Abstract
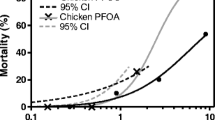
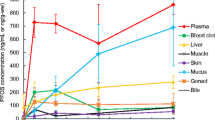
Ten-day-old mallards (Anas platyrhynchos) and northern bobwhite quail (Colinus virginianus) were fed perfluorooctanesulfonate (PFOS) in their diet for 5 days. The birds were then observed for 3 days while being given uncontaminated feed, and half of the birds were sacrificed on Day 8 of the trial. The remaining birds were maintained for an additional two weeks prior to being euthanized on Day 22 of the trial. Birds were assessed for growth, rate of feed consumption, behavior, physical injury, mortality, and gross abnormalities. Liver weight and concentrations of PFOS in blood serum and liver were also assessed. Based on the average daily intake (ADI) of PFOS calculated over the 5-day exposure period, the LD50 for juvenile mallards was determined to be 150 mg PFOS/kg body weight (bw)/day, equivalent to a total cumulative dose of 750 mg PFOS/kg bw calculated over a 5-day period. For juvenile quail, the LD50 based on the ADI was 61 mg PFOS/kg bw/day, equivalent to a total cumulative dose of 305 mg PFOS/kg bw. Reductions in weight gain and body weight were observed in quail from the 141 mg PFOS/kg treatment, but these measures returned to control levels by Day 22. The no-mortality dietary treatments were 70.3 and 141 mg PFOS/kg feed for quail and mallards, respectively. Both mallards and quail accumulated PFOS in blood serum and liver in a dose-dependent manner. The half-lives of PFOS in mallard blood serum and liver were estimated to be 6.86 and 17.5 days, respectively. In quail, the half-life of PFOS in liver was estimated to be 12.8 days, while the half-life of PFOS in quail blood serum could not be estimated. Concentrations of PFOS in juvenile mallard and quail liver associated with mortality are at least 50-fold greater than the single maximum PFOS concentration that has been measured in livers of avian wildlife.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Berthiaume J, Wallace KB (2002) Perfluorooctonate, perfluorooctane sulfonate, and N-ethyl perfluoroocatnesulfonamido ethanol, peroxisome proliferation and mitochondrial biogenesis. Toxicol Lett 129:23–32
Case MT, York RG, Christian MS (2001) Rat and rabbit oral developmental toxicology study with two perfluorinated compounds. Int J Toxicol 20:101–109
Christian MS, Hyberman AM, York RG (1999) Combined oral (gavage) fertility, developmental and perinatal/postnatal reproduction toxicity of PFOS in rats. Argus Res. Laboratory, Inc., Horsham, PA. Available at USEPA Docket 8EHQ-0200-00374
Davidson IWF, Parker JC, Beliles RP (1986) Biological basis for extrapolation across mammalian species. Reg Toxicol Pharmacol 6:211–237
Dean WP, Jessup DC, Thompson G, Romig G, Powell D (1978) Fluorad fluorochemical surfactant FC-95 acute oral (LD50) study in rats. Study No. 137-083, IRDC. Available at USEPA Docket 8EHQ-0200-00374
Gallagher SP, Casey CS, Beavers J.B, Van Hoven RL (2004a) PFOS: A dietary LC50 study with the mallard. Amended Report, Wildlife International Ltd., Project No. 454-102. Available at USEPA Docket AR-226-1735
Gallagher SP, Casey CS, Beavers JB, Van Hoven RL (2004b) PFOS: A dietary LC50 study with the Northern Bobwhite. Amended report, Wildlife International Ltd., Project No. 454-103. Available at USEPA Docket AR-226-1825
Giesy JP, Kannan K (2001) Global distribution of perfluorooctane sulfonate in wildlife. Environ Sci Technol 35:1339–1342
Giesy JP, Kannan K (2002) Perfluorochemical surfactants in the environment. Environ Sci Technol 36:146A–152A
Goldenthal EI, Jessup DC, Geil RG, Jefferson ND, Areco RJ, Ruecker FA (1978a) 90-day subacute rat study. Study No. 137-085, International Research and Development Corp., Mattawan, MI. Available at USEPA Docket AR-226-0139
Goldenthal EI, Jessup DC, Geil RG, Mehring JS (1978b) Ninety-day subacute Rhesus monkey toxicity study. Study No. 137-085, International Research and Development Corp., Mattawan, MI. Available at USEPA Docket AR-226-0137
Gulley DD (1990) TOXSTAT Release 3.2. The University of Wyoming
Hansen KJ, Clemen LA, Ellefsen ME, Johnson HO (2001) Compound-specific, quantitative characterization of organic fluorochemicals in biological matrices. Environ Sci Technol 35:766–770
Hu W, Jones PD, Upham BC, Trosko JE, Lau C, Giesy JP (2002) Inhibition of gap junctional intercellular communication by perfluorinated compounds in rat liver and dolphin kidney epithelial cell lines in vitro and Sprague-Dawley rats in vivo. Toxicol Sci 68:429–436
Inoue K, Okada F, Ito R, Kato S, Sasaki S, Nakajima S, Uno A, Saijo Y, Sato F, Yoshimura Y, Kishi R, Nakazawa H (2004) Perfluorooctane sulfonate (PFOS) and related perfluorinated compounds in human maternal and cord blood samples: assessment of PFOS exposure in a susceptible population during pregnancy. Environ Health Perspect 112:1204–1207
Johnson JD, Gibson SJ, Ober RE (1984). Cholestramine-enhanced fecal elimination of carbon-14 in rats after administration of ammonium [14C]perfluorooctanoate or potassium [14C] perfluorooctane sulfonate. Fund Appl Toxicol 4:972–976
Jones PD, Hu W, DeCoen W, Newsted J, Giesy JP (2003) Binding of perfluorinated fatty acids to serum protein. Environ Toxicol Chem 22:2639–2649
Kannan K, Franson JC, Bowerman WW, Hansen KJ, Jones PD, Giesy JP (2001) Perfluorooctane sulfonate in fish eating water birds including bald eagles and albatrosses. Environ Sci Technol 35:3065–3070
Kannan K, Choi J, Iseki N, Senthilkumar K, Kim DH, Masunaga S, Giesy JP (2002a) Concentrations of perfluorinated acids in livers of birds from Japan and Korea. Chemosphere 49:225–231
Kannan K, Corsolini S, Falandysz J, Oehme G, Focardi S, Giesy JP (2002b) Perfluorooctane sulfonate and related fluorinated hydrocarbons in marine mammals, fishes, and birds from Coasts of the Baltic and the Mediterranean Seas. Environ Sci Technol 36:3210–3216
Kannan K, Corsolini S, Falandysz J, Fillmann G, Kumar KS, Loganathan BG (2004) Perfluorooctane sulfonate and related fluorochemicals in human blood from several countries. Environ Sci Technol 38:4489–4495
Kissa E (2001). Fluorinated surfactants and repellents, 2nd ed. Marcel Dekker, New York
Lau C, Thibodeaux JR, Hanson RG, Rogers JM, Grey BE, Stanton ME, Butenhoff JL, Stevenson LA (2003) Exposure to perfluorooctane sulfonate during pregnancy in rat and mouse. II. Postnatal evaluation. Toxicol Sci 74:382–392
Lau C, Butenhoff JL, Rogers JM (2004) The developmental toxicity of perfluoroalkyl acids and their derivatives. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 15:231–241
Luebker DJ, Hansen KJ, Bass NM, Butenhoff JL, Seacat AM (2002) Interactions of fluorochemicals with rat liver fatty acid-binding protein. Toxicol 176:175–185
Martin JW, Smithwick MM, Braune BM, Hoekstra PE, Muir DCG, Mabury SA (2004) Identification of long-chain perfluorinated acids in biota from the Canadian Arctic. Environ Sci Technol 38:373–380
Mineau P, Collins BT, Baril A (1996) On the use of scaling factors to improve interspecies extrapolation of acute toxicity in birds. Reg Toxicol Pharmacol 24:24–29
National Research Council (1996) Guide for care and use of laboratory animals. Washington DC. National Academy Press, 125 p
Newsted JL, Coady KC, Beach SA, Butenhoff JL, Gallagher S, Geisy JP (2005) Effects of perfluorooctanesulfonate on mallard (Anas platyrhynchos) and Northern bobwhite quail (Colinus virginianus) when chronically exposed via the diet. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol (in press)
Noker PE, Gorman GS (2003) A pharmacokinetic study of potassium perfluorooctane sulfonate in the cynomolgus monkey. Southern Research Institute, Research Triangle Park, NC, Unpublished report. Available on USEPA Docket AR-226-1228
Olsen GW, Hansen KJ, Stevenson LA, Burris JM, Mandel JH (2003) Human donor liver and serum concentrations of perfluorooctane sulfonate and other perfluorochemicals. Environ Sci Technol 37:888–891
Olsen GW, Church TR, Larson EB, van Belle G, Lundberg JK, Hansen KJ, Burris JM, Mandel JH, Zobel LR (2004) Serum concentrations of perfluorooctane sulfonate and other fluorochemicals in an elderly population from Seattle, Washington. Chemosphere 54:1599–15611
SAS Institute (1999) SAS/STAT User’s Guide, Release 8.02 Edition, SAS Institute, Cary, NC
Seacat AM, Thomford PJ, Hansen KJ, Olsen GW, Case MT, Butenhoff JL (2002) Subchronic toxicity studies on perfluorooctanesulfonate potassium salt in cynomolgus monkeys. Toxicol Sci 68:249–264
Seacat AM, Thomford PJ, Hansen KJ, Clemen LA, Eldridge SR, Elcombe CR, Butenhoff JL (2003) Sub-chronic dietary toxicity of potassium perfluorooctane sulfonate in rats. Toxicol 183:117–131
Shipley JM, Hurst CH, Tanaka SS, DeRoos FL, Butenhoff JL, Seacat AM, Waxman DJ (2004) Trans-activation of PPARα and induction of PPARα target genes by perfluorooctane-based chemicals. Toxicol Sci 80:151–160
Sohlenius AK, Andersson K, DePierre JW (1993) Perfluorooctane sulfonic acid is a potent inducer of peroxisomal fatty acid B-oxidation and other activities known to be affected by peroxisome proliferators in mouse liver. Pharmacol Toxicol 72:90–93
Starkov AA, Wallace KB (2002) Structural determinants of fluorochemical-induced mitochondrial dysfunction. Toxicol Sci 66:244–252
Thibodeaux JR, Hanson RG, Rogers JM, Grey BE, Barbee BD, Richards JH, Butenhoff JL, Stevenson LA, Lau C (2003) Exposure to perfluorooctancesulfonate during pregnancy in rat and mouse. I: maternal and prenatal evaluations. Reprod Dev Toxicol 74:369–381
3M (2003) Environmental and health assessment of perfluorooctane sulfonate and its salts. Available on USEPA Docket AR-226-1486
Wagner JG (1979) Fundamentals of clinical pharmacokinetics. Drug Intelligence Publications Inc, Hamilton, IL, 461 p
Acknowledgments
The authors thank 3M for financial support for this project. They also thank John Butenhoff and others for their insightful comments and helpful advice on this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Newsted, J.L., Beach, S.A., Gallagher, S.P. et al. Pharmacokinetics and Acute Lethality of Perfluorooctanesulfonate (PFOS) to Juvenile Mallard and Northern Bobwhite. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 50, 411–420 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00244-005-1137-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00244-005-1137-x