Abstract
Neuroblastoma is an extremely heterogeneous tumor that commonly occurs in children. The diagnosis and treatment of this tumor pose considerable challenges due to its varied clinical presentations and intricate genetic aberrations. Presently, various imaging modalities, including computed tomography, magnetic resonance imaging, and positron emission tomography, are utilized to assess neuroblastoma. Nevertheless, these conventional imaging modalities have limitations in providing quantitative information for accurate diagnosis and prognosis. Radiomics, an emerging technique, can extract intricate medical imaging information that is imperceptible to the human eye and transform it into quantitative data. In conjunction with deep learning algorithms, radiomics holds great promise in complementing existing imaging modalities. The aim of this review is to showcase the potential of radiomics and deep learning advancements to enhance the diagnostic capabilities of current imaging modalities for neuroblastoma.
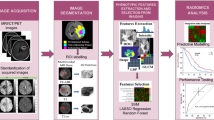
Graphical abstract




Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Not applicable.
References
Jiang M, Stanke J, Lahti JM (2011) The connections between neural crest development and neuroblastoma. Curr Top Dev Biol 94:77–127
Cao Y, Jin Y, Yu J et al (2017) Research progress of neuroblastoma related gene variations. Oncotarget 8:18444–18455
Tolbert VP, Matthay KK (2018) Neuroblastoma: clinical and biological approach to risk stratification and treatment. Cell Tissue Res 372:195–209
Smith V, Foster J (2018) High-risk neuroblastoma treatment review. Child (Basel) 5:114
Liu Z, Wang S, Dong D et al (2019) The applications of radiomics in precision diagnosis and treatment of oncology: opportunities and challenges. Theranostics 9:1303–1322
Zhang X, Zhang Y, Zhang G et al (2022) Deep learning with radiomics for disease diagnosis and treatment: challenges and potential. Front Oncol 12:773840
Sarker IH (2021) Deep learning: a comprehensive overview on techniques, taxonomy, applications and research directions. SN Comput Sci 2:420
Chu CM, Rasalkar DD, Hu YJ et al (2011) Clinical presentations and imaging findings of neuroblastoma beyond abdominal mass and a review of imaging algorithm. Br J Radiol 84:81–91
Shimada H, Umehara S, Monobe Y et al (2001) International neuroblastoma pathology classification for prognostic evaluation of patients with peripheral neuroblastic tumors: a report from the Children’s Cancer Group. Cancer 92:2451–2461
Shimada H, Ambros IM, Dehner LP et al (1999) Terminology and morphologic criteria of neuroblastic tumors: recommendations by the International Neuroblastoma Pathology Committee. Cancer 86:349–363
Shimada H, Ambros IM, Dehner LP et al (1999) The International Neuroblastoma Pathology Classification (the Shimada system). Cancer 86:364–372
Campbell K, Gastier-Foster JM, Mann M et al (2017) Association of MYCN copy number with clinical features, tumor biology, and outcomes in neuroblastoma: a report from the Children’s Oncology Group. Cancer 123:4224–4235
Zhang X, Sjöblom T (2021) Targeting loss of heterozygosity: a novel paradigm for cancer therapy. Pharmaceuticals (Basel) 14:57
Ambros PF, Ambros IM, Brodeur GM et al (2009) International consensus for neuroblastoma molecular diagnostics: report from the International Neuroblastoma Risk Group (INRG) Biology Committee. Br J Cancer 100:1471–1482
Tomioka N, Oba S, Ohira M et al (2008) Novel risk stratification of patients with neuroblastoma by genomic signature, which is independent of molecular signature. Oncogene 27:441–449
Irwin MS, Naranjo A, Zhang FF et al (2021) Revised neuroblastoma risk classification system: a report from the Children’s Oncology Group. J Clin Oncol 39:3229–3241
Burnand K, Barone G, McHugh K et al (2019) Preoperative computed tomography scanning for abdominal neuroblastomas is superior to magnetic resonance imaging for safe surgical planning. Pediatr Blood Cancer 66:e27955
Callahan MJ, MacDougall RD, Bixby SD et al (2018) Ionizing radiation from computed tomography versus anesthesia for magnetic resonance imaging in infants and children: patient safety considerations. Pediatr Radiol 48:21–30
Chen AM, Trout AT, Towbin AJ (2018) A review of neuroblastoma image-defined risk factors on magnetic resonance imaging. Pediatr Radiol 48:1337–1347
Sirignano M, Dillman JR, Weiss BD et al (2018) Change in liver, spleen and bone marrow magnetic resonance imaging signal intensity over time in children with solid abdominal tumors. Pediatr Radiol 48:325–332
Man S, Yan J, Li J et al (2021) Value of pretreatment 18F-FDG PET/CT in prognosis and the reflection of tumor burden: a study in pediatric patients with newly diagnosed neuroblastoma. Int J Med Sci 18:1857–1865
El-Maghraby T (2007) 131I-MIBG in the diagnosis of primary and metastatic neuroblastoma. Gulf J Oncolog:33–41
Seo ES, Shin M, Lim H et al (2022) Clinical implication of residual MIBG-positive disease in the follow-up of high-risk neuroblastoma treated with tandem high-dose chemotherapy and autologous stem cell transplantation. Pediatr Blood Cancer 69:e29502
Soffer S, Ben-Cohen A, Shimon O et al (2019) Convolutional neural networks for radiologic images: a radiologist’s guide. Radiology 290:590–606
Chen X, Wang H, Huang K et al (2021) CT-based radiomics signature with machine learning predicts MYCN amplification in pediatric abdominal neuroblastoma. Front Oncol 11:687884
Di Giannatale A, Di Paolo PL, Curione D et al (2021) Radiogenomics prediction for MYCN amplification in neuroblastoma: a hypothesis generating study. Pediatr Blood Cancer 68:e29110
Wang H, Chen X, Liu H et al (2021) Computed tomography-based radiomics for differential of retroperitoneal neuroblastoma and ganglioneuroblastoma in children. Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao 41:1569–1576
Wu H, Wu C, Zheng H et al (2021) Radiogenomics of neuroblastoma in pediatric patients: CT-based radiomics signature in predicting MYCN amplification. Eur Radiol 31:3080–3089
Feng L, Qian L, Yang S et al (2022) Prediction for mitosis-karyorrhexis index status of pediatric neuroblastoma via machine learning based 18F-FDG PET/CT radiomics. Diagnostics (Basel) 12:262
Feng L, Lu X, Yang X et al (2022) An 18F-FDG PET/CT radiomics nomogram for differentiation of high-risk and non-high-risk patients of the International Neuroblastoma Risk Group Staging System. Eur J Radiol 154:110444
Feng L, Yang X, Lu X et al (2022) 18F-FDG PET/CT-based radiomics nomogram could predict bone marrow involvement in pediatric neuroblastoma. Insights Imaging 13:144
Feng L, Qian L, Yang S et al (2022) Clinical parameters combined with radiomics features of PET/CT can predict recurrence in patients with high-risk pediatric neuroblastoma. BMC Med Imaging 22:102
Fiz F, Bottoni G, Bini F et al (2022) Prognostic value of texture analysis of the primary tumour in high-risk neuroblastoma: an 18F-DOPA PET study. Pediatr Blood Cancer 69:e29910
Liu G, Poon M, Zapala MA et al (2022) Incorporating radiomics into machine learning models to predict outcomes of neuroblastoma. J Digit Imaging 35:605–612
Qian L, Yang S, Zhang S et al (2022) Prediction of MYCN amplification, 1p and 11q aberrations in pediatric neuroblastoma via pre-therapy 18F-FDG PET/CT radiomics. Front Med (Lausanne) 9:840777
Tan E, Merchant K, Kn BP et al (2022) CT-based morphologic and radiomics features for the classification of MYCN gene amplification status in pediatric neuroblastoma. Childs Nerv Syst 38:1487–1495
Ghosh A, Yekeler E, Teixeira SR et al (2023) Role of MRI radiomics for the prediction of MYCN amplification in neuroblastomas. Eur Radiol 33:6726–6735
Feng L, Yang X, Lu X et al (2023) Diagnostic value of 18F-FDG PET/CT-based radiomics nomogram in bone marrow involvement of pediatric neuroblastoma. Acad Radiol 30:940–951
Feng L, Zhang S, Wang C et al (2023) Axial skeleton radiomics of 18F-FDG PET/CT: impact on event-free survival prediction in high-risk pediatric neuroblastoma. Acad Radiol. Epub ahead of print
Feng L, Zhang S, Lu X et al (2023) An optimal radiomics nomogram based on 18F-FDG PET/CT for identifying event-free survival in pediatric neuroblastoma. Acad Radiol 30:2309–2320
Qian LD, Feng LJ, Zhang SX et al (2023) 18F-FDG PET/CT imaging of pediatric peripheral neuroblastic tumor: a combined model to predict the International Neuroblastoma Pathology classification. Quant Imaging Med Surg 13:94–107
Wang H, Xie M, Chen X et al (2023) Development and validation of a CT-based radiomics signature for identifying high-risk neuroblastomas under the revised Children’s Oncology Group classification system. Pediatr Blood Cancer 70:e30280
Wang H, Chen X, Yu W et al (2023) Whole-tumor radiomics analysis of T2-weighted imaging in differentiating neuroblastoma from ganglioneuroblastoma/ganglioneuroma in children: an exploratory study. Abdom Radiol (NY) 48:1372–1382
Wang H, Xie M, Chen X et al (2023) Radiomics analysis of contrast-enhanced computed tomography in predicting the International Neuroblastoma Pathology classification in neuroblastoma. Insights Imaging 14:106
Wang H, Li T, Xie M et al (2023) Association of computed tomography radiomics signature with progression-free survival in neuroblastoma patients. Clin Oncol (R Coll Radiol) 35:e639–e647
Wang H, Qin J, Chen X et al (2023) Contrast-enhanced computed tomography radiomics in predicting primary site response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy in high-risk neuroblastoma. Abdom Radiol (NY) 48:976–986
Zhang Y, Yang Y, Ning G et al (2023) Contrast computed tomography-based radiomics is correlation with COG risk stratification of neuroblastoma. Abdom Radiol (NY) 48:2111–2121
Zhao L, Shi L, Huang SG et al (2023) Identification and validation of radiomic features from computed tomography for preoperative classification of neuroblastic tumors in children. BMC Pediatr 23:262
Ghosh A, Yekeler E, Dalal D et al (2022) Whole-tumour apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) histogram analysis to identify MYCN-amplification in neuroblastomas: preliminary results. Eur Radiol 32:8453–8462
Li C, Zhang J, Chen S et al (2018) Prognostic value of metabolic indices and bone marrow uptake pattern on preoperative 18F-FDG PET/CT in pediatric patients with neuroblastoma. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 45:306–315
Schmelz K, Toedling J, Huska M et al (2021) Spatial and temporal intratumour heterogeneity has potential consequences for single biopsy-based neuroblastoma treatment decisions. Nat Commun 12:6804
Yoo SY, Kim JS, Sung KW et al (2013) The degree of tumor volume reduction during the early phase of induction chemotherapy is an independent prognostic factor in patients with high-risk neuroblastoma. Cancer 119:656–664
Matthay KK, Maris JM, Schleiermacher G et al (2016) Neuroblastoma. Nat Rev Dis Primers 2:16078
Li C, Wang S, Li C et al (2022) Improved risk stratification by PET-based intratumor heterogeneity in children with high-risk neuroblastoma. Front Oncol 12:896593
Florkow MC, Guerreiro F, Zijlstra F et al (2020) Deep learning-enabled MRI-only photon and proton therapy treatment planning for paediatric abdominal tumours. Radiother Oncol 153:220–227
Guerreiro F, Seravalli E, Janssens GO et al (2021) Deep learning prediction of proton and photon dose distributions for paediatric abdominal tumours. Radiother Oncol 156:36–42
Mayampurath A, Ramesh S, Michael D et al (2021) Predicting response to chemotherapy in patients with newly diagnosed high-risk neuroblastoma: a report from the International Neuroblastoma Risk Group. JCO Clin Cancer Inform 5:1181–1188
Veiga-Canuto D, Cerdà-Alberich L, Sangüesa Nebot C et al (2022) Comparative multicentric evaluation of inter-observer variability in manual and automatic segmentation of neuroblastic tumors in magnetic resonance images. Cancers (Basel) 14:3648
Veiga-Canuto D, Cerdà-Alberich L, Jiménez-Pastor A et al (2023) Independent validation of a deep learning Nnu-Net Tool for neuroblastoma detection and segmentation in MR images. Cancers (Basel) 15:1622
Yeow LY, Teh YX, Lu X et al (2023) Prediction of MYCN gene amplification in pediatric neuroblastomas: development of a deep learning-based tool for automatic tumor segmentation and comparative analysis of computed tomography-based radiomics features harmonization. J Comput Assist Tomogr 47:786–795
Szmul A, Taylor S, Lim P et al (2023) Deep learning based synthetic CT from cone beam CT generation for abdominal paediatric radiotherapy. Phys Med Biol 68:105006
Hu F, Chen AA, Horng H et al (2023) Image harmonization: a review of statistical and deep learning methods for removing batch effects and evaluation metrics for effective harmonization. NeuroImage 274:120125
Tomaszewski MR, Gillies RJ (2021) The biological meaning of radiomic features. Radiology 298:505–516
Wang C, Lue W, Kaalia R et al (2022) Network-based integration of multi-omics data for clinical outcome prediction in neuroblastoma. Sci Rep 12:15425
Funding
This study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of Chongqing ((CSTB)2023NSCQ-BHX0127).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
X.C. and L.H. conceived, supervised, and supported the study. H.W. performed the literature search and drafted the initial manuscript. X.C. and L.H. reviewed and edited the draft of the manuscript. All authors reviewed and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Conflicts of interest
None
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, H., Chen, X. & He, L. A narrative review of radiomics and deep learning advances in neuroblastoma: updates and challenges. Pediatr Radiol 53, 2742–2755 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00247-023-05792-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00247-023-05792-6