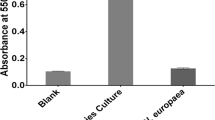
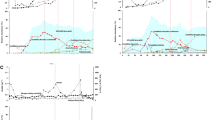
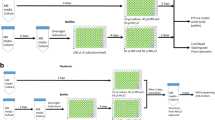
Abstract
Dual-species microbial interactions have been extensively reported for batch and continuous culture environments. However, little research has been performed on dual-species interaction in a biofilm. This research examined the effects of growth rate and substrate concentration on dual-species population densities in batch and biofilm reactors. In addition, the feasibility of using batch reactor kinetics to describe dual-species biofilm interactions was explored. The scope of the research was directed toward creating a dual-species biofilm for the biodegradation of trichloroethylene, but the findings are a significant contribution to the study of dual-species interactions in general. The two bacterial species used were Burkholderia cepacia PR1-pTOM31c, an aerobic organism capable of constitutively mineralizing trichloroethylene (TCE), and Klebsiella oxytoca, a highly mucoid, facultative anaerobic organism. The substrate concentrations used were different dilutions of a nutrient-rich medium resulting in dissolved organic carbon (DOC) concentrations on the order of 30, 70, and 700 mg/L. Presented herein are single- and dual-species population densities and growth rates for these two organisms grown in batch and continuous-flow biofilm reactors. In batch reactors, planktonic growth rates predicted dual-species planktonic species dominance, with the faster-growing organism (K. oxytoca) outcompeting the slower-growing organism (B. cepacia). In a dual-species biofilm, however, dual-species planktonic growth rates did not predict which organism would have the higher dual-species biofilm population density. The relative fraction of each organism in a dual-species biofilm did correlate with substrate concentration, with B. cepacia having a greater proportional density in the dual-species culture with K. oxytoca at low (30 and 70 mg/L DOC) substrate concentrations and K. oxytoca having a greater dual-species population density at a high (700 mg/L DOC) substrate concentration. Results from this research demonstrate the effectiveness of using substrate concentration to control population density in this dual-species biofilm.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
R Bakke MG Trulear JA Robinson WG Characklis (1984) ArticleTitleActivity of Pseudomonas aeruginosa in biofilms: steady state. Biotechnol Bioeng 26 1418–1424 Occurrence Handle10.1002/bit.260261204 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaL2MXhtFWnsbk%3D
MK Banks JD Bryers (1992) ArticleTitleDeposition of bacterial cells onto glass and biofilm surfaces. Biofouling 6 81–86 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK2cXisFejsrc%3D
MK Banks JD Bryers (1991) ArticleTitleBacterial species dominance within a binary culture biofilm. Appl Environ Microbiol 57 1974–1979 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:By6A28bitVc%3D Occurrence Handle1892387
DJ Bibel R Aly C Bayles WG Strauss HR Shinefield HI Maibach (1983) ArticleTitleCompetitive adherence as a mechanism of bacterial interference. Can J Microbiol 29 700–703 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:BiyB1cvmsFc%3D Occurrence Handle6411317
T Bühler S Ballestero M Desai MRW Brown (1998) ArticleTitleGeneration of a reproducible nutrient-depleted biofilm of Escherichia coli and Burkholderia cepacia. J Appl Microbiol 85 457–462 Occurrence Handle10.1046/j.1365-2672.1998.853501.x Occurrence Handle9750276
AK Camper WJ Jones JT Hayes (1996) ArticleTitleEffect of growth conditions and substratum composition on the persistence of coliforms in mixed-population biofilms. Appl Environ Microbiol 62 4014–4018 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK28Xms1Kitbk%3D Occurrence Handle8899991
YS Cao GJ Alaerts (1995) ArticleTitleAerobic biodegradation and microbial population of a synthetic wastewater in a channel with suspended and attached biomass. Wat Sci Tech 31 181–189 Occurrence Handle10.1016/0273-1223(95)00335-K Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK2MXpsVansrY%3D
JE Ciardi GFA McCray PE Kolenbrander A Lau (1987) ArticleTitleCell-to-cell interactions of Streptococcus sanguis and Propionibacterium acnes on saliva-coated hydroxyapatite. Infect Immun 55 1441–1446 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaL2sXksFGlt7w%3D Occurrence Handle3570474
DD Cleland VH Smith DW Graham (1997) Microbial population dynamics during hydrogen biodegradation under variable nutrient conditions. Proceedings from the Fourth International in situ and On-Site Bioremediation Symposium, vol. 4 Battelle Press Columbus 105–110
MM Cowan TM Warren M Fletcher (1991) ArticleTitleMixed-species colonization of solid surfaces in laboratory biofilms. Biofouling 3 23–34
AB Cunningham B Warwood P Sturman K Horrigan G James JW Costerton R Hiebert (1997) Biofilm processes in porous media—practical applications. PS Amy DL Haldeman (Eds) The Microbiology of the Terrestrial Deep Subsurface Lewis Publishers New York 325–344
RMM Diks SPP Ottengraf (1991) ArticleTitleVerification studies of a simplified model for the removal of dichloromethane from waste gases using a biological trickling filter (part I). Bioprocess Eng 6 93–99 Occurrence Handle10.1007/BF00369061 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK3MXksFGrurw%3D
H Harms AJB Zehnder (1994) ArticleTitleInfluence of substrate diffusion on degradation of dibenzofuran and 3-chlorodibenzofuran by attached and suspended bacteria. Appl Environ Microbiol 60 2736–2745 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK2cXltVWmtrg%3D Occurrence Handle8085817
J Houtmeyers E Van den Eynde R Poffe H Verachtert (1980) ArticleTitleRelations between substrate feeding pattern and development of filamentous bacteria in activated sludge processes, Part 1. Influence of process parameters. Eur J Microb Biotecnol 9 63–77 Occurrence Handle10.1007/BF00500004 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaL3cXltVSqt7s%3D
WH Jeffrey JH Paul (1986) ArticleTitleActivity of an attached and free-living Vibrio sp. as measured by thymidine incorporation, p-iodonitrotetrazolium reduction, and ATP/DNA ratios. Appl Environ Microbiol 51 150–156 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaL28XosFWhuw%3D%3D
J Komlos AB Cunningham AK Camper RR Sharp (2004) ArticleTitleBiofilm barriers to contain and degrade dissolved trichloroethylene (TCE). Environmental Progress 23 69–77 Occurrence Handle10.1002/ep.10003 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD2cXjtVaqtb0%3D
Komlos, J, Cunningham, AB, Sharp, RR (1999) Population dynamics in a multi-species biofilm for the creation of a reactive biobarrier. Proceedings of the 1999 Conference on Hazardous Waste Research, pp 158–166
FA MacLeod HM Lappin-Scott JW Costertonn (1988) ArticleTitlePlugging of a model rock system by using starved bacteria. Appl Environ Microbiol 54 1365–1372 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaL1cXksVSgurs%3D
PD Marsh JR Hunter GH Bowden IR Hamilton AS McKee JM Hardie DC Ellwood (1983) ArticleTitleThe influence of growth rate and nutrient limitation on the microbial composition and biochemical properties of a mixed culture of oral bacteria grown in a chemostat. J Gen Microbiol 129 755–770 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaL3sXhslGqurw%3D Occurrence Handle6348208
S McEldowney M Fletcher (1987) ArticleTitleAdhesion of bacteria from mixed cell suspension to solid surfaces. Arch Microbiol 148 57–62 Occurrence Handle10.1007/BF00429648 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:BiiA38rjvFQ%3D Occurrence Handle3115220
R Mirpuri W Jones JD Bryers (1997) ArticleTitleToluene degradation kinetics for planktonic and biofilm-grown cells of Pseudomonas putida 54G. Biotechnol Bioeng 53 535–546 Occurrence Handle10.1002/(SICI)1097-0290(19970320)53:6<535::AID-BIT1>3.0.CO;2-N
S Møller DR Korber GM Wolfaardt S Molin DE Caldwell (1997) ArticleTitleImpact of nutrient composition on a degradative biofilm community. Appl Environ Microbiol 63 2432–2438
S Okabe Y Oozawa K Hirata Y Watanabe (1996) ArticleTitleRelationship between population dynamics of nitrifiers in biofilms and reactor performance at various C:N ratios. Wat Res 30 1563–1572 Occurrence Handle10.1016/0043-1354(95)00321-5 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK28XjvFamsbY%3D
PJ Partidario MJT Carrondo (1993) ArticleTitleMass transfer and reaction of trimethylamine in a three-phase biological reactor. J Chem Tech Biotechnol 57 299–307 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK3sXlsVGmsrs%3D
G Pinar K Kovarova T Egli JL Ramos (1998) ArticleTitleInfluence of carbon source on nitrate removal by nitrate-tolerant Klebsiella oxytoca CECT 4460 in batch and chemostat cultures. Appl Environ Microbiol 64 2970–2976 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaK1czltlertQ%3D%3D Occurrence Handle9687459
Z Shareefdeen BC Baltzis O Young-Sook R Bartha (1993) ArticleTitleBiofiltration of methanol vapor. Biotechnol Bioeng 41 512–524 Occurrence Handle10.1002/bit.260410503 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK3sXhtlSqtL0%3D
RR Sharp JD Bryers WG Jones MS Shields (1998) ArticleTitleActivity and stability of a recombinant plasmid-borne TCE degradative pathway in biofilm cultures. Biotechnol Bioeng 59 318–327 Occurrence Handle10.1002/(SICI)1097-0290(19980805)59:3<318::AID-BIT8>3.0.CO;2-E Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK1cXktFWgsbc%3D Occurrence Handle10099343
MS Shields MJ Reagin RR Gerger R Campbell C Somerville (1995) ArticleTitleTOM, a new aromatic degradative plasmid from Burkholderia (Pseudomonas) cepacia G4. Appl Environ Microbiol 61 1352–1356 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK2MXksl2ls7w%3D Occurrence Handle7538275
MS Shields MJ Reagin (1992) ArticleTitleSelection of a Pseudomonas cepacia strain constitutive for the degradation of trichloroethylene. Appl Environ Microbiol 58 3977–3983 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK3sXlsFygug%3D%3D Occurrence Handle1282314
MA Siebel WG Characklis (1991) ArticleTitleObservations of binary population biofilms. Biotechnol Bioeng 37 778–789 Occurrence Handle10.1002/bit.260370813 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK3MXhs1ans7Y%3D
PS Stewart AK Camper SD Handran CT Huang M Warnecke (1997) ArticleTitleSpatial distribution and coexistence of Klebsiella pneumoniae and Pseudomonas aeruginosa in biofilms. Microb Ecol 33 2–10 Occurrence Handle10.1007/s002489900002 Occurrence Handle9039760
P Sturman WL Jones WG Characklis (1994) ArticleTitleInterspecies competition in colonized porous pellets. Wat Res 28 831–839 Occurrence Handle10.1016/0043-1354(94)90089-2 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK2cXit1Knsbk%3D
E Van Der Wende WG Characklis DB Smith (1989) ArticleTitleBiofilms and bacterial drinking water quality. Wat Res 23 1313–1322 Occurrence Handle10.1016/0043-1354(89)90193-0 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK3cXisFegtg%3D%3D
O Wanner W Gujer (1986) ArticleTitleA multispecies biofilm model. Biotechnol Bioeng 28 314–328 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaL28XhsVOisLk%3D
N Zelver M Hamilton B Pitts D Goeres D Walker P Sturman J Heersink (1999) Measuring antimicrobial effects on biofilm bacteria: from laboratory to field. RJ Doyle (Eds) Biofilms: Methods in Enzymology, vol. 310 Academic Press San Diego 608–628
Acknowledgments
This article has been funded in part by the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency under assistance agreement R-815709 through the Great Plains/Rocky Mountain Hazardous Substance Research Center, headquartered at Kansas State University, the National Science Foundation, and MSE Technology Applications Inc., Butte, Montana. The Biofilm Systems Training Lab (BSTL) is acknowledged for loan of the rotating-disk reactors. We also thank Laura Jennings and Allison Rhoads for providing technical assistance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Komlos, J., Cunningham, A., Camper, A. et al. Interaction of Klebsiella oxytoca and Burkholderia cepacia in Dual-Species Batch Cultures and Biofilms as a Function of Growth Rate and Substrate Concentration. Microb Ecol 49, 114–125 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00248-003-1066-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00248-003-1066-z