Abstract
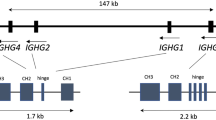
A limited number of deletions and duplications within the human immunoglobulin heavy chain constant locus (IGHC) has previously been reported. We studied the IGHC locus in about 500 individuals representing three major races of human, Negroid (Gambian), Mongoloid (Japanese and Chinese), and Caucasoid (Iranian and Swedish). The haplotype frequency of duplications is highest in the Mongoloid population (22%), followed by the Caucasian (10%) and Negroid (5%) populations. The corresponding frequency of deletions are 2, 1.5, and 3.5%, respectively. New types of multiple duplications were found in this study on different genetic (H haplotype and racial) backgrounds. The most common duplication, found in all populations studied, encompasses the IGHA1-IGHE genes. The only deletion common to all racial groups is an isolated deletion of the IGHG4 gene. Our data are consistent with the hypothesis that the Caucasoid-Mongoloid group diverged from the hominoid ancestor after development of the Negroid populations, with subsequent evolution within the respective groups thereafter.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 14 June 1996/Revised: 2 August 1996
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rabbani, H., Pan, Q., Kondo, N. et al. Duplications and deletions of the human IGHC locus: evolutionary implications. Immunogenetics 45, 136–141 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/s002510050181
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s002510050181