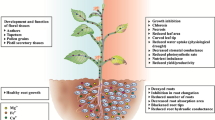
Abstract
It is a common practice in India to irrigate agricultural fields with wastewater originating from industries and domestic sources. At Jajmau (Kanpur), India, tannery effluent is used for irrigation purposes. This practice has been polluting the soil directly and groundwater and food crops indirectly. This study is aimed at evaluating the mutagenic impact of soil irrigated with tannery effluent. Soil extracts were prepared using four organic solvents (dichloromethane, methanol, acetonitrile, and acetone) and tested with Ames Salmonella/microsome test and DNA repair-defective E. coli k-12 mutants. Gas Chromatography-mass spectrometric analysis of soil samples revealed the presence of a large number of organic compounds including bis(2-ethylhexyl)phthalate, benzene, 1,3-hexadien-5-yne, 2,4-bis(1,1-dimethyl)phenol, Docosane, 10-methylnonadecane, and many higher alkanes. The soil extracts exhibited significant mutagenicity with Ames tester strains. TA98 was found to be the most sensitive strains to all the soil extracts, producing maximum response in terms of mutagenic index of 14.2 (–S9) and 13.6 (+S9) in the presence of dichloromethane extract. Dichloromethane-extracted soil exhibited a maximum mutagenic potential of 17.3 (–S9) and 20.0 (+S9) revertants/mg soil equivalent in TA100. Methanol, acetonitrile, and acetone extracts were also found to be mutagenic. A significant decline in the survival of DNA repair-defective E. coli K-12 mutants was observed compared to their isogenic wild-type counterparts when treated with different soil extracts. PolA mutant was found to be the most sensitive strain toward all four soil extracts.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aleem A, Malik A (2003) Genotoxic hazards of long term application of wastewater on agricultural soil. Mutat Res 538:145–154
Aleem A, Isar J, Malik A (2003) Impact of long term application of industrial wastewater on the emergence of resistance traits in Azotobacter chroococcum isolated from rhizospheric soil. Biores Technol 86:7–13. doi:10.1016/S0960-8524(02)00134-7
Ames BN (1971) The detection of chemical mutagens with enteric bacteria. In: Hollaender A (ed) Chemical mutagens, principles and methods for their detection, vol 1. Plenum Press, New York, pp 267–282
Ames BN, Lee FD, Durston WE (1973) An improved bacterial test system for the detection and classification of mutagens and carcinoges. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 70:782–786. doi:10.1073/pnas.70.3.782
Ames BN, McCann J, Yamasaki E (1975) Methods for detecting carcinogens and mutagens with the Salmonella/mammalian microsome mutagenicity test. Mutat Res 31:347–364
Ates E, Orhon D, Tunay O (1997) Characterization of tannery wastewater for pretreatment—selected case studies. Water Sci Tech 36:217–223. doi:10.1016/S0273-1223(97)00390-9
Bansal OP (1998) Heavy metal pollution of soils and plants due to sewage irrigation. Ind J Environ Health 40:51–52
Barnhart J (1997) Chromium chemistry and implications for environmental fate and toxicity. Soil Sediment Contam: An Int J 6:561–568
Battista G, Comba P, Orsi D, Norpoth K, Maier A (1995) Nasal cancer in leather workers: an occupational disease. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 121:1–6. doi:10.1007/BF01202722
Betowski LD, Kendall DS, Pace CM, Donnelly JR (1996) Characterization of groundwater samples from superfund sites by gas chromatography/mass spectrometry and liquid chromatography/mass spectrometry. Environ Sci Technol 30:3558–3564. doi:10.1021/es9602206
Cabrera GL, Rodriguez DM (1999) Genotoxicity of soil from farmland irrigated with wastewater using three plant bioassays. Mutat Res 426:211–214. doi:10.1016/S0027-5107(99)00070-6
Castillo M, Barcelo D, Pereira AS, Aquino Neto FR (1999) Characterization of organic pollutants in industrial effluents by high-temperature gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. Trends Anal Chem 18:26–36. doi:10.1016/S0165-9936(98)00066-1
Claxton LD, Douglas G, Krewski D, Lewtas J, Matsushita H, Rosenkranz H (1992) Overview, conclusions and recommendations of the IPCS collaborative study on complex mixtures. Mutat Res 276:61–80
Courty B, Curieux FL, Milon V, Marzin D (2004) Influence of extraction parameters on the mutagenicity of soil samples. Mutat Res 565:23–34
Czyz A, Szpilewska H, Dutkiewicz R, Kowalska W, Godlewska AB, Wegrzyn G (2002) Comparison of the Ames test and a newly developed assay for detection of mutagenic pollution of marine environments. Mutat Res 519:67–74
Dizer H, Wittekindt E, Fischer B, Hansen PD (2002) The cytotoxic and genotoxic potential of surface water and wastewater effluents as determined by bioluminescence, umu assay and selected biomarkers. Chemosphere 46:225–233. doi:10.1016/S0045-6535(01)00062-5
Edenharder R, Ortseifen M, Koch M, Wesp HF (2000) Soil mutagens are airborne mutagens: variation of mutagenic activities induced in Salmonella typhimurium TA 98 and TA 100 by organic extracts of agricultural and forest soils in dependence on location and season. Mutat Res 472:23–36
Fernandez de Henestrosa AR, Ogi T, Aoyagi S, Chafin D, Hayes JJ, Ohmori H, Woodgate R (2000) Identification of additional genes belonging to the LexA regulon in Escherichia coli. Mol Microbiol 35:1560–1572. doi:10.1046/j.1365-2958.2000.01826.x
Goggleman W, Spitzauer P (1982) Mutagenic activity in agricultural soils. In: Stich H (ed) Carcinogens and mutagens in the environment, vol 3. CRC Press, Orlando, pp 178–183
Grover IS, Kaur S (1999) Genotoxicity of wastewater samples from sewage and industrial effluent detected by the Allium cepa root anaphase aberration and micronucleus assays. Mutat Res 426:183–188. doi:10.1016/S0027-5107(99)00065-2
Hartnik T, Norli HR, Eggen T, Breedveld GD (2007) Bioassay-directed identification of toxic organic compounds in creosote-contaminated groundwater. Chemosphere 66:435–443. doi:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2006.06.031
Jochimsen JC, Jekel MR (1997) Partial oxidation effects during the combined oxidative and biological treatment of separated streams of tannery wastewater. Water Sci Technol 35:337–345. doi:10.1016/S0273-1223(97)00043-7
Klinkow N, Oleksy-Frenzel J, Jekel M (1998) Toxicity-directed fractionation of organic compounds in tannery wastewater with regard to their molecular weight and polarity. Water Res 32:2583–2592. doi:10.1016/S0043-1354(98)00017-7
Knize MG, Takemoto BT, Lewis PR, Felton JS (1987) The characterization of the mutagenic activity of soil. Mutat Res 192:23–30. doi:10.1016/0165-7992(87)90121-7
Kuzminov A (1999) Recombinational repair of DNA damage in Escherichia coli and bacteriophage lambda. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 63:751–813
Maron DM, Ames BN (1983) Revised methods for the Salmonella mutagenicity test. Mutat Res 113:173–215
Martin FL, Piearce TG, Hewer A, Phillips DH, Semple KT (2005) A biomarker model of sublethal genotoxicity (DNA single-strand breaks and adducts) using the sentinel organism Aporrectodea longa in spiked soil. Environ Pollut 138:307–315. doi:10.1016/j.envpol.2005.03.012
Matsumoto ST, Mantovani MS, Malaguttii MIA, Dias ALFonseca IC, Morales MAM (2006) Genotoxicity and mutagenicity of water contaminated with tannery effluents, as evaluated by the micronucleus test and comet assay using the fish Oreochromis niloticus and chromosome aberrations in onion root-tips. Gen Mol Biol 29:148–158. doi:10.1590/S1415-47572006000100028
McGeorge LJ, louis JB, Atherholt TB, McGarrit GJ (1983) Mutagenicity analysis of industrial effluents: background results to date. Report of New Jersey Department of Environmental Protection, Trenton
Meric S, DeNicola E, Iaccarino M, Gallo M, DiGennaro A, Morrone G, Warnau M, Belgiorno V, Pagano G (2005) Toxicity of leather tanning wastewater effluents in sea urchin early development and in marine microalgae. Chemosphere 61:208–217. doi:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2005.02.037
Mikoczy Z, Schutz A, Stromberg U, Hagmar L (1996) Cancer incidence and specific occupational exposures in the Swedish leather tanning industry: a cohort based casecontrol study. Occup Environ Med 53:463–467. doi:10.1136/oem.53.7.463
Monarca S, Feretti D, Zerbini I, Alberti A, Zani C, Resola S, Gellati U, Nardi G (2002) Soil contamination detected using bacterial and plant mutagenicity tests and chemical analysis. Environ Res (Sect A) 88:64–69. doi:10.1006/enrs.2001.4317
Mouchet F, Gauthier L, Mailhes C, Jourdain MJ, Ferrier V, Triffault G et al (2006) Biomonitoring of the genotoxic potential of aqueous extracts of soils and bottom ash resulting from municipal solid waste incineration using the comet and micronucleus tests on amphibian (Xenopus laevis) larave and bacterial assays (Mutatox and Ames tests). Sci Total Environ 355:232–246. doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2005.02.031
Nielsen PA (1992) Mutagenicity studies on complex environmental mixtures: selection of solvent system for extraction. Mutat Res 276:117–123
Pagano DA, Zeiger E (1992) Conditions for detecting the mutagenicity of divalent metals in Salmonella typhimurium. Environ Mol Mutagen 19:139–146. doi:10.1002/em.2850190208
Reemtsma T, Jekel M (1997) Dissolved organics in tannery wastewater and their alteration by a combined anaerobic and aerobic treatment. Water Res 31:1035–1046. doi:10.1016/S0043-1354(96)00382-X
Renzette N, Gumlaw N, Nordman JT, Krieger M, Yeh SP, Long E, Centore R, Boonsombat R, Sandler SJ (2005) Localization of recA in Escherichia coli K-12 using recA-GFP. Mol Microbiol 57:1074–1085. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2958.2005.04755.x
Sinha S, Gupta AK, Bhatt K, Pandey K, Rai UN, Singh KP (2006) Distribution of metals in the edible plants grown at Jajmau, Kanpur (India) receiving treated tannery Wastewater: relation with physico-chemical properties of the soil. Environ Monit Assess 115:1–22. doi:10.1007/s10661-006-5036-z
Smith JW (1982) Mutagenicity of extracts from agricultural soils in the Salmonella microsome test. Environ Mutagen 4:369–370
Stahl RG Jr (1991) The genetic toxicology of organic compounds in natural waters and wastewaters. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 22:94–125. doi:10.1016/0147-6513(91)90051-P
Strauss BS (1989) In vitro mutagenesis and DNA repair. Ann 1st Super Sanita 25:177–189
Sunahara GI, Dodard S, Sarrazin M, Paquet L, Ampleman G, Thiboutot S, Hawari J, Renoux AY (1998) Development of a soil extraction procedure for ecotoxicity characterization of energetic compounds. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 39:185–194. doi:10.1006/eesa.1997.1624
Tiler T, Zagorc-Koncan J, Cotman M, Drolc A (2004) Toxicity potential of disinfection agent in tannery wastewater. Water Res 38:3503–3510. doi:10.1016/j.watres.2004.05.011
Umbuzeiro GA, Roubicek DA, Sanchez PS, Sato MIZ (2001) The Salmonella mutagenicity assay in surface water quality monitoring program based on a 20-year survey. Mutat Res 491:119–126
Vargas VMF, Guidobono FR, Jordao RC, Henriques JAP (1995) Use of two short term test to evaluate the genotoxicity of river water treated with different concentration/extraction procedure. Mutat Res 343:31–52. doi:10.1016/0165-1218(95)90060-8
Walker GC (1985) Inducible DNA repair system. Annu Rev Biochem 54:425–457. doi:10.1146/annurev.bi.54.070185.002233
Watanabe T, Hirayama T (2001) Genotoxicity of soil. J Health Sci 47:433–438. doi:10.1248/jhs.47.433
Wesp HF, Tang X, Edenharder R (2000) The influence of automobile exhausts on mutagenicity of soils: contamination with, fractionation, separation, and preliminary identification of mutagens in the Salmonella/reversion assay and effects of solvent fractions on the sister-chromatid exchanges in human lymphocyte cultures and in the in vivo mouse bone marrow micronucleus assay. Mutat Res 472:1–21
Acknowledgments
Financial support from the Council of Scientific and Industrial Research (File No. 24(0271)/04/EMR-II), Government of India, is gratefully acknowledged. S.A.I.F. at the Indian Institute of Technology, Bombay, is also acknowledged for carrying out GC-MS analysis.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Alam, M.Z., Ahmad, S. & Malik, A. Genotoxic and Mutagenic Potential of Agricultural Soil Irrigated with Tannery Effluents at Jajmau (Kanpur), India. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 57, 463–476 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00244-009-9284-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00244-009-9284-0