Abstract
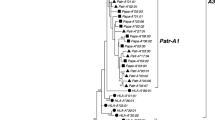
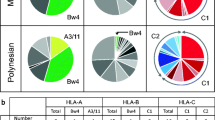
In humans, the classical antigen presentation function of major histocompatibility complex (MHC) class I molecules is controlled by the human leukocyte antigen HLA -A, HLA-B and HLA-C loci. A similar observation has been made for great apes and Old World monkey species. In contrast, a New World monkey species such as the cotton-top tamarin (Saguinus oedipus) appears to employ the G locus for its classical antigen presentation function. At present, little is known about the classical MHC class I repertoire of the common marmoset (Callithrix jacchus), another New World monkey that is widely used in biomedical research. In the present population study, no evidence has been found for abundant transcription of classical I class genes. However, in each common marmoset, four to seven different G-like alleles were detected, suggesting that the ancestral locus has been subject to expansion. Segregation studies provided evidence for at least two G-like genes present per haplotype, which are transcribed by a variety of cell types. The alleles of these Caja-G genes cluster in separate lineages, suggesting that the loci diversified considerably after duplication. Phylogenetic analyses of the introns confirm that the Caja-G loci cluster in the vicinity of HLA-G, indicating that both genes shared an ancestor. In contrast to HLA-G, Caja-G shows considerable polymorphism at the peptide-binding sites. This observation, together with the lack of detectable transcripts of A and B-like genes, indicates that Caja-G genes have taken over the function of classical class I genes. These data highlight the extreme plasticity of the MHC class I gene system.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Antunes SG, de Groot NG, Brok H, Doxiadis G, Menezes AA, Otting N, Bontrop RE (1998) The common marmoset: a new world primate species with limited Mhc class II variability. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 95:11745–11750
Arnaiz-Villena A, Morales P, Gomez-Casado E, Castro MJ, Varela P, Rojo-Amigo R, Martinez-Laso J (1999) Evolution of MHC-G in primates: a different kind of molecule for each group of species. J Reprod Immunol 43:111–125
Benirschke K, Anderson JM, Brownhill LE (1962) Marrow chimerism in marmosets. Science 138:513–515
Bontrop RE (2006) Comparative genetics of MHC polymorphisms in different primate species: duplications and deletions. Hum Immunol 67:388–397
Boyson JE, Iwanaga KK, Golos TG, Watkins DI (1996) Identification of the rhesus monkey HLA-G ortholog. Mamu-G is a pseudogene. J Immunol 157:5428–5437
Boyson JE, Iwanaga KK, Golos TG, Watkins DI (1997) Identification of a novel MHC class I gene, Mamu-AG, expressed in the placenta of a primate with an inactivated G locus. J Immunol 159:3311–3321
Cadavid LF, Hughes AL, Watkins DI (1996) MHC class I-processed pseudogenes in New World primates provide evidence for rapid turnover of MHC class I genes. J Immunol 157:2403–2409
Cadavid LF, Shufflebotham C, Ruiz FJ, Yeager M, Hughes AL, Watkins DI (1997) Evolutionary instability of the major histocompatibility complex class I loci in New World primates. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 94:14536–14541
Castro MJ, Morales P, Fernandez-Soria V, Suarez B, Recio MJ, Alvarez M, Martin-Villa M, Arnaiz-Villena A (1996) Allelic diversity at the primate Mhc-G locus: exon 3 bears stop codons in all Cercopithecinae sequences. Immunogenetics 43:327–336
Cox C, Chang S, Karran L, Griffin B, Wedderburn N (1996) Persistent Epstein–Barr virus infection in the common marmoset (Callithrix jacchus). J Gen Virol 77(Pt 6):1173–1180
Daza-Vamenta R, Glusman G, Rowen L, Guthrie B, Geraghty DE (2004) Genetic divergence of the rhesus macaque major histocompatibility complex. Genome Res 14:1501–1515
de Groot NG, Otting N, Robinson J, Blancher A, Lafont BA, Marsh SG, O’Connor DH, Shiina T, Walter L, Watkins DI, Bontrop RE (2012) Nomenclature report on the major histocompatibility complex genes and alleles of Great Ape, Old and New World monkey species. Immunogenetics 64:615–631
Doxiadis GG, van der Wiel MK, Brok HP, de Groot NG, Otting N, t Hart BA, van Rood JJ, Bontrop RE (2006) Reactivation by exon shuffling of a conserved HLA-DR3-like pseudogene segment in a New World primate species. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 103:5864–5868
Geula C, Nagykery N, Wu CK (2002) Amyloid-beta deposits in the cerebral cortex of the aged common marmoset (Callithrix jacchus): incidence and chemical composition. Acta Neuropathol 103:48–58
Greene JM, Wiseman RW, Lank SM, Bimber BN, Karl JA, Burwitz BJ, Lhost JJ, Hawkins OE, Kunstman KJ, Broman KW, Wolinsky SM, Hildebrand WH, O’Connor DH (2011) Differential MHC class I expression in distinct leukocyte subsets. BMC Immunol 12:39
Jagessar SA, Heijmans N, Blezer EL, Bauer J, Blokhuis JH, Wubben JA, Drijfhout JW, van den Elsen PJ, Laman JD, Hart BA (2012) Unravelling the T-cell-mediated autoimmune attack on CNS myelin in a new primate EAE model induced with MOG34-56 peptide in incomplete adjuvant. Eur J Immunol 42:217–227
Knapp LA, Cadavid LF, Watkins DI (1998) The MHC-E locus is the most well conserved of all known primate class I histocompatibility genes. J Immunol 160:189–196
Kovats S, Main EK, Librach C, Stubblebine M, Fisher SJ, DeMars R (1990) A class I antigen, HLA-G, expressed in human trophoblasts. Science 248:220–223
Kulski JK, Anzai T, Shiina T, Inoko H (2004) Rhesus macaque class I duplicon structures, organization, and evolution within the alpha block of the major histocompatibility complex. Mol Biol Evol 21:2079–2091
Langat DK, Morales PJ, Fazleabas AT, Mwenda JM, Hunt JS (2002) Baboon placentas express soluble and membrane-bound Paan-AG proteins encoded by alternatively spliced transcripts of the class Ib major histocompatibility complex gene, Paan-AG. Immunogenetics 54:164–173
Lin ZY, Imamura M, Sano C, Nakajima R, Suzuki T, Yamadera R, Takehara Y, Okano HJ, Sasaki E, Okano H (2012) Molecular signatures to define spermatogenic cells in common marmoset (Callithrix jacchus). Reproduction 143:597–609
Marsh SG, Albert ED, Bodmer WF, Bontrop RE, Dupont B, Erlich HA, Fernandez-Vina M, Geraghty DE, Holdsworth R, Hurley CK, Lau M, Lee KW, Mach B, Maiers M, Mayr WR, Muller CR, Parham P, Petersdorf EW, Sasazuki T, Strominger JL, Svejgaard A, Terasaki PI, Tiercy JM, Trowsdale J (2010) Nomenclature for factors of the HLA system, 2010. Tissue Antigens 75:291–455
O’Connor DH, Mothe BR, Weinfurter JT, Fuenger S, Rehrauer WM, Jing P, Rudersdorf RR, Liebl ME, Krebs K, Vasquez J, Dodds E, Loffredo J, Martin S, McDermott AB, Allen TM, Wang C, Doxiadis GG, Montefiori DC, Hughes A, Burton DR, Allison DB, Wolinsky SM, Bontrop R, Picker LJ, Watkins DI (2003) Major histocompatibility complex class I alleles associated with slow simian immunodeficiency virus disease progression bind epitopes recognized by dominant acute-phase cytotoxic-T-lymphocyte responses. J Virol 77:9029–9040
Otting N, Heijmans CM, Noort RC, de Groot NG, Doxiadis GG, van Rood JJ, Watkins DI, Bontrop RE (2005) Unparalleled complexity of the MHC class I region in rhesus macaques. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 102:1626–1631
Ouyang D, He X, Xu L, Wang X, Gao Q, Guo H (2010) Differential cell surface expression of rhesus macaque’s major histocompatibility complex class I alleles Mamu-B*1703 and Mamu-B*0101. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai) 42:281–287
Parham P, Moffett A (2013) Variable NK cell receptors and their MHC class I ligands in immunity, reproduction and human evolution. Nat Rev Immunol 13:133–144
Parham P, Ohta T (1996) Population biology of antigen presentation by MHC class I molecules. Science 272:67–74
Parham P, Norman PJ, Abi-Rached L, Hilton HG, Guethlein LA (2012) Review: immunogenetics of human placentation. Placenta 33(Suppl):S71–S80
Philippens IH, t Hart BA, Torres G (2010) The MPTP marmoset model of parkinsonism: a multi-purpose non-human primate model for neurodegenerative diseases. Drug Discov Today 15:985–990
Pinto MA, Marchevsky RS, Baptista ML, de Lima MA, Pelajo-Machado M, Vitral CL, Kubelka CF, Pissurno JW, Franca MS, Schatzmayr HG, Gaspar AM (2002) Experimental hepatitis A virus (HAV) infection in Callithrix jacchus: early detection of HAV antigen and viral fate. Exp Toxicol Pathol 53:413–420
Prasad S, Humphreys I, Kireta S, Gilchrist RB, Bardy P, Russ GR, Coates PT (2007) The common marmoset as a novel preclinical transplant model: identification of new MHC class II DRB alleles and prediction of in vitro alloreactivity. Tissue Antigens 69(Suppl 1):72–75
Rolleke U, Flugge G, Plehm S, Schlumbohm C, Armstrong VW, Dressel R, Uchanska-Ziegler B, Ziegler A, Fuchs E, Czeh B, Walter L (2006) Differential expression of major histocompatibility complex class I molecules in the brain of a New World monkey, the common marmoset (Callithrix jacchus). J Neuroimmunol 176:39–50
Rosner C, Kruse PH, Lubke T, Walter L (2010) Erratum to: rhesus macaque MHC class I molecules show differential subcellular localizations. Immunogenetics 62:409–418
Seehase S, Lauenstein HD, Schlumbohm C, Switalla S, Neuhaus V, Forster C, Fieguth HG, Pfennig O, Fuchs E, Kaup FJ, Bleyer M, Hohlfeld JM, Braun A, Sewald K, Knauf S (2012) LPS-induced lung inflammation in marmoset monkeys - an acute model for anti-inflammatory drug testing. PLoS One 7:e43709
Shiina T, Kono A, Westphal N, Suzuki S, Hosomichi K, Kita YF, Roos C, Inoko H, Walter L (2011) Comparative genome analysis of the major histocompatibility complex (MHC) class I B/C segments in primates elucidated by genomic sequencing in common marmoset (Callithrix jacchus). Immunogenetics 63:485–499
t Hart BA, van Meurs M, Brok HP, Massacesi L, Bauer J, Boon L, Bontrop RE, Laman JD (2000) A new primate model for multiple sclerosis in the common marmoset. Immunol Today 21:290–297
Tamura K, Dudley J, Nei M, Kumar S (2007) MEGA4: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis (MEGA) software version 4.0. Mol Biol Evol 24:1596–1599
Trowsdale J, Moffett A (2008) NK receptor interactions with MHC class I molecules in pregnancy. Semin Immunol 20:317–320
van Bergen J, Trowsdale J (2012) Ligand specificity of Killer cell immunoglobulin-like receptors: a brief history of KIR. Front Immunol 3:394
von Schonfeldt V, Chandolia R, Kiesel L, Nieschlag E, Schlatt S, Sonntag B (2011) Advanced follicle development in xenografted prepubertal ovarian tissue: the common marmoset as a nonhuman primate model for ovarian tissue transplantation. Fertil Steril 95:1428–1434
Ward JM, Vallender EJ (2012) The resurgence and genetic implications of New World primates in biomedical research. Trends Genet 28:586–591
Watkins DI, Hodi FS, Letvin NL (1988) A primate species with limited major histocompatibility complex class I polymorphism. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 85:7714–7718
Watkins DI, Chen ZW, Hughes AL, Evans MG, Tedder TF, Letvin NL (1990) Evolution of the MHC class I genes of a New World primate from ancestral homologues of human non-classical genes. Nature 346:60–63
Watkins DI, Garber TL, Chen ZW, Toukatly G, Hughes AL, Letvin NL (1991) Unusually limited nucleotide sequence variation of the expressed major histocompatibility complex class I genes of a New World primate species (Saguinus oedipus). Immunogenetics 33:79–89
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank Ms. Donna Devine for editing the manuscript and Henk van Westbroek for preparing the figures. The research was financed by the Biomedical Primate Research Centre.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Marit K. van der Wiel and Nel Otting contributed equally to this study.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
van der Wiel, M.K., Otting, N., de Groot, N.G. et al. The repertoire of MHC class I genes in the common marmoset: evidence for functional plasticity. Immunogenetics 65, 841–849 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00251-013-0732-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00251-013-0732-7