Abstract
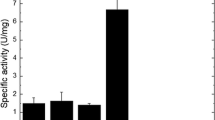
We have previously reported the identification of a small, basic and cysteine-rich antifungal peptide (AcAFP) secreted by Aspergillus clavatus and shown its ability to prevent growth of various human- and plant-pathogenic filamentous fungi. In this study, we sought to determine the physiological/microbiological requirements to enhance the AcAFP production and the conditions influencing its stability. The maximum of AcAFP production was obtained when A. clavatus was grown on 2% glycerol as sole carbon source and 100 mM NaCl. The AcAFP expression was shown to be influenced by pH, being suppressed under acidic (pH 5) and strongly induced under alkaline conditions. The activity of the purified AcAFP was not affected by temperature; it loosed approximately 20% of its activity after 3 h at 100°C and was efficient through a large pH range (pH 5-12) with an optimum at pH 8. AcAFP activity decreased at high ionic strength and in the presence of 10 mM of divalent cations (Mn2+, Fe2+ and Ca2+).






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anderson RC, Yu PL (2005) Factors affecting the antimicrobial activity of ovine-derived cathelicidins against E. coli 0157:H4. Int J Antimicrob Agents 25:205–210
Baker B, Zambryski P, Staskawicz B, Dinesh-Kumar SP (1997) Signalling in plant-microbe interaction. Science 276:726–733
Bradford MM (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 72:248–254
Ekengren S, Hultmark D (1999) Drosophila cecropin as an antifungal agent. Insect Biochem Mol Biol 29:965–972
Fernández D, Ouinten M, Tantaoui A, Geiger JP, Daboussi MJ, Langin T (1998) Fot1 insertions in the Fusarium oxysporum f. sp. albedinis genome provide diagnostic PCR targets for detection of the date palm pathogen. Appl Environ Microbiol 64:633–636
Fritig B, Heitz T, Legrand M (1999) Antimicrobial proteins in induced plant defense. Curr Opin Immunol 11:23–27
Geison R (2000) P. nalgiovense carries a gene which is homologous to the paf gene of P. chrysogenum which codes for an antifungal peptide. Int J Food Microbiol 62:95–101
Gun Lee D, Shin SY, Maeng CY, Jin ZZ, Kim KL, Ham KS (1999) Isolation and characterization of a novel antifungal peptide from Aspergillus niger. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 263:646–651
Hoffman HL, Ernest EJ, Klepser EE (2000) Novel triazole antifungal agents. Expert Opin Investig Drugs 9:593–605
Kaiserer L, Oberparleiter C, Weiler-Görz R, Burgstaller W, Leiter E, Marx F (2003) Characterization of the Penicillium chrysogenum antifungal protein PAF. Arch Microbiol 180:204–210
Laemmli UK, Favre M (1973) Maturation of the head of bacteriophage T4. I. DNA packaging events. J Mol Biol 80:573–599
Lehrer R, Ganz T (1999) Antimicrobial peptides in mammalian and insect host defence. Curr Opin Immunol 11:23–27
Martinez-Ruiz A, Martinez del Pozo A, Mancheno JM, Lacadena J, Onaderra M, Gavilanes JG (1997) Characterization of a natural larger form of the antifungal protein (AFP) from Aspergillus giganteus. Biochim Biophys Acta 1340:81–87
Marx F (2004) Small, basic antifungal proteins secreted from filamentous ascomycetes: comparative study regarding expression, structure, function and potential application. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 65:133–142
Marx F, Haas H, Reindl M, Stöffler G, Lottspeich F, Redl B (1995) Cloning, structural organization and regulation of expression of the Penicillium chrysogenum paf gene encoding an abundantly secreted protein of Aspergillus giganteus. Gene 167:167–171
Marx F, Binder U, Leitner E, Pocsi I (2008) The Penicillium chrysogenum antifungal protein PAF, a promising tool for the development of new antifungal therapies and fungal cell biology studies. Cell Mol Life Sci 65:445–454
Meyer V (2008) A small protein that fights fungi: AFP as a new promising antifungal agent of biotechnological value. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 78:17–28
Meyer V, Stahl U (2002) New insights in the regulation of the afp gene encoding the antifungal protein of Aspergillus giganteus. Curr Genet 45:36–42
Meyer V, Stahl U (2003) The influence of co-cultivation on expression of the antifungal protein in Aspergillus giganteus. J Basic Microbiol 43:68–74
Meyer V, Wedde M, Stahl U (2002) Transcriptional regulation of the antifungal protein in Aspergillus giganteus. Mol Genet Genomics 266:747–757
Osborn RW, De Samblanx GW, Thevissen K, Goderis I, Torrekens S, Van Leuven F, Attenborough S, Rees SB, Broekaert WF (1995) Isolation and characterisation of plants defensins from seeds of Asteraceae, Fabaceae, Hippocastanaceae and Saxifragaceae. FEBS Lett 368:257–262
Raj PA, Dentino AR (2002) Current status of defensins and their role in innate and adaptive immunity. FEMS Microbiol Lett 206:9–18
Skouri-Gargouri H, Gargouri A (2008) First isolation of a novel thermostable antifungal peptide secreted by Aspergillus clavatus. Peptides 29:1871–1877
Theis T, Stahl A (2004) Antifungal proteins: targets, mechanisms and prospective applications. Cell Mol Life Sci 61:437–455
Theis T, Wedde M, Meyer V, Stahl U (2003) The antifungal protein from Aspergillus giganteus causes membrane permeabilization. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 47:588–593
Theis T, Marx F, Salvenmoser W, Stahl U, Meyer V (2005) New insights into the target site and mode of action of the antifungal protein of Aspergillus giganteus. Res Microbiol 156:47–56
Thevissen K, Terras FRG, Broekaert WF (1999) Permeabilization of fungal membranes by plant defensins inhibits fungal growth. Appl Environ Microbiol 65:5451–5458
Wnendt S, Ulbrich N, Stahl U (1994) Molecular cloning sequence analysis and expression of the gene encoding an antifungal-protein from Aspergillus giganteus. Curr Genet 25:519–523
Acknowledgment
This work is dedicated to the memory of Professors Piotr Slonimski and Mohamed Marrakchi. Khmaies Benhaj and Radhia Gargouri are deeply thanked for reading the manuscript. This work was supported by the Tunisian “Ministry of Higher Education, Scientific Research and Technology.”
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Skouri-Gargouri, H., Jellouli-Chaker, N. & Gargouri, A. Factors affecting production and stability of the AcAFP antifungal peptide secreted by Aspergillus clavatus . Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 86, 535–543 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-009-2279-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-009-2279-y