrospinal fluid, and Paenibacillus urinalis sp. nov., isolated from human urine. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 58:682–687
Rueckert A, Morgan HW (2007) Removal of contaminating DNA from polymerase chain reaction using ethidium monoazide. J Microbiol Methods 68:596–600
Schultz RA, Nielsen T, Zavaleta JR, Ruch R, Wyatt R, Garner HR (2001) Hyperspectral imaging: a novel approach for microscopic analysis. Cytometry 43:239–247
Seiler H, Schmidt V, Wenning M, Scherer S (2013) Bacillus kochii sp. nov., isolated from foods and a pharmaceuticals manufacturing site. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 24:1092–1097
Setlow P (2003) Spore germination. Curr Opin Microbiol 6:550–556
Setlow P (2006) Spores of Bacillus subtilis: their resistance to and killing by radiation, heat and chemicals. J Appl Microbiol 101:514–525
Setlow P (2007) I will survive: DNA protection in bacterial spores. Trends Microbiol 15:172–180
Shafaat HS, Ponce A (2006) Application of a rapid endospore viability assay for monitoring UV inactivation and characterizing arctic ice cores. Appl Environ Microbiol 72:6808–6814
Sheridan GE, Masters CI, Shallcross JA, MacKey BM (1998) Detection of mRNA by reverse transcription-PCR as an indicator of viability in Escherichia coli cells. Appl Environ Microbiol 64:1313–1318
Shida O, Takagi H, Kadowaki K, Nakamura LK, Komagata K (1997) Emended description of Paenibacillus amylolyticus and description of Paenibacillus illinoisensis sp. nov. and Paenibacillus chibensis sp. nov. Int J Syst Bacteriol 47:299–306
Stam CN, Bruckner J, Spry JA, Venkateswaran K, La Duc MT (2012) A molecular method to assess bioburden embedded within silicon-based resins used on modern spacecraft materials. Int J Astrobiol 11:141–145
Stocks SM (2004) Mechanism and use of the commercially available viability stain, BacLight. Cytometry A 61:189–195
Swannell RPJ, Williamson FA (1988) An investigation of staining methods to determine total cell numbers and the number of respiring micro-organisms in samples obtained from the field and the laboratory. FEMS Microbiol Lett 53:315–324
Tamura K, Dudley J, Nei M, Kumar S (2007) MEGA 4: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis (MEGA) software version 4.0. Mol Biol Evol 24:1596–1599
Teng JLL, Woo PCY, Leung KW, Lau SKP, Wong MKM, Yuen KY (2003) Pseudobacteremia in a patient with neutropenic fever caused by a novel Paenibacillus species: Paenibacillus hongkongensis sp. nov. Mol Pathol 56:29–35
Thomas KW, Griffiths FR (1987) Natural establishment of thiaminase activity in the alimentary tract of newborn lambs and effects on thiamine status and growth rates. Aust Vet J 64:207–210
Ullrich S, Karrasch B, Hoppe HG, Jeskulke K, Mehrens M (1996) Toxic effects on bacterial metabolism of the redox dye 5-cyano-2,3-ditolyl tetrazolium chloride. Appl Environ Microbiol 62:4587–4593
Vaishampayan P, Probst AJ, La Duc MT, Bargoma E, Benardini JN, Andersen GL, Venkateswaran K (2013) New perspectives on viable microbial communities in low-biomass cleanroom environments. ISME J 7:312–324
Vanandel RA, Franklin CL, Besch-Williford CL, Hook RR, Riley LK (2000) Prolonged perturbations of tumour necrosis factor-α and interferon-γ in mice inoculated with Clostridium piliforme. J Med Microbiol 49:557–563
Venkateswaran K, Hattori N, La Duc MT, Kern R (2003) ATP as a biomarker of viable microorganisms in clean-room facilities. J Microbiol Methods 52:367–377
Vesper S, McKinstry C, Hartmann C, Neace M, Yoder S, Vesper A (2008) Quantifying fungal viability in air and water samples using quantitative PCR after treatment with propidium monoazide (PMA). J Microbiol Methods 72:180–184
WHO (2012) Environmental monitoring of cleanrooms in vaccine manufacturing facilities. World Health Organization, Geneva, Switzerland
Wilson T, Hastings JW (1998) Bioluminescence. Ann Rev Cell Dev Biol 14:197–230
Yang W, Ponce A (2009) Rapid endospore viability assay of Clostridium sporogenes spores. Int J Food Microbiol 133:213–216
Yang W-W, Crow-Willard E, Ponce A (2009) Production and characterization of pure spore suspensions of Clostridium sporogenes and C. hungatei. Appl Environ Microbiol 106:27–33
Yung PT, Shafaat HS, Connon SA, Ponce A (2007) Quantification of viable endospores from a Greenland ice core. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 59:300–306
Zimmerman R, Strurriga R, Becker-Brik J (1978) Simultaneous determination of the total number of aquatic bacteria and the number thereof involved in respiration. Appl Environ Microbiol 36:926–935
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Dr. K. Venkateswaran for valuable collegial discussion, advice, and encouragement. Part of this research was carried out at the Jet Propulsion Laboratory, California Institute of Technology, under a contract with the National Aeronautics and Space Administration.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mohapatra, B.R., La Duc, M.T. Detecting the dormant: a review of recent advances in molecular techniques for assessing the viability of bacterial endospores. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 97, 7963–7975 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-013-5115-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-013-5115-3