Summary
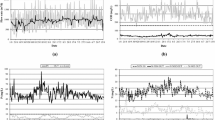
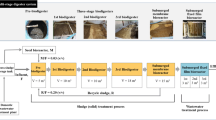
Laboratory scale activated sludge systems were operated under regimes of continuous or intermittent feeding of substrate. It was found that continuously fed systems repeatedly resulted in the development of filamentous bacteria and bulking of the sludge. Intermittently fed systems did form good settling sludges, without filamentous bacteria. The same results were found using different sludge loadings and different concentrations of mixed liquor suspended solids. High dissolved oxygen concentration did not prevent bulking in continuous systems while low dissolved oxygen concentration resulted in bulking with intermittently fed systems. It was found that the substrate removal rate of intermittently operated systems was always higher than for continuously fed systems. The hypothesis is formulated that intermittent feeding leads to higher substrate removal rates by floc forming bacteria and their predominance in intermittently fed systems, which can be compared to plug flow systems.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adamse AD (1968) Bulking of dairy waste activated sludge. Water Res 2:715–722
Benefield LD, Randall CW, King PH (1975) The stimulation of filamentous microorganisms in activated sludge by high oxygen concentrations. Water Air Soil Pollut 5: 113–123
Bhatla MN (1967) Relationship of activated sludge bulking to oxygen tension. J Water Pollut Control Fed 39:1978–1985
Chapman TD, Matsch LC, Zander EH (1976) Effect of high dissolved oxygen concentration in activated sludge systems J Water Pollut Control Fed 48:2486–2510
Chudoba J, Blaha J, Madera V (1974) Control of activated sludge filamentous bulking. III. Effect of sludge loading. Water Res 8:231–237
Chudoba J, Ottova V, Madera V (1973a) Control of activated sludge filamentous bulking. I. Effect of the hydraulic regime or degree of mixing in an aeration tank. Water Res 7:1163–1182
Chudoba J, Grau P, Ottova V (1973b) Control of activated sludge filamentous bulking. II. Selection of micro-organisms by means of a selector. Water Res 7:1389–1406
Dias FF, Dondero NC, Finstein MS (1968) Attached growth of Sphaerotilus and mixed populations in a continuous-flow apparatus. Appl Microbiol 16:1191–1199
Eikelboom DH (1975) Filamentous organisms observed in activated sludge. Water Res 9:365–388
Farquhar GJ, Boyle WC (1972) Control of Thiothrix in activated sludge. J Water Pollut Control Fed 44:14–24
Ford DL, Eckenfelder WW Jr (1967) Effect of process variables on sludge floc formation and settling characteristics. J Water Pollut Control Fed 39:1850–1859
Ganczarczyk J (1970) Variation in the activated sludge volume index. Water Res 4: 69–78
Genetelli EJ, Heukelekian H (1964) The influence of loading and chemical composition of substrate on the performance of activated sludge. J Water Pollut Control Fed 36:643–649
Heide BA, Pasveer A (1974) Oxidation ditch: Prevention and control of filamentous sludge. H2O 7:373–377
Jones PH (1964) Studies on the ecology of the filamentous sewage fungus, Geotricbum candidum. Thesis presented to Northwestern University at Evanston, Ill, in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the degree of Doctor of Philosophy
Merkel GJ (1975) Observations on the attachment of Thiothrix to biological surfaces in activated sludge. Water Res 9:881–885
Metcalf and Eddy Inc (1972) Wastewater engineering. McGraw-Hill, New York, 531–533
Mulder, EG (1964) Iron bacteria, particularly those of the Sphaerotilus-Leptothrix group and industrial problems. J Appl Bacteriol 27:151–173
Mulder EG, Antheunisse J, Crombach WHJ (1971) Microbial aspects of pollution in the food and dairy industries. In: Sykes G, Skinner FA (eds) Microbial aspects of pollution. Soc Appl Bacteriol Symp Series No 1. Academic Press, London, pp 71–89
Nelson N (1944) A photometric adaption of the Somogyi method for the determination of glucose J Biol Chem 153:375–380
Painter HA, Denton RS, Quarmby C (1968) Removal of sugars by activated sludge. Water Res 2:427–447
Parker RB (1967) Gravity flow system for continuous culture feed. Appl Microbiol 15: 197
Pasveer A (1969) An investigation on development and control of filamentous sludge (Dutch). H2O 2:28–34
Pipes WO (1967) Bulking of activated sludge. Adv Appl Microbiol 9:185–234
Rensink JH (1974) New approach to preventing bulking sludge. J Water Pollut Control Fed 46:1888–1894
Rensink JH, Jellema K, Ywema T (1977) The influence of the substrate gradient on the development of bulking sludge H2O 10:338–340
Sezgin M, Jenkins D, Parker DS (1978) A unified theory of filamentous activated sludge bulking. J Water Pollut Control Fed 50:362–381
Standard Methods (1971) 13th edn. APHA, AWWA & WPCF, New York
Stokes JL (1954) Studies on the filamentous sheathed iron bacterium Sphaerotilus natans. J Bacteriol 67:278–291
Gils HW Van (1964) Bacteriology of activated sludge. Thesis, Wageningen University
Voelkel KG, Martin DW, Deering RW (1974) Joint treatment of municipal and pulp mill effluents J Water Pollut Control Fed 46:634–656
Wood DK, Tchobanoglous G (1975) Trace elements in biological waste treatment. J. Water Pollut Control Fed 47:1933–1945
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Houtmeyers, J., van den Eynde, E., Poffé, R. et al. Relations between substrate feeding pattern and development of filamentous bacteria in activated sludge processes. European J. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 9, 63–77 (1980). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00500004
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00500004