Abstract
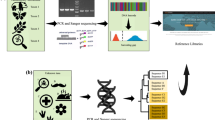
The selection of specific bioinformatic pipelines to analyse Next Generation Sequencing (NGS) data is instrumental for generating accurate biological inferences; users should understand the limitations of the pipelines and incorporate existing biodiversity information to evaluate results. Pipelines that maximize the coverage and precision of taxonomic inventories and are in line with local biodiversity characteristics should be preferred. Environmental DNA (eDNA) metabarcoding based on NGS technology is projected to be widely employed for biomonitoring applications and to supplement established ways of monitoring marine biodiversity. In Indonesia, research has concentrated on assessing taxonomic composition in various geographical and environmental situations and on identifying taxa that are susceptible to environmental changes. This study aims to compare four NGS data analysis pipelines (Anacapa, QIIME2 with DADA2, QIIME2 with Deblur and Galaxy) using a 28-sample subset of published eDNA seawater samples collected from seawater across Indonesia. The outputs of the bioinformatics analyses between the pipelines differed. Anacapa, QIIME2 with DADA2, and Galaxy pipelines provide more comprehensive taxonomic coverage relevant to existing biodiversity records from the regions compared to QIIME2 with Deblur. Anacapa in particular could successfully detect taxa that have not been detected with other pipelines tested. These findings should be taken into account when doing eDNA metabarcoding analyses, especially when assessing marine biodiversity in terms of species diversity and abundance.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Afgan E, Baker D, Batut B, Van Den Beek M et al (2018) The Galaxy platform for accessible, reproducible and collaborative biomedical analyses: 2018 update. Nucleic Acids Res 46(W1):W537–W544. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gky37
Agostino M (2012) Introduction to the BLAST suite and BLASTN. In: Agostino M (ed) Practical bioinformatics. Garland Science, New York, pp 47–71
Allali I, Arnold JW, Roach J et al (2017) A comparison of sequencing platforms andbioinformatics pipelines for compositional analysis of the gut microbiome. BMC Microbiol 17:194. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12866-017-1101-8
Altschul SF, Gish W, Miller W et al (1990) Basic local alignment search tool. J Mol Biol 215(3):403–410. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0022-2836(05)80360-2
Amir A, McDonald D, Navas-Molina JA et al (2017) Deblur rapidly resolves single-nucleotide community sequence patterns. MSystems 2(2):e00191-16. https://doi.org/10.1128/mSystems.00191-16
Andréfouët S, Paul M, Farhan AR (2022) Indonesia’s 13558 islands: a new census from space and a first step towards a one map for small islands policy. Mar Policy 135:104848
Andriyono S, Alam MJ, Kim, HW (2019) Environmental DNA (eDNA) metabarcoding: diversity study around the pondok dadap fish landing station, Malang, Indonesia. Biodiversitas 20(12). https://doi.org/10.13057/biodiv/d201241
Anslan S, Nilsson RH, Wurzbacher C, Baldrian P, Tedersoo L, Bahram M (2018) Great differences in performance and outcome of high-throughput sequencing data analysis platforms for fungal metabarcoding. MycoKeys 39:29–40. https://doi.org/10.3897/mycokeys.39.28109
Bailet B, Apothéloz-Perret-Gentil L, Baričević A et al (2020) Diatom DNA metabarcoding for ecological assessment: comparison among bioinformatics pipelines used in six European countries reveals the need for standardization. Sci Total Environ 745:140948. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.140948
Bellwood DR, Meyer CP (2009) Searching for heat in a marine biodiversity hotspot. J Biogeogr 36(4):569–576. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2699.2008.02029.x
Bolyen E, Rideout JR, Dillon MR et al (2019) Reproducible, interactive, scalable and extensible microbiome data science using QIIME 2. Nat Biotechnol 37:852–857. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41587-019-0209-9
Bray SA, Lucas X, Kumar A, Grüning BA (2020) The ChemicalToolbox: reproducible, user-friendly cheminformatics analysis on the Galaxy platform. J Cheminf 12(1):1–7. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13321-020-00442-7
Cahyani NKD, Kasanah N, Kurna DS, Hamman MT (2023) Profiling prokaryotic communities and aaptamines of sponge Aaptos suberitoides from Tulamben, Bali. Mar Biotechnol. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10126-023-10268-7
Callahan BJ, McMurdie PJ, Rosen MJ et al (2016) DADA2: High-resolution sample inference from Illumina amplicon data. Nat Methods 13(7):581–583. https://doi.org/10.1038/nmeth.3869
Capo E, Spong G, Königsson H, Byström P (2020) Effects of filtration methods and water volume on the quantification of brown trout (Salmo trutta) and Arctic char (Salvelinus alpinus) eDNA concentrations via droplet digital PCR. Environ DNA 2(2):152–160. https://doi.org/10.1002/edn3.52
Caporaso JG, Kuczynski J, Stombaugh J et al (2010) QIIME allows analysis of high-throughput community sequencing data. Nat Methods 7(5):335–336. https://doi.org/10.1038/nmeth.f.303
Chen Y, Ye W, Zhang Y, Xu Y (2015) High speed BLASTN: an accelerated MegaBLAST search tool. Nucleic Acids Res 43(16):7762–7768. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkv784
Clarke KR (1993) Non-parametric multivariate analyses of changes in community structure. Aust J Ecol 18(1):117–143
Curd EE, Gold Z, Kandlikar GS et al (2019) Anacapa Toolkit: an environmental DNA toolkit for processing multilocus metabarcode datasets. Methods Ecol Evol 10(9):1469–1475. https://doi.org/10.1101/488627
Effendi H, Aprilia M, Permatasari PA, Amalo LF (2022) Aquatic eDNA for monitoring fish biodiversity in Ciliwung River, Indonesia. AACL Bioflux 15(6):3311–3318
Evans NT, Li Y, Renshaw MA et al (2017) Fish community assessment with eDNA metabarcoding: effects of sampling design and bioinformatic filtering. Can J Fish Aquat Sci 74(9):1362–1374. https://doi.org/10.1139/cjfas-2016-0306
Fahmi, Oktaviyani S, Bennett MB, Dudgeon CL, Tibbetts I (2021) Reproductive biology of abamboo shark as a framework for better fisheries management. Mar Freshw Res 72(7):964–977. https://doi.org/10.1071/MF20189
Gao X, Lin H, Revanna K, Dong Q (2017) A Bayesian taxonomic classification method for 16S rRNA gene sequences with improved species-level accuracy. BMC Bioinf 18(1):1–10. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12859-017-1670-4
Giardine B, Riemer C, Hardison RC et al (2005) Galaxy: a platform for interactive large-scale genome analysis. Genome Res 15(10):1451–1455. https://doi.org/10.1101/gr.4086505
Gilbey J, Carvalho G, Castilho R et al (2021) Life in a drop: sampling environmental DNA for marine fishery management and ecosystem monitoring. Mar Policy 124:104331. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpol.2020.104331
Gold Z, Sprague J, Kushner DJ, Zerecero Marin E, Barber PH (2021) eDNA metabarcoding as a biomonitoring tool for marine protected areas. PLoS ONE 16(2):e0238557. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0238557
Goldberg CS, Turner CR, Deiner K et al (2016) Critical considerations for the application of environmental DNA methods to detect aquatic species. Methods Ecol Evol 7(11):1299–1307. https://doi.org/10.1111/2041-210X.12595
Gutierrez-Rodriguez A, Stukel MR, Lopes Dos Santos A et al (2019) High contribution of Rhizaria (Radiolaria) to vertical export in the California Current Ecosystem revealed by DNA metabarcoding. ISME J 13(4):964–976. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41396-018-0322-7
Hadi S, Andayani N, Muttaqin E, Simeon BM et al (2020) Genetic connectivity of the scalloped hammerhead shark Sphyrna lewini across Indonesia and the Western Indian Ocean. PLoS ONE 15(10):e0230763. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0230763
Hakimzadeh A, Abdala Asbun A, Albanese D et al (2023) A pile of pipelines: an overview of the bioinformatics software for metabarcoding data analyses. Mol Ecol Resour 00:1–17. https://doi.org/10.1111/1755-0998.13847
Harper LR, Buxton AS, Rees HC et al (2019) Prospects and challenges of environmental DNA (eDNA) monitoring in freshwater ponds. Hydrobiologia 826(1):25–41. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-018-3750-5
Hildebrand F, Tadeo R, Voigt AY et al (2014) LotuS: an efficient and user-friendly OTU processing pipeline. Microbiome 2(1):1–7. http://www.microbiomejournal.com/content/2/1/37
Hunter ME, Ferrante JA, Meigs-Friend G, Ulmer A (2019) Improving eDNA yield and inhibitor reduction through increased water volumes and multi-filter isolation techniques. Sci Rep 9(1):1–9. https://doi.org/10.5066/P9ULOPXB
Jalili V, Afgan E, Gu Q et al (2020) The Galaxy platform for accessible, reproducible and collaborative biomedical analyses: 2020 update. Nucleic Acids Res. 48(W1):W395–W402. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkaa554
Juhel JB, Utama RS, Marques V et al (2020) Accumulation curves of environmental DNA sequences predict coastal fish diversity in the coral triangle. Proc R Soc B 287:20200248. https://doi.org/10.1098/rspb.2020.0248rspb20200248
Knowlton N, Brainard RE, Fisher R et al (2010) Coral reef biodiversity. Life in the world’s oceans: diversity distribution and abundance. 65–74. https://doi.org/10.1002/9781444325508.ch4
Kuncoro I, Zamani NP, Subhan B, Cahyani NKD (2023) eDNA assessment of scleractinian diversity and distribution in Lemukutan Island, Indonesia. Biodiversitas. 24(7):4185–4191. https://doi.org/10.13057/biodiv/d240758
Lan Y, Wang Q, Cole JR, Rosen GL (2012) Using the RDP classifier to predict taxonomic novelty and reduce the search space for finding novel organisms. PLoS ONE 7(3):e32491. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0032491
Langmead B, Salzberg SL (2012) Fast gapped-read alignment with Bowtie 2. Nat Methods 9(4):357–359. https://doi.org/10.1038/nmeth.1923
Laroche O, Kersten O, Smith CR, Goetze E (2020) From sea surface to seafloor: a benthic allochthonous eDNA survey for the abyssal ocean. Front Mar Sci 7:682. https://doi.org/10.1101/2020.05.07.082602
Leray M, Yang JY, Meyer CP et al (2013) A new versatile primer set targeting a short fragment of the mitochondrial COI region for metabarcoding metazoan diversity: application for characterizing coral reef fish gut contents. Front Zool 10(1):1–14. https://doi.org/10.1186/1742-9994-10-34
Liu G, Li T, Zhu X et al (2023) An independent evaluation in a CRC patient cohort of microbiome 16S rRNA sequence analysis methods: OTU clustering, DADA2, and Deblur. Front. Microbiol. 14. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2023.1178744
Madduppa H, Cahyani NKD, Anggoro AW et al (2021) eDNA metabarcoding illuminates species diversity and composition of three phyla (chordata, mollusca and echinodermata) across Indonesian coral reefs. Biodivers Conserv 30(11):3087–3114. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10531-021-02237-0
Martin M (2011) Cutadapt removes adapter sequences from high-throughput sequencing reads. EMBnet J 17(1):10–12. https://doi.org/10.14806/ej.17.1.200
Marwayana ON, Gold Z, Meyer CP, Barber PH (2022) Environmental DNA in a global biodiversity hotspot: lessons from coral reef fish diversity across the Indonesian archipelago. Environ DNA 4(1):222–238. https://doi.org/10.1002/edn3.257
Mathon L, Valentini A, Guérin PE et al (2021) Benchmarking bioinformatic tools for fast and accurate eDNA metabarcoding species identification. Mol Ecol Resour 21(7):2565–2579. https://doi.org/10.1111/1755-0998.13430
McMurdie PJ, Holmes S (2013) phyloseq: an R package for reproducible interactive analysis and graphics of microbiome census data. PLoS ONE 8(4):e61217. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0061217
Meier-Kolthoff JP, Auch AF, Huson DH, Göker M (2007) COPYCAT: cophylogenetic analysis tool. Bioinformatics 23(7):898–900. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btm027
Mikkelsen PM, Cracraft J (2001) Marine biodiversity and the need for systematic inventories. Bull Mar Sci 69:525–534
Moore AM, Jompa J, Tassakka ACMA et al (2021) Sharks and rays (Chondrichthyes) around Banggai Island, Banggai MPA, Indonesia: biodiversity data from an environmental DNA pilot study. AACL Bioflux 14:725–745
Muha TP, Robinson CV, Garcia de Leaniz C, Consuegra S (2019) An optimised eDNA protocol for detecting fish in lentic and lotic freshwaters using a small water volume. PLoS ONE 14(7):e0219218. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0219218
Nguyen BN, Shen EW, Seemann J et al (2020) Environmental DNA survey captures patterns of fish and invertebrate diversity across a tropical seascape. Sci Rep 10(1):1–14. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-63565-9
Pauvert C, Buée M, Laval V, Edel-Hermann V, Fauchery L, Gautier A et al (2019) Bioinformatics matters: the accuracy of plant and soil fungal community data is highly dependent on the metabarcoding pipeline. Fungal Ecol 41:23–33. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.funeco.2019.03.005
Piredda R, Tomasino MP, D'erchia AM et al (2017) Diversity and temporal patterns of planktonic protist assemblages at a Mediterranean Long Term Ecological Research site. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 93(1). https://doi.org/10.1093/femsec/fiw200
Plaisance L, Knowlton N, Paulay G, Meyer C (2009) Reef-associated crustacean fauna: biodiversity estimates using semi-quantitative sampling and DNA barcoding. Coral Reefs 28:977–986. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00338-009-0543-3
Plaisance L, Caley MJ, Brainard RE, Knowlton N (2011) The diversity of coral reefs: what are we missing? PLoS ONE 6(10):e25026. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0025026
Polanco Fernández A, Marques V, Fopp F et al (2021) Comparing environmental DNA metabarcoding and underwater visual census to monitor tropical reef fishes. Environ DNA 3(1):142–156. https://doi.org/10.1002/edn3.140
Porter TM, Hajibabaei M (2022) MetaWorks: a flexible, scalable bioinformatic pipeline for high-throughput multi-marker biodiversity assessments. PLos ONE 17(9):e0274260. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0274260
Prehadi P, Sembiring A, Kurniasih EM et al (2015) DNA barcoding and phylogenetic reconstruction of shark species landed in Muncar fisheries landing site in comparison with Southern Java fishing port. Biodiversitas 16(1). https://doi.org/10.13057/biodiv/d160107
Prodan A, Tremaroli V, Brolin H et al (2020) Comparing bioinformatic pipelines for microbial 16S rRNA amplicon sequencing. PLoS ONE 15(1):e0227434. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0227434
Ransome E, Geller JB, Timmers M et al (2017) The importance of standardization for biodiversity comparisons: a case study using autonomous reef monitoring structures (ARMS) and metabarcoding to measure cryptic diversity on Mo’orea coral reefs, French Polynesia. PLoS ONE 12(4):e0175066. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0175066
Roesma DI, Tjong DH, Syaifullah S et al (2023) The importance of DNA barcode reference libraries and selection primer pair in monitoring fish diversity using environmental DNA Metabarcoding. Biodiversitas 24(4). https://doi.org/10.13057/biodiv/d240438
Rognes T, Flouri T, Nichols B et al (2016) VSEARCH: a versatile open source tool for metagenomics. PeerJ 4:e2584. https://doi.org/10.7717/peerj.2584
Sani LMI, Husna AK, Subhan B, Madduppa H (2021) Environmental DNA (eDNA) reveals endangered narrow sawfish across Indonesian Reefs. In IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science, vol 944, no 1, p 012020. IOP Publishing. https://doi.org/10.1088/1755-1315/944/1/012020
Schloss PD, Westcott SL, Ryabin T et al (2009) Introducing mothur: open-source, platform-independent, community-supported software for describing and comparing microbial communities. AEM 75(23):7537–7541. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.01541-09
Sembiring A, Pertiwi NPD, Mahardini A et al (2015) DNA barcoding reveals targeted fisheries for endangered sharks in Indonesia. Fish Res 164:130–134. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fishres.2014.11.003
Siegwald L, Caboche S, Even G et al (2019) The impact of bioinformatics pipelines on microbiota studies: does the analytical “microscope” affect the biological interpretation? Microorganisms 7(10):393. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms7100393
Sigsgaard EE, Torquato F, Frøslev TG et al (2020) Using vertebrate environmental DNA from seawater in biomonitoring of marine habitats. Conserv Biol Conserv 34(3):697–710. https://doi.org/10.1111/cobi.13437
Sinniger F, Pawlowski J, Harii S et al (2016) Worldwide analysis of sedimentary DNA reveals major gaps in taxonomic knowledge of deep-sea benthos. Front Mar Sci 3:92. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmars.2016.00092
Suharsono, (2014) Biodivesitas Laut Indonesia. LIPI Press, Jakarta
Thomsen PF, Willerslev E (2015) Environmental DNA–an emerging tool in conservation for monitoring past and present biodiversity. Biol Conserv 183:4–18. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biocon.2014.11.019
Tittensor DP, Mora C, Jetz W et al (2010) Global patterns and predictors of marine biodiversity across taxa. Nature 466(7310):1098–1101. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature09329
Valdivia-Carrillo T, Rocha-Olivares A, Reyes-Bonilla H et al (2021) Integrating eDNA metabarcoding and simultaneous underwater visual surveys to describe complex fish communities in a marine biodiversity hotspot. Mol Ecol Resour 21(5):1558–1574. https://doi.org/10.1111/1755-0998.13375
Veron JEN, Devantier LM, Turak E, Green AL (2009) Delineating the coral triangle. Galaxea, J Coral Reef Stud 11:91–100
Wang Q, Garrity GM, Tiedje JM, Cole JR (2007) Naive Bayesian classifier for rapid assignment of rRNA sequences into the new bacterial taxonomy. AEM 73(16):5261–5267. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.00062-07
West KM, Stat M, Harvey ES et al (2020) eDNA metabarcoding survey reveals fine-scale coral reef community variation across a remote, tropical island ecosystem. Mol Ecol 29(6):1069–1086. https://doi.org/10.1111/mec.15382
Wickham H (2016) Data analysis. ggplot2. Springer International Publishing, Cham, pp 189–201
Xiong F, Shu L, Gan X et al (2022) Methodology for fish biodiversity monitoring with environmental DNA metabarcoding: the primers, databases and bioinformatic pipelines. Water Biol Secur 100007. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watbs.2022.100007
Zafeiropoulos H, Viet HQ, Vasileiadou K et al (2020) PEMA: a flexible pipeline for environmental DNA metabarcoding analysis of the 16S/18S ribosomal RNA, ITS, and COI marker genes. Gigascience 9:1–12. https://doi.org/10.1093/GIGASCIENCE/GIAA022
Zaiko A, Pochon X, Garcia-Vazquez E et al (2018) Advantages and limitations of environmental DNA/RNA tools for marine biosecurity: management and surveillance of non-indigenous species. Front Mar Sci 5:322. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmars.2018.00322
Acknowledgements
This project was partly funded by IPB University (project number 15734/IT3/TU.00.01/M/B/2021) through the Post-Doctoral grant awarded to HM with the research title “Resolution and Composition of Taxa in Indonesian Marine Biodiversity: Application of Bioinformatics pipeline variety to Environmental DNA (eDNA) data”, and supported under World Class Research scheme No: 2346 /IT3.L1/PN/2021 awarded to HM for the research project entitled “Redefining hotspots of marine fishes across Indonesian coral reefs with different anthropogenic pressure using environmental DNA metabarcoding for sustainable fisheries”. We would like to thank the reviewers for taking the time and effort necessary to review the manuscript. We sincerely appreciate all valuable comments and suggestions, which helped us to improve the quality of the manuscript.
Funding
Post-Doctoral grant, 15734/IT3/TU.00.01/M/B/2021, Hawis Madduppa, World Class Research Schame, 2346 /IT3.L1/PN/2021, Hawis Madduppa.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
No animal testing was performed during this study.
Sampling and field studies
All necessary permits for sampling and observational field studies have been obtained by the authors from the competent authorities and are mentioned in the acknowledgements, if applicable. The study is compliant with CBD and Nagoya protocols.
Data availability
The raw FASTQ data results from this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
Author contribution
NKDC, AWA and HM conceived and designed the research. BS, LMI and HM contributed to sample collection and laboratory work. NKDC, AWA and MDAM analysed the data. All authors wrote the manuscript, read and approved the manuscript. HM sadly passed away before the submission of this paper; he had approved an initial draft but not the revised versions.
Additional information
Communicated by D. Huang
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Cahyani, N.K.D., Anggoro, A.W., Al Malik, M.D. et al. Inventorizing marine biodiversity using eDNA data from Indonesian coral reefs: comparative high throughput analysis using different bioinformatic pipelines. Mar. Biodivers. 54, 39 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12526-024-01432-w
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12526-024-01432-w