Abstract
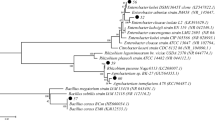
A survey of symbiotic bacteria from legumes grown in high mercury-contaminated soils (Almadén, Spain) was performed to produce a collection of rhizobia which could be well adapted to the environmental conditions of this region and be used for restoration practices. Nineteen Hg-tolerant rhizobia were isolated from nodules of 11 legume species (of the genera Medicago, Trifolium, Vicia, Lupinus, Phaseolus, and Retama) and characterized. Based on their growth on Hg-supplemented media, the isolates were classified into three susceptibility groups. The minimum inhibitory concentrations (MICs) and the effective concentrations that produce 50% mortality identified the patterns of mercury tolerance and showed that 15 isolates were tolerant. The dynamics of cell growth during incubation with mercury showed that five isolates were unaffected by exposure to Hg concentrations under the MICs. Genetic analyses of the 16S rRNA gene assigned ten strains to Rhizobium leguminosarum, six to Ensifer medicae, two to Bradyrhizobium canariense, and one to Rhizobium radiobacter. Inoculation of host plants and analysis of the nodC genes revealed that most of them were symbiotically effective. Finally, three isolates were selected for bioremediation processes with restoration purposes on the basis of their levels of Hg tolerance, their response to high concentrations of this heavy metal, and their genetic affiliation and nodulation capacity.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abou-Shanab RAI, Van Berkum P, Angle JS (2007) Heavy metal resistance and genotypic analysis of metal resistance genes in gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria present in Ni-rich serpentine soil and in the rhizosphere of Alyssum murale. Chemosphere 68:360–367
Almeida Pereira SI, Gusmao Lima AI, Almeida Paula Figueira EM (2006) Screening possible mechanisms mediating cadmium resistance in Rhizobium leguminosarum bv. viceae isolated from contaminated Portuguese soils. Microb Ecol 52:176–18
Barkay T, Miller SM, Summers AO (2003) Bacterial mercury resistance from atoms to ecosystems. FEMS Microbiol Rev 27:355–384
Boening DW (2000) Ecological effects, transport, and fate of mercury: a general review. Chemosphere 40:1335–1351
Calabrese EJ (2005) Paradigm lost, paradigm found: the re-emergence of hormesis as a fundamental dose response model in the toxicological sciences. Environ Pollut 138:378–411
Carrasco JA, Armario P, Pajuelo E, Burgos A, Caviedes MA, López R, Chamber MA, Palomares AJ (2005) Isolation and characterisation of symbiotically effective Rhizobium resistant to arsenic and heavy metals after the toxic spill at the Aznalcóllar pyrite mine. Soil Biol Biochem 37:1131–1140
Chadhain Ní SM, Schaefer JK, Crane S, Zylstra GJ, Barkay T (2006) Analysis of mercuric reductase (merA) gene diversity in an anaerobic mercury-contaminated sediment enrichment. Environ Microbiol 8(10):1746–1752
De Andrés F, Walter I, Tenorio JL (2007) Revegetation of abandoned agricultural land amended with biosolids. Sci Total Environ 378:81–83
Fernández-Pascual M, de Felipe MR, Serra T, Pozuelo JM (1988) Effects of cianazine and Linuron on chloroplast development, nodule activity and protein metabolism in Lupinus albus L. J Plant Physiol 133:288–294
Franche C, Lindstrom K, Elmerich C (2009) Nitrogen-fixing bacteria associated with leguminous and non-leguminous plants. Plant Soil 321:35–59
Gray JE, Hines ME, Higueras PL, Adatto I, Lasorsa BK (2004) Mercury speciation and microbial transformations in mine wastes, stream sediments, and surface waters at the Almadén Mining District, Spain. Environ Sci Technol 38:4285–4292
Higueras P, Oyarzun R, Lillo J, Sánchez-Hernández JC, Molina JA, Esbrí JM, Lorenzo S (2006) The Almadén district (Spain): anatomy of one of the world’s largest Hg-contaminated sites. Sci Total Environ 356:112–124
Hou BC, Wang ET, Li Y, Jia RZ, Chen WF, Man CX, Sui XH, Chen WX (2009) Rhizobial resource associated with epidemic legumes in Tibet. Microb Ecol 57:69–81
Hungria M, Chueir LMO, Coca RG, Megías M (2001) Preliminary characterization of fast growing rhizobial strains isolated from soybean nodules in Brazil. Soil Biol Biochem 33:1349–1361
Laguerre G, Allard MR, Revoy F, Amarger N (1994) Rapid identification of rhizobia by restriction fragment length polymorphism analysis of PCR-amplified 16S rRNA genes. Appl Environ Microbiol 60:56–63
Laguerre G, Nour SM, Macheret V, Sanjuan J, Drouin P, Amarger N (2001) Classification of rhizobia based on nodC and nifH gene analysis reveals a close phylogenetic relationship among Phaseolus vulgaris symbionts. Microbiology 147:981–993
Lane DJ (1991) 16S/23S rRNA sequencing. In: Strackebrandt E, Goodfellow M (eds) Nucleic acid techniques in bacterial systematics. Wiley, Chichester, pp 115–175
Liebert CA, Wireman J, Smith T, Summers AO (1997) Phylogeny of mercury resistance (mer) operons of gram-negative bacteria isolated from the fecal flora of primates. Appl Environ Microbiol 63:1066–1076
Maliszewska-Kordybach B, Klimkowicz-Pawlas A, Smrezak B (2007) Ecotoxic effect of phenanthrene on nitrifying bacteria in soils of different properties. J Environ Qual 16:1635–1645
Mhamdi R, Mrabet M, Laguerre G, Tiwari R, Aouani ME (2005) Colonization of Phaseolus vulgaris nodules by Agrobacterium-like strains. Can J Microbiol 51:105–111
Millán R, Gamarra R, Schmid T, Sierra MJ, Quejido AJ, Sánchez DM, Cardona AI, Fernández M, Vera R (2006) Mercury content in vegetation and soils of the Almadén mining area (Spain). Sci Total Environ 368:79–87
Molina JA, Oyarzun R, Esbrí JM, Higueras P (2006) Mercury accumulation in soils and plants in the Almadén mining district, Spain: one of the most contaminated sites on Earth. Environ Geochem Health 28:487–498
Moreno-Jiménez E, Gamarra R, Carpena-Ruiz RO, Millán R, Peñalosa JM, Esteban E (2006) Mercury bioaccumulation and phytotoxicity in two wild plant species of Almadén area. Chemosphere 63:1969–1973
Moschetti G, Peluso AL, Protopapa A, Anastasio M, Pepe O, Defez R (2005) Use of nodulation pattern, stress tolerance, nodC gene amplification, RAPD-PCR and RFLP-16S rDNA analysis to discriminate genotypes of Rhizobium leguminosarum biovar viceae. Syst Appl Microbiol 28:619–631
Muresu R, Polone E, Sulas L, Baldan B, Tondello A, Delogu G, Cappuccinelli P, Alberghini S, Benhizia Y, Benhizia H, Benguedouar A, Mori B, Calamassi R, Dazzo FB, Squartini A (2008) Coexistence of predominantly nonculturable rhizobia with diverse, endophytic bacterial taxa within nodules of wild legumes. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 63:383–400
Odee DW, Sutherland JM, Makatiani ET, McInroy SG, Sprent JI (1997) Phenotypic characteristics and composition of rhizobia associated with woody legumes growing in diverse Kenyan conditions. Plant Soil 188:165–175
OECD (Organization for Economic Co-Operation and Development) (2003) Draft guidance document on the statistical analysis of ecotoxicity data. OECD, Paris
Pajuelo E, Dary M, Palomares AJ, Rodriguez-Llorente ID, Carrasco JA, Chamber MA (2008) Biorhizoremediation of heavy metals toxicity using rhizobium–legume symbioses. In: Dakora FD, Chimphango SBM, Valentine AJ, Elmeric C, Newton WE (eds) Biological nitrogen fixation: towards poverty alleviation through sustainable agriculture, vol 42, Book Series: Current plant science and biotechnology in agriculture. Springer, Dordrecht, Netherlands, pp 101–104
Pastor J, Hernández AJ, Prieto N, Fernández-Pascual M (2003) Accumulating behaviour of Lupinus albus L. growing in a normal and a decalcified calcic luvisol polluted with Zn. J Plant Physiol 160:1455–1463
Pepi M, Lobianco A, Renzi M, Perra G, Bernardini E, Marvasi M, Gasperini S, Volterrani M, Franchi E, Heipieper HJ, Focardi SE (2009) Two naphthalene degrading bacteria belonging to the genera Paenibacillus and Pseudomonas isolated from a highly polluted lagoon perform different sensitivities to the organic and heavy metal contaminants. Extremophiles 13:839–848
Rasmussen LD, Sorensen S (2001) Effect of mercury contamination on the culturable heterotrophic, functional and genetic diversity of the bacterial community in soil. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 36:1–9
Ruiz-Díez B, Fajardo S, Puertas-Mejía MA, de Felipe MR, Fernández-Pascual M (2009) Stress tolerance, genetic analysis and symbiotic properties of root-nodulating bacteria isolated from Mediterranean leguminous shrubs in Central Spain. Arch Microbiol 191:35–46
Ruiz-Díez B, Fajardo S, de Felipe MR, Fernandez-Pascual M (2011) The characterization of rhizobia from legumes of agronomic interest grown in semi-arid areas of Central Spain relates genetic differences to soil properties. J Basic Microbiol. doi:10.1002/jobm.201100058
Saitou N, Nei M (1987) The neighbour-joining method: a new method for reconstructing phylogenetic trees. Mol Biol Evol 4:406–425
Sambrook J, Fritsch EF, Maniatis T (eds) (1989) Molecular cloning: a laboratory manual, 2nd edn. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, Cold Spring Harbor, New York
Stacey G (1995) Bradyrhizobium japonicum nodulation genetics. FEMS Microbiol Lett 127:1–9
Tamura K, Dudley J, Nei M, Kumar S (2007) MEGA4: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis (MEGA) software version 4.0. Mol Biol Evol 24:1596–1599
Van Beelen P, Doelman P (1997) Significance and application of microbial toxicity tests in assessing ecotoxicological risks of contaminants in soil and sediment. Chemosphere 34:455–499
Villar-Salvador P, Valladares F, Domínguez-Lerena S, Ruiz-Díez B, Fernandez-Pascual M, Delgado AC, Peñuelas J (2008) Functional traits related to seedling performance in a Mediterranean leguminous shrub: insights from a provenance, fertilization, and rhizobial inoculation study. Environ Exp Bot 64:145–154
Vincent JM (1970) A manual for the practical study of root nodule bacteria. Blackwell Scientific, Oxford
Weir BS (2010) The current taxonomy of rhizobia. New Zealand rhizobia website, http://www.rhizobia.co.nz/taxonomy/rhizobia.html. Last update: 21st October (2010)
Weisburg WG, Barns SM, Pelletier DA, Lane DJ (1991) 16S ribosomal DNA amplification for phylogenetic study. J Bacteriol 173:697–703
Young JM, Kuykendall LD, Martinez-Romero E, Kerr A, Sawada H (2001) A revision of Rhizobium Frank (1889), with emended description of the genus, and the inclusion of all species of Agrobacterium Conn (1492) and Allorhizobium undicola de Lajudie et al. (1988) as new combinations: Rhizobium radiobacter, R. rhizogenes, R. rubi, R. undicola and R. vitis. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 51:89–103
Zornoza P, Vázquez S, Esteban E, Fernández-Pascual M, Carpena R (2002) Cd-stress in nodulated white lupin: strategies to avoid toxicity. Plant Physiol Biochem 40:1003–1009
Zurdo-Piñeiro JL, García-Fraile P, Rivas R, Peix A, León-Barrios M, Willems A, Mateos P, Martínez-Molina FE, Velázquez E, Van Berkum P (2009) Rhizobia from Lanzarote, the Canary Islands, that nodulate Phaseolus vulgaris have characteristics in common with Sinorhizobium meliloti isolates from Mainland Spain. Appl Environ Microbiol 75:2354–2359
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by the Junta de Comunidades de Castilla-La Mancha grants PII1I09-0142-4389 and POII10-0211-5015, Ministerio Español de Ciencia e Innovación AGL2009-10371, the Comunidad de Madrid S-0505/AMB/0321, and Fundación Areces. The authors would like to thank Dr. F Minchin for critical proofreading of the manuscript. BRD was supported by contracts of Junta de Comunidades de Castilla-La Mancha (POII09-0182-3834 and POII10-0211-5015).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
Mercury-resistant rhizobial bacteria isolated from nodules of leguminous plants growing in high Hg-contaminated soils (DOC 925 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ruiz-Díez, B., Quiñones, M.A., Fajardo, S. et al. Mercury-resistant rhizobial bacteria isolated from nodules of leguminous plants growing in high Hg-contaminated soils. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 96, 543–554 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-011-3832-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-011-3832-z