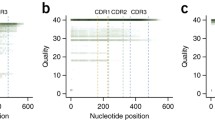
Abstract
Immunoglobulins (IGs), crucial components of the adaptive immune system, are encoded by three genomic loci. However, the complexity of the IG loci severely limits the effective use of short read sequencing, limiting our knowledge of population diversity in these loci. We leveraged existing long read whole-genome sequencing (WGS) data, fosmid technology, and IG targeted single-molecule, real-time (SMRT) long-read sequencing (IG-Cap) to create haplotype-resolved assemblies of the IG Lambda (IGL) locus from 6 ethnically diverse individuals. In addition, we generated 10 diploid assemblies of IGL from a diverse cohort of individuals utilizing IG-Cap. From these 16 individuals, we identified significant allelic diversity, including 36 novel IGLV alleles. In addition, we observed highly elevated single nucleotide variation (SNV) in IGLV genes relative to IGL intergenic and genomic background SNV density. By comparing SNV calls between our high quality assemblies and existing short read datasets from the same individuals, we show a high propensity for false-positives in the short read datasets. Finally, for the first time, we nucleotide-resolved common 5-10 Kb duplications in the IGLC region that contain functional IGLJ and IGLC genes. Together these data represent a significant advancement in our understanding of genetic variation and population diversity in the IGL locus.




Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All custom code and scripts used in this study were written in R, Python, and Bash. All scripts are available upon request along with usage explanations. Assemblies are available through VDJbase [66]. Fosmid sequences submitted to GenBank through project id PRJNA555323 and are available at the following link: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/bioproject/PRJNA555323.
References
Wardemann H, Hammersen J, Nussenzweig MC. Human autoantibody silencing by immunoglobulin light chains. J Exp Med. 2004;200:191–9.
Hershberg U, Shlomchik MJ. Differences in potential for amino acid change after mutation reveals distinct strategies for and light-chain variation. Proc Natl Acad Sci. 2006;103:15963–8.
Collins AM, Watson CT. Immunoglobulin light chain gene rearrangements, receptor editing and the development of a self-tolerant antibody repertoire. Front Immunol. 2018;9:2249.
Schatz DG. V(D)J recombination. Immunol Rev. 2004;200:5–11.
Townsend CL, Laffy JMJ, Wu YCB, Silva O’Hare J, Martin V, Kipling D, et al. Significant differences in physicochemical properties of human immunoglobulin kappa and lambda CDR3 regions. Front Immunol [Internet]. 2016 Sep [cited 2021 May 20];7. Available from: http://journal.frontiersin.org/Article/10.3389/fimmu.2016.00388/abstract
Watson CT, Steinberg KM, Graves TA, Warren RL, Malig M, Schein J, et al. Sequencing of the human IG light chain loci from a hydatidiform mole BAC library reveals locus-specific signatures of genetic diversity. Genes Immun. 2015;16:24–34.
Moraes Junta C, Passos GAS. Genomic EcoRI polymorphism and cosmid sequencing reveal an insertion/deletion and a new IGLV5 allele in the human immunoglobulin lambda variable locus (22q11.2/IGLV). Immunogenetics 2003;55:10–5.
Nurk S, Koren S, Rhie A, Rautiainen M, Bzikadze AV, Mikheenko A, et al. The complete sequence of a human genome. Science. 2022;376:44–53. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.abj6987
Giudicelli V. IMGT/GENE-DB: a comprehensive database for human and mouse immunoglobulin and T cell receptor genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2004;33:D256–61.
Lefranc MP. IMGT (ImMunoGeneTics) locus on focus. A new section of experimental and clinical immunogenetics. Exp Clin Immunogenet. 1998;15:1–7.
Mikocziova I, Peres A, Gidoni M, Greiff V, Yaari G, Sollid LM. Germline polymorphisms and alternative splicing of human immunoglobulin light chain genes. iScience. 2021;24:103192.
Tümkaya T, van der Burg M, Garcia Sanz R, Gonzalez Diaz M, Langerak A, San Miguel J, et al. Immunoglobulin lambda isotype gene rearrangements in B cell malignancies. Leukemia. 2001;15:121–7.
Lefranc MP, Pallarès N, Frippiat JP. Allelic polymorphisms and RFLP in the human immunoglobulin lambda light chain locus. Hum Genet. 1999;104:361–9.
van der Burg M, Barendregt BH, van Gastel-Mol EJ, Tümkaya T, Langerak AW, van Dongen JJM. Unraveling of the polymorphic Cλ2-Cλ3 amplification and the Ke + Oz − polymorphism in the human Igλ locus. J Immunol. 2002;169:271–6.
Byrska-Bishop M, Evani US, Zhao X, Basile AO, Abel HJ, Regier AA, et al. High coverage whole genome sequencing of the expanded 1000 Genomes Project cohort including 602 trios [Internet]. Genomics. 2021 Feb [cited 2022 Jan 9]. Available from: http://biorxiv.org/lookup/doi/10.1101/2021.02.06.430068
Rodriguez OL, Gibson WS, Parks T, Emery M, Powell J, Strahl M, et al. A novel framework for characterizing genomic haplotype diversity in the human immunoglobulin heavy chain locus. Front Immunol. 2020;11:2136.
Benichou J, Ben-Hamo R, Louzoun Y, Efroni S. Rep-Seq: uncovering the immunological repertoire through next-generation sequencing: Rep-Seq: NGS for the immunological repertoire. Immunology. 2012;135:183–91.
Corcoran MM, Phad GE, Bernat NV, Stahl-Hennig C, Sumida N, Persson MAA, et al. Production of individualized V gene databases reveals high levels of immunoglobulin genetic diversity. Nat Commun. 2016;7:13642.
Gadala-Maria D, Yaari G, Uduman M, Kleinstein SH. Automated analysis of high-throughput B-cell sequencing data reveals a high frequency of novel immunoglobulin V gene segment alleles. Proc Natl Acad Sci. 2015;112:E862–70.
Gadala-Maria D, Gidoni M, Marquez S, Vander Heiden JA, Kos JT, Watson CT, et al. Identification of subject-specific immunoglobulin alleles from expressed repertoire sequencing data. Front Immunol. 2019;10:129.
Ohlin M, Scheepers C, Corcoran M, Lees WD, Busse CE, Bagnara D, et al. Inferred allelic variants of immunoglobulin receptor genes: a system for their evaluation, documentation, and naming. Front Immunol. 2019;10:435.
Ralph DK, Matsen FA. Per-sample immunoglobulin germline inference from B cell receptor deep sequencing data. Buhler J, editor. PLOS Comput Biol. 2019;15:e1007133.
Watson CT, Breden F. The immunoglobulin heavy chain locus: genetic variation, missing data, and implications for human disease. Genes Immun. 2012;13:363–73.
Kidd JM, Cooper GM, Donahue WF, Hayden HS, Sampas N, Graves T, et al. Mapping and sequencing of structural variation from eight human genomes. Nature. 2008;453:56–64.
DeKosky BJ, Lungu OI, Park D, Johnson EL, Charab W, Chrysostomou C, et al. Large-scale sequence and structural comparisons of human naive and antigen-experienced antibody repertoires. Proc Natl Acad Sci. 2016;113:E2636–45.
Siniscalco M, Robledo R, Orru S, Contu L, Yadav P, Ren Q, et al. A plea to search for deletion polymorphism through genome scans in populations. Trends Genet. 2000;16:435–7.
Irony-Tur Sinai M, Salamon A, Stanleigh N, Goldberg T, Weiss A, Wang YH, et al. AT-dinucleotide rich sequences drive fragile site formation. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019;47:9685–95.
Li S, Wu X. Common fragile sites: protection and repair. Cell Biosci. 2020;10:29.
Pu L, Lin Y, Pevzner PA. Detection and analysis of ancient segmental duplications in mammalian genomes. Genome Res. 2018;28:901–9.
Kidd JM, Graves T, Newman TL, Fulton R, Hayden HS, Malig M, et al. A human genome structural variation sequencing resource reveals insights into mutational mechanisms. Cell. 2010;143:837–47.
Watson CT, Steinberg KM, Huddleston J, Warren RL, Malig M, Schein J, et al. Complete haplotype sequence of the human immunoglobulin heavy-chain variable, diversity, and joining genes and characterization of allelic and copy-number variation. Am J Hum Genet. 2013;92:530–46.
Piovesan A, Pelleri MC, Antonaros F, Strippoli P, Caracausi M, Vitale L. On the length, weight and GC content of the human genome. BMC Res Notes. 2019;12:106.
Chen JM, Cooper DN, Chuzhanova N, Férec C, Patrinos GP. Gene conversion: mechanisms, evolution and human disease. Nat Rev Genet. 2007;8:762–75.
Mikocziova I, Greiff V, Sollid LM. Immunoglobulin germline gene variation and its impact on human disease. Genes Immun [Internet]. 2021 Jun [cited 2021 Jul 8]; Available from: http://www.nature.com/articles/s41435-021-00145-5
Glanville J, Kuo TC, von Budingen HC, Guey L, Berka J, Sundar PD, et al. Naive antibody gene-segment frequencies are heritable and unaltered by chronic lymphocyte ablation. Proc Natl Acad Sci. 2011;108:20066–71.
Avnir Y, Watson CT, Glanville J, Peterson EC, Tallarico AS, Bennett AS, et al. IGHV1-69 polymorphism modulates anti-influenza antibody repertoires, correlates with IGHV utilization shifts and varies by ethnicity. Sci Rep. 2016;6:20842.
Collins AM, Yaari G, Shepherd AJ, Lees W, Watson CT. Germline immunoglobulin genes: disease susceptibility genes hidden in plain sight? Curr Opin Syst Biol. 2020;24:100–8.
Meyer D, Aguiar VRC, Bitarello BD, Brandt DYC, Nunes K. A genomic perspective on HLA evolution. Immunogenetics. 2018;70:5–27.
Penn DJ, Damjanovich K, Potts WK. MHC heterozygosity confers a selective advantage against multiple-strain infections. Proc Natl Acad Sci. 2002;99:11260–4.
Norman PJ, Hollenbach JA, Nemat-Gorgani N, Guethlein LA, Hilton HG, Pando MJ, et al. Co-evolution of human leukocyte antigen (HLA) Class I ligands with killer-cell immunoglobulin-like receptors (KIR) in a genetically diverse population of sub-saharan Africans. Gibson G, editor. PLoS Genet. 2013;9:e1003938.
D’Antonio M, Reyna J, Jakubosky D, Donovan MK, Bonder MJ, Matsui H, et al. Systematic genetic analysis of the MHC region reveals mechanistic underpinnings of HLA type associations with disease. eLife. 2019;8:e48476.
Taub RA, Hollis GF, Hieter PA, Korsmeyer S, Waldmann TA, Leder P. Variable amplification of immunoglobulin λ light-chain genes in human populations. Nature. 1983;304:172–4.
Tamura K, Nei M. Estimation of the number of nucleotide substitutions in the control region of mitochondrial DNA in humans and chimpanzees. Mol Biol Evol [Internet]. 1993 May [cited 2022 Jun 8]; Available from: https://academic.oup.com/mbe/article/10/3/512/1016366/Estimation-of-the-number-of-nucleotide
Ohno S. Evolution by Gene Duplication. Berlin: Springer Berlin; 2014.
Lynch M, Katju V. The altered evolutionary trajectories of gene duplicates. Trends Genet. 2004;20:544–9.
Clarke L, Fairley S, Zheng-Bradley X, Streeter I, Perry E, Lowy E, et al. The international Genome sample resource (IGSR): a worldwide collection of genome variation incorporating the 1000 genomes project data. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017;45:D854–9.
Tuzun E, Sharp AJ, Bailey JA, Kaul R, Morrison VA, Pertz LM, et al. Fine-scale structural variation of the human genome. Nat Genet. 2005;37:727–32.
Koren S, Walenz BP, Berlin K, Miller JR, Bergman NH, Phillippy AM. Canu: scalable and accurate long-read assembly via adaptive k -mer weighting and repeat separation. Genome Res. 2017;27:722–36.
Chen Y, Zhang Y, Wang AY, Gao M, Chong Z. Accurate long-read de novo assembly evaluation with Inspector. Genome Biol. 2021;22:312.
Steinberg KM, Lindsay TG, Schneider VA, Chaisson MJP, Tomlinson C, Huddleston J, et al. High-Quality Assembly of an Individual of Yoruban Descent [Internet]. Bioinformatics; 2016 Aug [cited 2021 Nov 3]. Available from: http://biorxiv.org/lookup/doi/10.1101/067447
Brochet X, Lefranc MP, Giudicelli V. IMGT/V-QUEST: the highly customized and integrated system for IG and TR standardized V-J and V-D-J sequence analysis. Nucleic Acids Res. 2008;36:W503–8.
Giudicelli V, Brochet X, Lefranc MP. IMGT/V-QUEST: IMGT standardized analysis of the immunoglobulin (IG) and T cell receptor (TR) nucleotide sequences. Cold Spring Harb Protoc. 2011;2011:pdb.prot5633.
Li H. A statistical framework for SNP calling, mutation discovery, association mapping and population genetical parameter estimation from sequencing data. Bioinformatics. 2011;27:2987–93.
Cleary JG, Braithwaite R, Gaastra K, Hilbush BS, Inglis S, Irvine SA, et al. Comparing variant call files for performance benchmarking of next-generation sequencing variant calling pipelines [Internet]. Bioinformatics; 2015 Aug [cited 2022 May 29]. Available from: http://biorxiv.org/lookup/doi/10.1101/023754
Robinson JT, Thorvaldsdóttir H, Winckler W, Guttman M, Lander ES, Getz G, et al. Integrative genomics viewer. Nat Biotechnol. 2011;29:24–6.
Thorvaldsdottir H, Robinson JT, Mesirov JP. Integrative Genomics Viewer (IGV): high-performance genomics data visualization and exploration. Brief Bioinform. 2013;14:178–92.
Robinson JT, Thorvaldsdóttir H, Wenger AM, Zehir A, Mesirov JP. Variant review with the integrative genomics viewer. Cancer Res. 2017;77:e31–4.
Boratyn GM, Camacho C, Cooper PS, Coulouris G, Fong A, Ma N, et al. BLAST: a more efficient report with usability improvements. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013;41:W29–33.
Altschul SF, Gish W, Miller W, Myers EW, Lipman DJ. Basic local alignment search tool. J Mol Biol. 1990;215:403–10.
Altschul S. Gapped BLAST and PSI-BLAST: a new generation of protein database search programs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1997;25:3389–402.
Camacho C, Coulouris G, Avagyan V, Ma N, Papadopoulos J, Bealer K, et al. BLAST+: architecture and applications. BMC Bioinforma. 2009;10:421.
Edgar RC. MUSCLE: multiple sequence alignment with high accuracy and high throughput. Nucleic Acids Res. 2004;32:1792–7.
Saitou N, Nei M. The neighbor-joining method: a new method for reconstructing phylogenetic trees. Mol Biol Evol [Internet]. 1987 Jul [cited 2022 Jun 8]; Available from: https://academic.oup.com/mbe/article/4/4/406/1029664/The-neighborjoining-method-a-new-method-for
Letunic I, Bork P. Interactive Tree Of Life (iTOL) v5: an online tool for phylogenetic tree display and annotation. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021;49:W293–6.
Sievers F, Wilm A, Dineen D, Gibson TJ, Karplus K, Li W, et al. Fast, scalable generation of high‐quality protein multiple sequence alignments using Clustal Omega. Mol Syst Biol. 2011;7:539.
Omer A, Shemesh O, Peres A, Polak P, Shepherd AJ, Watson CT, et al. VDJbase: an adaptive immune receptor genotype and haplotype database. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020;48:D1051–6.
Funding
This work was supported, in part, by NIAID grant R24AI138963 to CW, MS. This work was supported, in part, by US National Institutes of Health (NIH) grant HG010169 to EEE. EEE is an investigator of the Howard Hughes Medical Institute. This research was supported in part by the U.S. National Science Foundation (NSF) under grant CNS1828521 and the University of Louisville’s Research Computing team.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
WSG, OLR, AB, MLS, CTW conceived and planned the study. EEE provided sample resources. RS, MLS provided sequencing resources. WSG, KS, CAS, ME, GD, MLS prepared sequencing libraries and performed sequencing. WSG, OLR, AD, CTW interpreted results. WSG, OLR wrote the code. CTW, MLS supervised the experiments, analysis, and data interpretation. WSG wrote the manuscript with contributions from CTW, MLS, and OLR. WSG, CTW, MLS, OLR, EEE, RS reviewed and edited the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
EEE is a scientific advisory board (SAB) member of Variant Bio, Inc. Robert Sebra is VP of Technology Development at Sema4.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Gibson, W.S., Rodriguez, O.L., Shields, K. et al. Characterization of the immunoglobulin lambda chain locus from diverse populations reveals extensive genetic variation. Genes Immun 24, 21–31 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41435-022-00188-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41435-022-00188-2
- Springer Nature Limited
This article is cited by
-
Contextualising the developability risk of antibodies with lambda light chains using enhanced therapeutic antibody profiling
Communications Biology (2024)
-
Looking to the future of antibody genetics: resolving the roles of immunoglobulin diversity in gene regulation, function, and immunity
Genes & Immunity (2023)