Abstract
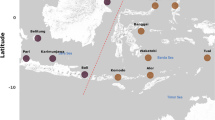
Gorgonians are key habitat-forming species of Mediterranean benthic communities, but their populations have suffered from mass mortality events linked to high summer seawater temperatures and microbial disease. However, our knowledge on the diversity, dynamics and function of gorgonian-associated microbial communities is limited. Here, we analysed the spatial variability of the microbiomes of five sympatric gorgonian species (Eunicella singularis, Eunicella cavolini, Eunicella verrucosa, Leptogorgia sarmentosa and Paramuricea clavata), collected from the Mediterranean Sea over a scale of ∼1100 km, using next-generation amplicon sequencing of the 16S rRNA gene. The microbiomes of all gorgonian species were generally dominated by members of the genus Endozoicomonas, which were at very low abundance in the surrounding seawater. Although the composition of the core microbiome (operational taxonomic units consistently present in a species) was found to be unique for each host species, significant overlap was observed. These spatially consistent associations between gorgonians and their core bacteria suggest intricate symbiotic relationships and regulation of the microbiome composition by the host. At the same time, local variations in microbiome composition were observed. Functional predictive profiling indicated that these differences could be attributed to seawater pollution. Taken together, our data indicate that gorgonian-associated microbiomes are composed of spatially conserved bacteria (core microbiome members) and locally variant members, and that local pollution may influence these local associations, potentially impacting gorgonian health.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gili JM, Ros J (1985) Study and cartography of the benthic communities of Medes Islands (NE Spain). Mar Ecol 6(3):219–238
Gili J-M, Coma R (1998) Benthic suspension feeders: their paramount role in littoral marine food webs. Trends Ecol Evol 13(8):316–321
Ballesteros E (2006) Mediterranean coralligenous assemblages: a synthesis of present knowledge. Oceanogr Mar Biol Annu Rev 44:123–195
Gili JM, Murillo J, Ros JD (1989) The distribution pattern of benthic Cnidarians in the western Mediterranean. Sci Mar 53(1):19–35
Ponti M, Perlini RA, Ventra V, Grech D, Abbiati M, Cerrano C (2014) Ecological shifts in Mediterranean coralligenous assemblages related to Gorgonian Forest loss. PLoS ONE 9(7):e102782
Garrabou J, Perez T, Sartoretto S, Harmelin JG (2001) Mass mortality event in red coral Corallium rubrum populations in the Provence region (France, NW Mediterranean). Mar Ecol Prog Ser 217:263–272
Cerrano C, Bavestrello G, Bianchi CN, Cattaneo-vietti R, Bava S, Morganti C, Morri C, Picco P, Sara G, Schiaparelli S, Siccardi A, Sponga F (2000) A catastrophic mass-mortality episode of gorgonians and other organisms in the Ligurian Sea (North-western Mediterranean), summer 1999. Ecol Lett 3(4):284–293
Harvell D, Kim K, Quirolo C, Weir J, Smith G (2001) Coral bleaching and disease: contributors to 1998 mass mortality in Briareum asbestinum (Octocorallia, Gorgonacea). Hydrobiologia 460(1):97–104
Vezzulli L, Previati M, Pruzzo C, Marchese A, Bourne DG, Cerrano C, The VibrioSea Consortium (2010) Vibrio infections triggering mass mortality events in a warming Mediterranean Sea. Environ Microbiol 12(7):2007–2019
Martin Y, Bonnefont JL, Chancerelle L (2002) Gorgonians mass mortality during the 1999 late summer in French Mediterranean coastal waters: the bacterial hypothesis. Water Res 36(3):779–782
Rohwer F, Seguritan V, Azam F, Knowlton N (2002) Diversity and distribution of coral-associated bacteria. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 243:1–10
Knowlton N, Rohwer F (2003) Multispecies microbial mutualisms on coral reefs: the host as a habitat. Am Nat 162(4 Suppl):S51–S62
Lema KA, Willis BL, Bourne DG (2012) Corals form characteristic associations with symbiotic nitrogen-fixing bacteria. Appl Environ Microbiol 78(9):3136–3144
Raina JB, Tapiolas D, Willis BL, Bourne DG (2009) Coral-associated bacteria and their role in the biogeochemical cycling of sulfur. Appl Environ Microbiol 75(11):3492–3501
Kvennefors EC, Sampayo E, Kerr C, Vieira G, Roff G, Barnes AC (2012) Regulation of bacterial communities through antimicrobial activity by the coral holobiont. Microb Ecol 63(3):605–618
Nissimov J, Rosenberg E, Munn CB (2009) Antimicrobial properties of resident coral mucus bacteria of Oculina patagonica. FEMS Microbiol Lett 292(2):210–215
Ritchie KB (2006) Regulation of microbial populations by coral surface mucus and mucus-associated bacteria. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 322:1–14
Shnit-Orland M, Sivan A, Kushmaro A (2012) Antibacterial activity of Pseudoalteromonas in the coral holobiont. Microb Ecol 64(4):851–859
Rypien KL, Ward JR, Azam F (2010) Antagonistic interactions among coral-associated bacteria. Environ Microbiol 12(1):28–39
Li J, Chen Q, Long L-J, Dong J-D, Yang J, Zhang S (2014) Bacterial dynamics within the mucus, tissue and skeleton of the coral Porites lutea during different seasons. Sci Rep 4:7320
Bourne DG, Munn CB (2005) Diversity of bacteria associated with the coral Pocillopora damicornis from the Great Barrier Reef. Environ Microbiol 7(8):1162–1174
Bayer T, Arif C, Ferrier-Pagès C, Zoccola D, Aranda M, Voolstra C (2013) Bacteria of the genus Endozoicomonas dominate the microbiome of the Mediterranean gorgonian coral Eunicella cavolini. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 479:75–84
van de Water JAJM, Melkonian R, Junca H, Voolstra CR, Reynaud S, Allemand D, Ferrier-Pagès C (2016) Spirochaetes dominate the microbial community associated with the red coral Corallium rubrum on a broad geographic scale. Sci Rep 6:27277
Schöttner S, Wild C, Hoffmann F, Boetius A, Ramette A (2012) Spatial scales of bacterial diversity in cold-water coral reef ecosystems. PLoS ONE 7(3):e32093
Morrow KM, Moss AG, Chadwick NE, Liles MR (2012) Bacterial associates of two Caribbean coral species reveal species-specific distribution and geographic variability. Appl Environ Microbiol 78(18):6438–6449
Gray MA, Stone RP, McLaughlin MR, Kellogg CA (2011) Microbial consortia of gorgonian corals from the Aleutian islands. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 76(1):109–120
Penn K, Wu D, Eisen JA, Ward N (2006) Characterization of bacterial communities associated with deep-sea corals on Gulf of Alaska seamounts. Appl Environ Microbiol 72(2):1680–1683
Sunagawa S, Woodley CM, Medina M (2010) Threatened corals provide underexplored microbial habitats. PLoS ONE 5(3):e9554
La Rivière M, Garrabou J, Bally M (2015) Evidence for host specificity among dominant bacterial symbionts in temperate gorgonian corals. Coral Reefs 1–12
Ransome E, Rowley SJ, Thomas S, Tait K, Munn CB (2014) Disturbance to conserved bacterial communities in the cold-water gorgonian coral Eunicella verrucosa. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 90(2):404–416
Correa H, Haltli B, Duque C, Kerr R (2013) Bacterial communities of the gorgonian octocoral Pseudopterogorgia elisabethae. Microb Ecol 66(4):972–985
Pike RE, Haltli B, Kerr RG (2013) Description of Endozoicomonas euniceicola sp. nov. and Endozoicomonas gorgoniicola sp. nov., bacteria isolated from the octocorals Eunicea fusca and Plexaura sp., and an emended description of the genus Endozoicomonas. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 63(Pt 11):4294–4302
Bayer T, Neave MJ, Alsheikh-Hussain A, Aranda M, Yum LK, Mincer T, Hughen K, Apprill A, Voolstra CR (2013) The microbiome of the Red Sea coral Stylophora pistillata is dominated by tissue-associated Endozoicomonas bacteria. Appl Environ Microbiol 79:4759–4762
Speck MD, Donachie SP (2012) Widespread Oceanospirillaceae bacteria in Porites spp. J Mar Biol 2012:7
Bourne DG, Dennis PG, Uthicke S, Soo RM, Tyson GW, Webster N (2013) Coral reef invertebrate microbiomes correlate with the presence of photosymbionts. ISME J 7(7):1452–1458
Goffredi SK, Johnson SB, Vrijenhoek RC (2007) Genetic diversity and potential function of microbial symbionts associated with newly discovered species of Osedax polychaete worms. Appl Environ Microbiol 73(7):2314–2323
Dishaw LJ, Flores-Torres J, Lax S, Gemayel K, Leigh B, Melillo D, Mueller MG, Natale L, Zucchetti I, De Santis R, Pinto MR, Litman GW, Gilbert JA (2014) The gut of geographically disparate Ciona intestinalis harbors a core microbiota. PLoS ONE 9(4):e93386
Forget NL, Kim Juniper S (2013) Free-living bacterial communities associated with tubeworm (Ridgeia piscesae) aggregations in contrasting diffuse flow hydrothermal vent habitats at the Main Endeavour Field, Juan de Fuca Ridge. MicrobiologyOpen 2(2):259–275
Mendoza M, Guiza L, Martinez X, Caraballo X, Rojas J, Aranguren LF, Salazar M (2013) A novel agent (Endozoicomonas elysicola) responsible for epitheliocystis in cobia Rachycentrum canadum larvae. Dis Aquat Org 106(1):31–37
Nishijima M, Adachi K, Katsuta A, Shizuri Y, Yamasato K (2013) Endozoicomonas numazuensis sp. nov., a gammaproteobacterium isolated from marine sponges, and emended description of the genus Endozoicomonas Kurahashi and Yokota 2007. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 63(Pt 2):709–714
Katharios P, Seth-Smith HMB, Fehr A, Mateos JM, Qi W, Richter D, Nufer L, Ruetten M, Guevara Soto M, Ziegler U, Thomson NR, Schlapbach R, Vaughan L (2015) Environmental marine pathogen isolation using mesocosm culture of sharpsnout seabream: striking genomic and morphological features of novel Endozoicomonas sp. Sci Rep 5:17609
Lawler SN, Kellogg CA, France SC, Clostio RW, Brooke SD, Ross SW (2016) Coral-associated bacterial diversity is conserved across two deep-sea anthothela species. Front Microbiol 7:458
Jensen PR, Harvell CD, Wirtz K, Fenical W (1996) Antimicrobial activity of extracts of Caribbean gorgonian corals. Mar Biol 125(2):411–419
Kim K, Harvell DC, Kim DP, Smith WG, Merkel MS (2000) Fungal disease resistance of Caribbean sea fan corals (Gorgonia spp.). Mar Biol 136(2):259–267
Kim K (1994) Antimicrobial activity in gorgonian corals (Coelenterata, Octocorallia). Coral Reefs 13(2):75–80
Hunt LR, Smith SM, Downum KR, Mydlarz LD (2012) Microbial regulation in gorgonian corals. Mar Drugs 10(6):1225
Hou X-M, Wang C-Y, She Z-G, Gu Y-C, Shao C-L (2016) Secondary metabolites isolated from the fungus Aspergillus sp. derived from Gorgonian Carijoa sp. Chemistry Nat Compd 1–2
Vezzulli L, Pezzati E, Huete-Stauffer C, Pruzzo C, Cerrano C (2013) 16SrDNA pyrosequencing of the mediterranean gorgonian Paramuricea clavata reveals a link among alterations in bacterial holobiont members, anthropogenic influence and disease outbreaks. PLoS ONE 8(6):e67745
Andersson AF, Lindberg M, Jakobsson H, Bäckhed F, Nyrén P, Engstrand L (2008) Comparative analysis of human gut microbiota by barcoded pyrosequencing. PLoS ONE 3(7):e2836
Caporaso JG, Kuczynski J, Stombaugh J, Bittinger K, Bushman FD, Costello EK, Fierer N, Pena AG, Goodrich JK, Gordon JI, Huttley GA, Kelley ST, Knights D, Koenig JE, Ley RE, Lozupone CA, McDonald D, Muegge BD, Pirrung M, Reeder J, Sevinsky JR, Turnbaugh PJ, Walters WA, Widmann J, Yatsunenko T, Zaneveld J, Knight R (2010) QIIME allows analysis of high-throughput community sequencing data. Nat Methods 7(5):335–336
Quast C, Pruesse E, Yilmaz P, Gerken J, Schweer T, Yarza P, Peplies J, Glöckner FO (2013) The SILVA ribosomal RNA gene database project: improved data processing and web-based tools. Nucleic Acids Res 41(D1):D590–D596
Edgar RC, Haas BJ, Clemente JC, Quince C, Knight R (2011) UCHIME improves sensitivity and speed of chimera detection. Bioinformatics 27(16):2194–2200
Edgar RC (2010) Search and clustering orders of magnitude faster than BLAST. Bioinformatics 26(19):2460–2461
Langille MGI, Zaneveld J, Caporaso JG, McDonald D, Knights D, Reyes JA, Clemente JC, Burkepile DE, Vega Thurber RL, Knight R, Beiko RG, Huttenhower C (2013) Predictive functional profiling of microbial communities using 16S rRNA marker gene sequences. Nat Biotechnol 31(9):814–821
Parks DH, Tyson GW, Hugenholtz P, Beiko RG (2014) STAMP: statistical analysis of taxonomic and functional profiles. Bioinformatics 30(21):3123–3124
Tamura K, Stecher G, Peterson D, Filipski A, Kumar S (2013) MEGA6: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 6.0. Mol Biol Evol 30(12):2725–2729
Anderson MJ, Walsh DCI (2013) PERMANOVA, ANOSIM, and the Mantel test in the face of heterogeneous dispersions: what null hypothesis are you testing? Ecol Monogr 83(4):557–574
Ziegler M, Roik A, Porter A, Zubier K, Mudarris MS, Ormond R, Voolstra CR (2015) Coral microbial community dynamics in response to anthropogenic impacts near a major city in the central Red Sea. Mar Pollut Bull 105(2):629–640
La Rivière M, Roumagnac M, Garrabou J, Bally M (2013) Transient shifts in bacterial communities associated with the temperate gorgonian Paramuricea clavata in the Northwestern Mediterranean Sea. PLoS ONE 8(2):e57385
Jessen C, Villa Lizcano JF, Bayer T, Roder C, Aranda M, Wild C, Voolstra CR (2013) In-situ effects of eutrophication and overfishing on physiology and bacterial diversity of the red sea coral Acropora hemprichii. PLoS ONE 8(4):e62091
Bourne D, Iida Y, Uthicke S, Smith-Keune C (2008) Changes in coral-associated microbial communities during a bleaching event. ISME J 2(4):350–363
Berkelmans R, van Oppen MJH (2006) The role of zooxanthellae in the thermal tolerance of corals: a ‘nugget of hope’ for coral reefs in an era of climate change. Proc R Soc Lond Biol 273(1599):2305–2312
Sunagawa S, DeSantis TZ, Piceno YM, Brodie EL, DeSalvo MK, Voolstra CR, Weil E, Andersen GL, Medina M (2009) Bacterial diversity and White Plague disease-associated community changes in the Caribbean coral Montastraea faveolata. ISME J 3(5):512–521
Hester ER, Barott KL, Nulton J, Vermeij MJA, Rohwer FL (2015) Stable and sporadic symbiotic communities of coral and algal holobionts. ISME J 10:1157–1169
Thurber RV, Willner-Hall D, Rodriguez-Mueller B, Desnues C, Edwards RA, Angly F, Dinsdale E, Kelly L, Rohwer F (2009) Metagenomic analysis of stressed coral holobionts. Environ Microbiol 11(8):2148–2163
Roder C, Bayer T, Aranda M, Kruse M, Voolstra CR (2015) Microbiome structure of the fungid coral Ctenactis echinata aligns with environmental differences. Mol Ecol 24(13):3501–3511. doi:10.1111/mec.13251
van de Water JAJM, Lamb JB, van Oppen MJH, Willis BL, Bourne DG (2015) Comparative immune responses of corals to stressors associated with offshore reef-based tourist platforms. Conserv Physiol 3(1):cov32
Siboni N, Ben-Dov E, Sivan A, Kushmaro A (2012) Geographic specific coral-associated ammonia-oxidizing archaea in the northern Gulf of Eilat (Red Sea). Microb Ecol 64(1):18–24
Kelly LW, Williams GJ, Barott KL, Carlson CA, Dinsdale EA, Edwards RA, Haas AF, Haynes M, Lim YW, McDole T, Nelson CE, Sala E, Sandin SA, Smith JE, Vermeij MJA, Youle M, Rohwer F (2014) Local genomic adaptation of coral reef-associated microbiomes to gradients of natural variability and anthropogenic stressors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 111(28):10227–10232
Reshef L, Koren O, Loya Y, Zilber-Rosenberg I, Rosenberg E (2006) The coral probiotic hypothesis. Environ Microbiol 8(12):2068–2073
Tovar-Sanchez A, Basterretxea G, Rodellas V, Sanchez-Quiles D, Garcia-Orellana J, Masque P, Jordi A, Lopez JM, Garcia-Solsona E (2014) Contribution of groundwater discharge to the coastal dissolved nutrients and trace metal concentrations in Majorca Island: karstic vs detrital systems. Environ Sci Technol 48(20):11819–11827
Lamb JB, True JD, Piromvaragorn S, Willis BL (2014) Scuba diving damage and intensity of tourist activities increases coral disease prevalence. Biol Conserve 178:88–96
Lamb JB, Williamson DH, Russ GR, Willis BL (2015) Protected areas mitigate diseases of reef-building corals by reducing damage from fishing. Ecology 96(9):2555–2567
Albertelli G, Covazzi-Harriague A, Danovaro R, Fabiano M, Fraschetti S, Pusceddu A (1999) Differential responses of bacteria, meiofauna and macrofauna in a shelf area (Ligurian Sea, NW Mediterranean): role of food availability. J Sea Res 42(1):11–26
Covazzi Harriague A, Misic C, Petrillo M, Albertelli G (2007) Stressors affecting the macrobenthic community in Rapallo Harbour (Ligurian Sea, Italy). Sci Mar 71(4):705–714
Eder W, Wanner G, Ludwig W, Busse H-J, Ziemke-Kägeler F, Lang E (2011) Description of Undibacterium oligocarboniphilum sp. nov., isolated from purified water, and Undibacterium pigrum strain CCUG 49012 as the type strain of Undibacterium parvum sp. nov., and emended descriptions of the genus Undibacterium and the species Undibacterium pigrum. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 61(2):384–391
Sheu SY, Lin YS, Chen JC, Kwon SW, Chen WM (2014) Undibacterium squillarum sp. nov., isolated from a freshwater shrimp culture pond. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 64(Pt 10):3459–3466
Pollock FJ, Lamb JB, Field SN, Heron SF, Schaffelke B, Shedrawi G, Bourne DG, Willis BL (2014) Sediment and turbidity associated with offshore dredging increase coral disease prevalence on nearby reefs. PLoS ONE 9(7):e102498
Ainsworth TD, Krause L, Bridge T, Torda G, Raina J-B, Zakrzewski M, Gates RD, Padilla-Gamino JL, Spalding HL, Smith C, Woolsey ES, Bourne DG, Bongaerts P, Hoegh-Guldberg O, Leggat W (2015) The coral core microbiome identifies rare bacterial taxa as ubiquitous endosymbionts. ISME J 9(10):2261–2274
Bally M, Garrabou J (2007) Thermodependent bacterial pathogens and mass mortalities in temperate benthic communities: a new case of emerging disease linked to climate change. Glob Chang Biol 13(10):2078–2088
Huete-Stauffer C, Vielmini I, Palma M, Navone A, Panzalis P, Vezzulli L, Misic C, Cerrano C (2011) Paramuricea clavata (Anthozoa, Octocorallia) loss in the marine protected area of Tavolara (Sardinia, Italy) due to a mass mortality event. Mar Ecol 32:107–116
Wang W, Gu W, Gasparich GE, Bi K, Ou J, Meng Q, Liang T, Feng Q, Zhang J, Zhang Y (2011) Spiroplasma eriocheiris sp. nov., associated with mortality in the Chinese mitten crab, Eriocheir sinensis. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 61(4):703–708
Thompson JR, Rivera HE, Closek CJ, Medina M (2015) Microbes in the coral holobiont: partners through evolution, development, and ecological interactions. Front Cell Infect Microbiol 4:176
Brown BE, Bythell JC (2005) Perspectives on mucus secretion in reef corals. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 296:291–309
Rosenberg E, Koren O, Reshef L, Efrony R, Zilber-Rosenberg I (2007) The role of microorganisms in coral health, disease and evolution. Nat Rev Microbiol 5(5):355–362
Brucker RM, Bordenstein SR (2013) The hologenomic basis of speciation: gut bacteria cause hybrid lethality in the genus Nasonia. Science 341(6146):667–669
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank Stéphanie Reynaud and Cécile Rottier (Scientific Centre of Monaco), Covadonga Orejas Saco del Valle (Spanish Institute of Oceanography, Majorca), Petar Kružić (University of Zagreb, Croatia), Joseph Gili (Marine Science Institute, Spain) and Giorgio Bavestrello (University of Genova, Italy) for their help with the sample collections and Ursula Pilat for the sample processing. Lauren Yum, the Bioscience Core Lab from King Abdullah University of Science and Technology (KAUST), and Till Bayer are thanked for their assistance with the 454 amplicon library preparation, sequencing and preliminary analysis, respectively. We would also like to thank the Paul Hamel Foundation and KAUST for the financial support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
van de Water, J.A.J.M., Melkonian, R., Voolstra, C.R. et al. Comparative Assessment of Mediterranean Gorgonian-Associated Microbial Communities Reveals Conserved Core and Locally Variant Bacteria. Microb Ecol 73, 466–478 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00248-016-0858-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00248-016-0858-x