Abstract
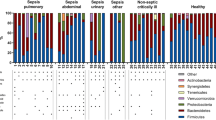
Understanding the composition of the microbial populations in the intestines of liver transplant patients is important to preventing postoperative infection. We investigated the relationship between the risk of postoperative infection and variation in the predominant fecal microbial composition during the perioperative period. We prospectively analyzed the predominant intestinal microbiome of five asymptomatic adult carriers of hepatitis B virus (as controls without any antibiotics) at four weekly follow-up visits and 12 patients before operation and at three weekly postoperative follow-up visits within the first month. Analysis was by denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis (DGGE) and sequencing with digital processing of DGGE profiles using BioNumerics software. Our results showed that the predominant intestinal microbial diversity decreased substantially in eight patients during the perioperative period. Among these, five patients experienced infection with a postoperative hospital stay of more than 30 days. The rest of the four patients who experienced shorter postoperative hospital stays showed only slight variation in predominant intestinal bacterial composition and temporal stability similar to asymptomatic controls. Postoperative fecal DGGE profiles showed mostly bands assigned to Bacteroides and Firmicutes. We conclude that an empiric prophylaxis strategy that destructs gut microecological balance will not be effective in reducing the risk of postoperative infection. Instead, the destruction of intestinal microbiota might result in the appearance of opportunistic pathogens such as Bifidobacterium dentium which rarely appears in the intestinal DGGE profiles of normal humans. Cognizance of the variation of intestinal microbial profiles during the perioperative period is a critical aspect of caring for liver transplant recipients.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
(2004) Immunosuppressive drug interactions with anti-infective agents. Am J Transplant 4 Suppl 10: 164–166
Arnow PM (1991) Infections following orthotopic liver transplantation. HPB Surg 3:221–232, discussion 232–223
Bartosch S, Fite A, Macfarlane GT, McMurdo ME (2004) Characterization of bacterial communities in feces from healthy elderly volunteers and hospitalized elderly patients by using real-time PCR and effects of antibiotic treatment on the fecal microbiota. Appl Environ Microbiol 70:3575–3581
Beighton D, Gilbert SC, Clark D, Mantzourani M, Al-Haboubi M, Ali F, Ransome E, Hodson N, Fenlon M, Zoitopoulos L, Gallagher J (2008) Isolation and identification of bifidobacteriaceae from human saliva. Appl Environ Microbiol 74:6457–6460
Berdaguer S, Bautista J, Brunet M, Cisneros JM (2012) Antimicrobial and immunosuppressive drug interactions in solid organ transplant recipients. Enferm Infecc Microbiol Clin 30(Suppl 2):86–92
Binder M, Otto F, Mertelsmann R, Veelken H, Trepel M (2006) The epitope recognized by rituximab. Blood 108:1975–1978
Cakir M, Arikan C, Akman SA, Baran M, Saz EU, Yagci RV, Zeytunlu M, Kilic M, Aydogdu S (2010) Infectious complications in pediatric liver transplantation candidates. Pediatr Transplant 14:82–86
Chen Y, Yang F, Lu H, Wang B, Lei D, Wang Y, Zhu B, Li L (2011) Characterization of fecal microbial communities in patients with liver cirrhosis. Hepatology 54:562–572
del Pozo JL (2008) Update and actual trends on bacterial infections following liver transplantation. World J Gastroenterol 14:4977–4983
Duineveld BM, Rosado AS, van Elsas JD, van Veen JA (1998) Analysis of the dynamics of bacterial communities in the rhizosphere of the chrysanthemum via denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis and substrate utilization patterns. Appl Environ Microbiol 64:4950–4957
Ferris MJ, Muyzer G, Ward DM (1996) Denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis profiles of 16S rRNA-defined populations inhabiting a hot spring microbial mat community. Appl Environ Microbiol 62:340–346
Garrett WS, Lord GM, Punit S, Lugo-Villarino G, Mazmanian SK, Ito S, Glickman JN, Glimcher LH (2007) Communicable ulcerative colitis induced by T-bet deficiency in the innate immune system. Cell 131:33–45
Hill DA, Hoffmann C, Abt MC, Du Y, Kobuley D, Kirn TJ, Bushman FD, Artis D (2010) Metagenomic analyses reveal antibiotic-induced temporal and spatial changes in intestinal microbiota with associated alterations in immune cell homeostasis. Mucosal Immunol 3:148–158
Joossens M, Huys G, Cnockaert M, De Preter V, Verbeke K, Rutgeerts P, Vandamme P, Vermeire S (2011) Dysbiosis of the faecal microbiota in patients with Crohn's disease and their unaffected relatives. Gut 60:631–637
Kuehl CJ, Wood HD, Marsh TL, Schmidt TM, Young VB (2005) Colonization of the cecal mucosa by Helicobacter hepaticus impacts the diversity of the indigenous microbiota. Infect Immun 73:6952–6961
Lorian V (1994) Colonization resistance. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 38:1693
Lu H, Wu Z, Xu W, Yang J, Chen Y, Li L (2011) Intestinal microbiota was assessed in cirrhotic patients with hepatitis B virus infection. Intestinal microbiota of HBV cirrhotic patients. Microb Ecol 61:693–703
Lumbreras C, Lizasoain M, Moreno E, Aguado JM, Gomez R, Garcia I, Gonzalez I, Loinaz C, Cisneros C, Noriega AR (1992) Major bacterial infections following liver transplantation: a prospective study. Hepatogastroenterology 39:362–365
Lupo L, Panzera P, Tandoi F, Carbotta G, Giannelli G, Santantonio T, Rendina M, Gentile A, Memeo V (2008) Basiliximab versus steroids in double therapy immunosuppression in liver transplantation: a prospective randomized clinical trial. Transplantation 86:925–931
Matto J, Maunuksela L, Kajander K, Palva A, Korpela R, Kassinen A, Saarela M (2005) Composition and temporal stability of gastrointestinal microbiota in irritable bowel syndrome—a longitudinal study in IBS and control subjects. FEMS Immunol Med Microbiol 43:213–222
Maukonen J, Matto J, Satokari R, Soderlund H, Mattila-Sandholm T, Saarela M (2006) PCR DGGE and RT-PCR DGGE show diversity and short-term temporal stability in the Clostridium coccoides–Eubacterium rectale group in the human intestinal microbiota. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 58:517–528
Mignat C (1997) Clinically significant drug interactions with new immunosuppressive agents. Drug Saf 16:267–278
Muller AK, Westergaard K, Christensen S, Sorensen SJ (2002) The diversity and function of soil microbial communities exposed to different disturbances. Microb Ecol 44:49–58
Muyzer G, de Waal EC, Uitterlinden AG (1993) Profiling of complex microbial populations by denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis analysis of polymerase chain reaction-amplified genes coding for 16S rRNA. Appl Environ Microbiol 59:695–700
Nakano V, Nascimento e Silva A, Merino VR, Wexler HM, Avila-Campos MJ (2011) Antimicrobial resistance and prevalence of resistance genes in intestinal Bacteroidales strains. Clinics (Sao Paulo) 66:543–547
Prakash S, Rodes L, Coussa-Charley M, Tomaro-Duchesneau C (2011) Gut microbiota: next frontier in understanding human health and development of biotherapeutics. Biologics 5:71–86
Rollinghoff M, Schrader J, Wagner H (1973) Effect of azathioprine and cytosine arabinoside on humoral and cellular immunity in vitro. Clin Exp Immunol 15:261–269
Salyers AAGA, Wang Y (2004) Human intestinal bacteria as reservoirs for antibiotic resistance genes. Trends Microbiol 12:412–416
Seki E, Brenner DA (2008) Toll-like receptors and adaptor molecules in liver disease: update. Hepatology 48:322–335
Simpson JM, Martineau B, Jones WE, Ballam JM, Mackie RI (2002) Characterization of fecal bacterial populations in canines: effects of age, breed and dietary fiber. Microb Ecol 44:186–197
Smith KG, Isbel NM, Catton MG, Leydon JA, Becker GJ, Walker RG (1998) Suppression of the humoral immune response by mycophenolate mofetil. Nephrol Dial Transplant 13:160–164
Son G, Kremer M, Hines IN (2010) Contribution of gut bacteria to liver pathobiology. Gastroenterol Res Pract 2010:453–563
Tamura K, Peterson D, Peterson N, Stecher G, Nei M, Kumar S (2011) MEGA5: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis using maximum likelihood, evolutionary distance, and maximum parsimony methods. Mol Biol Evol 28:2731–2739
Thompson JR, Marcelino LA, Polz MF (2002) Heteroduplexes in mixed-template amplifications: formation, consequence and elimination by 'reconditioning PCR'. Nucleic Acids Res 30:2083–2088
Vanhoutte T, Huys G, Brandt E, Swings J (2004) Temporal stability analysis of the microbiota in human feces by denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis using universal and group-specific 16S rRNA gene primers. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 48:437–446
Vanhoutte T, Huys G, De Brandt E, Fahey GC Jr, Swings J (2005) Molecular monitoring and characterization of the faecal microbiota of healthy dogs during fructan supplementation. FEMS Microbiol Lett 249:65–71
Vijay-Kumar M, Aitken JD, Carvalho FA, Cullender TC, Mwangi S, Srinivasan S, Sitaraman SV, Knight R, Ley RE, Gewirtz AT (2010) Metabolic syndrome and altered gut microbiota in mice lacking Toll-like receptor 5. Science 328:228–231
Wallemacq PE, Reding R (1993) FK506 (tacrolimus), a novel immunosuppressant in organ transplantation: clinical, biomedical, and analytical aspects. Clin Chem 39:2219–2228
Wiesner RH, Hermans PE, Rakela J, Washington JA 2nd, Perkins JD, DiCecco S, Krom R (1988) Selective bowel decontamination to decrease gram-negative aerobic bacterial and Candida colonization and prevent infection after orthotopic liver transplantation. Transplantation 45:570–574
Wu ZW, Ling ZX, Lu HF, Zuo J, Sheng JF, Zheng SS, Li LJ (2012) Changes of gut bacteria and immune parameters in liver transplant recipients. Hepatobiliary Pancreat Dis Int 11:40–50
Xie YR, Liu SL, Liu X, Luo ZB, Zhu B, Li ZF, Li LJ, He Y, Jiang L, Li H, Ruan B (2011) Intestinal microbiota and innate immunity-related gene alteration in cirrhotic rats with liver transplantation. Transplant Proc 43:3973–3979
Xing HC, Li LJ, Xu KJ, Shen T, Chen YB, Sheng JF, Yu YS, Chen YG (2005) Intestinal microflora in rats with ischemia/reperfusion liver injury. J Zhejiang Univ Sci B 6:14–21
Xu M, Wang B, Fu Y, Chen Y, Yang F, Lu H, Xu J, Li L (2012) Changes of fecal Bifidobacterium species in adult patients with hepatitis B virus-induced chronic liver disease. Microb Ecol 63:304–313
Zoetendal EG, Akkermans AD, De Vos WM (1998) Temperature gradient gel electrophoresis analysis of 16S rRNA from human fecal samples reveals stable and host-specific communities of active bacteria. Appl Environ Microbiol 64:3854–3859
Acknowledgments
We gratefully acknowledge the physicians at the Department of Infectious Diseases and the surgeons at the Department of Surgery in the First Affiliated Hospital, College of Medicine, Zhejiang University, for their collaboration and collection of stool specimens. This study was supported by the National Basic Research Program (973) of China (2009CB522400, 2013CB531401), the Zhejiang Chinese Medicine Administrative bureau project (no. 2009ZA012), and the Zhejiang Provincial Medical Scientific Research Foundation of China (2012RCB020).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lu, H., He, J., Wu, Z. et al. Assessment of Microbiome Variation During the Perioperative Period in Liver Transplant Patients: a Retrospective Analysis. Microb Ecol 65, 781–791 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00248-013-0211-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00248-013-0211-6