Abstract
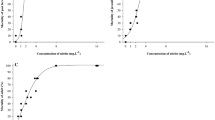
Lethal and sublethal effects of ammonia toxicity to juvenile barramundi (Lates calcarifer) were investigated under laboratory conditions following the OECD guidelines for testing of chemicals. Acute toxicity was tested in a static nonrenewal system at pH 9.0 and temperature around 29°C. The 24-, 48-, and 96-h LC50 values for barramundi were 3.89, 3.67, and 3.31 mg total ammonia N L−1 and 1.59, 1.47, and 1.3 mg nonionized ammonia N L−1, respectively. Estimated lethal concentrations indicated a relatively high sensitivity to acute ammonia toxicity for barramundi and equaled the 25th percentile most sensitive North American fish species with regard to the species mean acute value (USEPA 1999). A 3-week postexposure experiment on surviving individuals from the acute toxicity test, in clean water, indicated that exposure to acute concentrations up to 1.16 mg nonionized ammonia N L−1 did not have any significant effects on growth.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ali M, Nicieza A, Wotton RJ (2003) Compensatory growth in fishes: a response to growth depression. Fish and Fisheries 4:147–190
Allan GL, Maquire GB, Hopkins SJ (1990) Acute and chronic toxicity of ammonia to juvenile Metapenaeus macleayi and Penaeus monodon and the influence of low dissolved-oxygen levels. Aquaculture 9:265–280
Allen GR, Midgley SH, Allen M (2002) Freshwater fishes of Australia. CSIRO, Collingwood, VIC, Australia
ANZECC/ARMCANZ (2000) The Australian and New Zealand guidelines for fresh and marine water quality. Australian and New Zealand Environment and Conservation Council, Agriculture and Resource Management Council of Australia and New Zealand, Canberra, Australia
Bramley RGV, Johnson AKL (1995) Land use impacts on nutrient loading in the Herbert River. In: Hunter HM, Eyles AG, Rayment GE (eds) Downstream effects of land use. Department of Natural Resources, Brisbane, Australia, pp 93–96
Bramley RGV, Roth CH (2002) Land use effects of an intensively managed catchment in the Australian humid tropics. Mar Freshwater Res 53:931–940
Congdon RA, Lukacs GP (1995) Limnology and classification of tropical floodplain wetlands, with particular reference to the effects of irrigation drainage. Part 1: Temporal changes in water quality. Australian Centre for Tropical Freshwater Research and Department of Botany and Tropical Agriculture, James Cook University, Townsville, Rep No 95:12
Erickson RJ (1985) An evaluation of mathematical models for the effects of pH and temperature on ammonia toxicity to aquatic organisms. Water Res19:1047–1058
Emerson K, Russo R, Lund RE, Thurston RV (1975) Aqueous ammonia equilibrium calculations: effect of pH and temperature. J Fish Res Bd Can 32:2379–2383
Finney DJ (1978) Statistical method in biological assay, 3rd ed. Charles Griffen, London
Frances J, Nowak BF, Allan GL (2000) Effects of ammonia on juvenile silver perch Bidyanus bidyanus. Aquaculture 183:95–103
Guerney WS, Wayne J, Veitch AR, Nisbet RM (2003) Resource allocation, hyperphagia, and compensatory growth in juveniles. Ecology 84:2777–2787
Koppe W, Pokrandt J, Meyer-Burgdorff KH, Gunther KD (1993) Effects of realimentation after a period of restricted feeding on food intake, growth and body composition in Piaractus brachypomus (Cuvier 1818), a South American characoid species. In: Braunbeck T, Segner H (eds) Fish Ecotoxicol Ecophysiol, VCH, New York, pp 263–268
Mallet MJ, Sims I. (1994) Effects of ammonia on the early life stages of carp (Cyprinus carpio) and roach (Rutilus rutilus). In: Müller R, Lloyd R (eds) Sublethal and chronic effects of pollutants on freshwater fish. Fishing News Books, Blackwell Science, Oxford, pp 211–228
Meister R, Brink PJVD (2000) The analysis of laboratory experiments. In: Sparks T (ed) Statistics in ecotoxicology. John Wiley & Sons, West Sussex, UK, pp 99–118
Milne I, Seager J, Mallet M, Sims I (2000) Effects of short-term pulsed ammonia exposure on fish. Environ Toxicol Chem 19:2929–2936
OECD (1992) Guidelines for testing chemicals. No. 203. OECD, Paris
Pearson RG, Crossland M., Butler B, Manwaring S (2003) Effects of cane-field drainage on the ecology of tropical waterways James Cook University, Australian Centre for Tropical Freshwater Research, Townsville, Australia, Report No 3/04
Rand GM, Petrocelli SR (1985) Fundamentals of aquatic toxicology. Methods and applications. Hemisphere, New York
Raso S, Andersen A (2003) Effects of dietary fish oil replacement on growth and carcass proximate composition of juvenile barramundi (Lates calcarifer). Aquaculture 34:813–819
Richardson J (1997) Acute ammonia toxicity for eight New Zealand indigenous freshwater species. NZ J Mar Freshw Res 31:185–190
Solbè JF, De LG, Shurben DG (1989) Toxicity of ammonia to early life stages of rainbow trout Salmo gairdneri. Water Res 23:127–129
Smith CE, Piper RG (1975) Lesions associated with chronic exposure to ammonia. In: Ribelin WE, Migaki G (eds) The pathology of fishes. University of Wisconsin Press, Madison, pp 497–511
Thurston RV, Russo RC, Emerson K (1979) Aqueous ammonia equilibrium—tabulation of percent unionized ammonia (EPA 600/3-79-091). U.S. Environmental Protection Agency, Duluth, MN
Thurston RV, Russo RC (1983) Acute toxicity of ammonia to rainbow trout. Trans Am Fish Soc 112:696–704
Tian X, Qin JG (2003) A single phase of food deprivation provoked compensatory growth in barramundi Lates calcarifer. Aquaculture 224:169–179
USEPA (1985) Ambient water quality criteria for ammonia−1984. EPA 440-/5-85-001. U.S. Environmental Protection Agency, Office of Water Regulations and Standards Criteria and Standards Division, Washington, DC
USEPA (1993) Methods for measuring the acute toxicity of effluents and receiving waters to freshwater and marine organisms. EPA/600/4-90/027F. U.S. Environmental Protection Agency, Cincinnati, OH
USEPA (1999) Update of ambient water quality data criteria for ammonia. EPA-822-R-99-014. Office of Water,Office of Science and Technology, Washington, DC
Wajsbrot N, Gasith A, Krom MD, Popper DM (1991) Acute toxicity of ammonia to juvenile gilthead seabream Sparus aurata under reduced oxygen levels. Aquaculture 92:277–288
Zhu X, Cui Y, Ali M, Wotton RJ (2001) Comparison of compensatory growth responses of juvenile three-spined stickleback and minnow following similar food deprivation protocols. In: Ali M, Nicieza A, Wotton RJ (eds) Compensatory growth in fishes: a response to growth depression. Fish Fisheries 4:147–190
Acknowledgments
We thank Michael Crossland, Barry Butler, and Niall Connolly (James Cook University) for their advice regarding experimental design and data analysis and Russell Erickson (U.S. Environmental Protection Agency) for advice on the American ammonia criteria.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Økelsrud, A., Pearson, R.G. Acute and Postexposure Effects of Ammonia Toxicity on Juvenile Barramundi (Lates calcarifer [Bloch]). Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 53, 624–631 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00244-006-0215-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00244-006-0215-z