Abstract
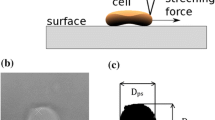
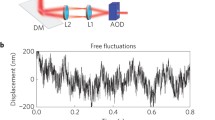
We study the thermal and out-of-equilibrium mechanical dynamics of single, living human red blood cells (RBCs) by combining two-probe passive and active microrheology techniques. Both experiments were performed quasisimultaneously on the same cell using two identical polystyrene probes, biochemically attached to the cell membrane. We obtained compelling evidence of nonequilibrium fluctuations in the RBCs under physiological condition and without the influence of any external chemicals. The spectral distributions of metabolically driven forces and viscoelastic response were evaluated in the relaxed and stretched states, intended to simulate the varying natural environment of the cells during blood circulation. We found that the internally generated forces are more pronounced in the stretched state, suggesting a stress-dependent RBC activity.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Atakhorrami M, Sulkowska JI, Addas KM, Koenderink GH, Tang JX, Levine AJ, MacKintosh FC, Schmidt CF (2006) Correlated fluctuations of microparticles in viscoelastic solutions: quantitative measurement of material properties by microrheology in the presence of optical traps. Phys Rev E 73:061501
Bao G, Suresh S (2003) Cell and molecular mechanics of biological materials. Nat Mater 2:715–725
Berg-Sorensen K, Flyvbjerg H (2004) Power spectrum analysis for optical tweezers. Rev Sci Instrum 75:594–612
Betz T, Lenz M, Joanny J-F, Sykes C (2009) ATP-dependent mechanics of red blood cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 106:15320–15325
Brau RR, Ferrer JM, Lee H, Castro CE, Tam BK, Tarsa PB, Matsudaira P, Boyce MC, Kamm RD, Lang MJ (2007) Passive and active microrheology with optical tweezers. J Opt A: Pure Appl Opt 9:103–112
Chien S (1987) Red cell deformability and its relevance to blood flow. Annu Rev Physiol 49:177–192
Dao M, Lim CT, Suresh S (2003) Mechanics of the human red blood cell deformed by optical tweezers. J Mech Phys Solids 51:2259–2280
Evans J, Gratzer W, Mohandas N, Parker K, Sleep J (2008) Fluctuations of the red blood cell membrane: relation to mechanical properties and lack of ATP dependence. Biophys J 94:4134–4144
Gallet F, Arcizet D, Bohec P, Richert A (2009) Power spectrum of out-of-equilibrium forces in living cells: amplitude and frequency dependence. Soft Matter 5:2947–2953
Gimzewski J, Stieg A (2011) Local probes: pushing the limits of detection and interaction. In: Sattler KD (ed) Handbook of nanophysics: principles and methods. CRC, Boca Raton
Gov N, Safran SA (2005) Red blood cell shape and fluctuations: cytoskeleton confinement and ATP activity. J Biol Phys 31:453–464
Gov NS, Safran SA (2005) Red blood cell membrane fluctuations and shape controlled by ATP-induced cytoskeletal defects. Biophys J 88:1859–1874
Hough LA, Ou-Yang HD (2002) Correlated motions of two hydrodynamically coupled particles confined in separate quadratic potential wells. Phys Rev E 65:021906
Johnson CP, Tang HY, Carag C, Speicher DW, Discher DE (2007) Forced unfolding of proteins within cells. Sci Technol Human Values 317:663–666
Lau AWC, Hoffman BD, Davies A, Crocker JC, Lubensky TC (2003) Microrheology, stress fluctuations, and active behavior of living cells. Phys Rev Lett 91:198101
Levin S, Korenstein R (1991) Membrane fluctuations in erythrocytes are linked to MgATP-dependent dynamic assembly of the membrane skeleton. Biophys J 60:733–737
Li J, Lykotrafitis G, Dao M, Suresh S (2007) Cytoskeletal dynamics of human erythrocyte. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 104:4937–4942
Mizuno D, Bacabac R, Tardin C, Head D, Schmidt CF (2009) High-resolution probing of cellular force transmission. Phys Rev Lett 102:168102
Mizuno D, Tardin C, Schmidt CF, MacKintosh FC (2007) Nonequilibrium mechanics of active cytoskeletal networks. Sci Technol Human Values 315:370–373
Mizuno D, Head DA, MacKintosh FC, Schmidt CF (2008) Active and passive microrheology in equilibrium and nonequilibrium systems. Macromolecules 41:7194–7202
Pasternack GR, Racusen RH (1989) Erythrocyte protein 4.1 binds and regulates myosin. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 86:9712–9716
Raj S, Marro M, Wojdyla M, Petrov D (2012) Mechanochemistry of single red blood cells monitored using Raman tweezers. Biomed Opt Exp 3:753–763
Raj S, Wojdyla M, Petrov D (2013) Studying single red blood cells under a tunable external force by combining passive microrheology with Raman spectroscopy. Cell Biochem Biophys 65:347–361
Svoboda K, Block SM (1994) Biological applications of optical forces. Annu Rev Biophys Biomol Struct 23:247–285
Tuvia S, Almagor A, Bitler A, Levin S, Korenstein R, Yedgar S (1997) Cell membrane fluctuations are regulated by medium macroviscosity: evidence for a metabolic driving force. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 94:5045–5049
Visscher K, Gross SP, Block SM (1996) Construction of multiple-beam optical traps with nanometer-resolution position sensing. IEEE J Sel Topics Quantum Electron 2:1066–1076
Wan J, Ristenpart WD, Stone HA (2008) Dynamics of shear-induced ATP release from red blood cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 105:16432–16437
Yoon Y-Z, Kotar J, Yoon G, Cicuta P (2008) Non-linear mechanical response of the red blood cell. Phys Biol 5:036007
Yoon YZ, Kotar J, Brown AT, Cicuta P (2011) Red blood cell dynamics: from spontaneous fluctuations to non-linear response. Soft Matter 7:2042–2051
Acknowledgments
We acknowledge the financial support from Fundació Privada Cellex Barcelona, the Spanish Ministry of Science and Innovation (MICINN FIS2008-00114, FIS2011-24409), and the Generalitat de Catalunya (grant 2009-SGR-159).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wojdyla, M., Raj, S. & Petrov, D. Nonequilibrium fluctuations of mechanically stretched single red blood cells detected by optical tweezers. Eur Biophys J 42, 539–547 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00249-013-0903-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00249-013-0903-3