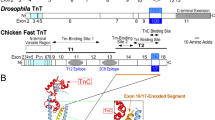
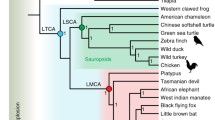
Abstract
Troponin-based Ca2+ regulation of striated muscle contraction emerged approximately 700 million years ago with largely conserved functions during evolution. Troponin I (TnI) is the inhibitory subunit of troponin and has evolved into three muscle type-specific isoforms in vertebrates. Cardiac TnI is specifically expressed in the adult heart and has a unique N-terminal extension implicating a specific value during natural selection. The N-terminal extension of cardiac TnI in higher vertebrates contains β-adrenergic-regulated protein kinase A (PKA) phosphorylation sites as a mechanism to enhance cardiac muscle relaxation and facilitate ventricular filling. Phylogenic studies showed that the N-terminal extension of cardiac TnI first emerged in the genomes of early tetrapods as well as primordial lobe-finned fishes such as the coelacanth whereas it is absent in ray-finned fish. This apparently rapid evolution of β-adrenergic regulation of cardiac function suggests a high selection value for the heart of vertebrate animals on land to work under higher metabolic demands. Sequencing and PKA phosphorylation data showed that lungfish cardiac TnI has evolved with an amphibian-like N-terminal extension with prototype PKA phosphorylation sites while its overall structure remained fish like. The data demonstrate that the submolecular structure of TnI may evolve ahead of the whole protein for cardiac muscle contractility to adapt to new environmental conditions. Understanding the evolution of the β-adrenergic regulation of TnI and cardiac adaptation to the increased energetic demands of life on land adds knowledge for the treatment of human heart diseases and failure.








Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
All data required to evaluate the conclusions of the paper are presented within the paper or supplementary materials, and all genome sequences are publicly available on NCBI GenBank. Any additional data may be requested from the authors.
References
Aho E, Vornanen M (2001) Cold acclimation increases basal heart rate but decreases its thermal tolerance in rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). J Comp Physiol 171(2):173–179. https://doi.org/10.1007/s003600000171
Akhter S, Zhang Z, Jin J-P (2012) The Heart-Specific NH2-terminal extension regulates the molecular conformation and function of cardiac troponin I. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpheart.00637.2011
Ausoni S, Campione M, Picard A, Moretti P, Vitadello M, De Nardi C, Schiaffino S (1994) Structure and regulation of the mouse cardiac troponin I gene. J Biol Chem 269(1):339–346
Baba ML, Goodman M, Berger-Cohn J, Demaille JG, Matsudag G (1984) The early adaptive evolution of calmodulin. Mol Biol Evol 1(6):442–455. https://doi.org/10.1093/oxfordjournals.molbev.a040330
Barbato JC, Huang QQ, Hossain MM, Bond M, Jin JP (2005) Proteolytic N-terminal truncation of cardiac troponin I enhances ventricular diastolic function. J Biol Chem 280(8):6602–6609. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M408525200
Barnes DE, Hwang H, Ono K, Lu H, Ono S (2016) Molecular evolution of troponin I and a role of its N-terminal extension in nematode locomotion. Cytoskeleton 73(3):117–130. https://doi.org/10.1002/cm.21281
Biesiadecki BJ, Tachampa K, Yuan C, Jin J-P, De Tombe PP, Solaro RJ (2010) Removal of the cardiac troponin I N-terminal extension improves cardiac function in aged mice. J Biol Chem 285(25):19688–19698. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M109.086892
Brunet T, Fischer AHL, Steinmetz PRH, Lauri A, Bertucci P, Arendt D (2016) The evolutionary origin of bilaterian smooth and striated myocytes. Elife 5:1–24. https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.19607
Burggren WW, Bautista GM, Coop SC, Couturier GM, Delgadillo SP, García RM, Alvarez González CA (2016) Developmental cardiorespiratory physiology of the air-breathing tropical gar, Atractosteus tropicus. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 311(4):R689–R701. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpregu.00022.2016
Cao T, Thongam U, Jin J-P (2019) Invertebrate troponin: Insights into the evolution and regulation of striated muscle contraction. Arch Biochem Biophys 666:40–45. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.abb.2019.03.013
Chong SM, Jin J-P (2009) To Investigate Protein Evolution by Detecting Suppressed Epitope Structures. J Mol Evol 68(5):448–460. https://doi.org/10.1038/jid.2014.371
Ecker PM, Lin CC, Powers J, Kobilka BK, Dubin AM, Bernstein D (2006) Effect of targeted deletions of β1- and β2-adrenergic-receptor subtypes on heart rate variability. Am J Physiol Hear Circ 290(1):192–199. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpheart.00032.2005
Edgar RC (2004) MUSCLE: multiple sequence alignment with high accuracy and high throughput. Nucleic Acids Res 32(5):1792–1797. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkh340
Fabbri E, Capuzzo A, Moon TW (1998) The role of circulating catecholamines in the regulation of fish metabolism: an overview. Comp Biochem Physiol C Toxicol Pharmacol 120(2):177–192. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0742-8413(98)10017-8
Farrell AP (1985) A protective effect of adrenalin on the acidotic teleost heart. J Exp Biol 116:503–508
Feng H-Z, Chen M, Weinstein LS, Jin J-P (2008) Removal of the N-terminal extension of cardiac troponin i as a functional compensation for impaired myocardial β-adrenergic signaling. J Biol Chem 283(48):33384–33393. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M803302200
Feng HZ, Hossain MM, Huang XP, Jin JP (2009) Myofilament incorporation determines the stoichiometry of troponin I in transgenic expression and the rescue of a null mutation. Arch Biochem Biophys 487(1):36–41. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.abb.2009.05.001
Feng H-Z, Chen X, Hossain MM, Jin J-P (2012) Toad heart utilizes exclusively slow skeletal muscle troponin T: an evolutionary adaptation with potential functional benefits. J Biol Chem 287(35):29753–29764. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M112.373191
Feng H-Z, Jin J-P (2020) High efficiency preparation of skinned mouse cardiac muscle strips from cryosections for contractility studies. Exp Physiol 105(11):1869–1881. https://doi.org/10.1113/EP088521
Forey PL (1988) Golden jubilee for the coelacanth Latimeria chalumnae. Nature 336:727–732. https://doi.org/10.1038/336727a0
George D, Blieck A (2011) Rise of the earliest tetrapods: an early Devonian origin from marine environment. PLoS ONE 6(7):1–7. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0022136
Gillis TE, Klaiman JM (2011) The influence of PKA treatment on the Ca2+ activation of force generation by trout cardiac muscle. J Exp Biol 214(12):1989–1996. https://doi.org/10.1242/jeb.052084
Gordon AM, Homsher E, Regnier M (2000) Regulation of contraction in striated muscle. Physiol Rev 80(2):853–924. https://doi.org/10.1152/physrev.2000.80.2.853
Gross SM, Lehman SL (2016) Functional phosphorylation sites in cardiac myofilament proteins are evolutionarily conserved in skeletal myofilament proteins. Physiol Gen 48(6):377–387. https://doi.org/10.1152/physiolgenomics.00112.2015
Gunther LK, Feng H-Z, Wei H, Raupp J, Jin J-P, Sakamoto T (2016) Effect of N-terminal extension of cardiac troponin I on the Ca2+ regulation of ATP binding and ADP dissociation of Myosin II in native cardiac Myofibrils. Biochemistry 55(12):1887–1897. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.biochem.5b01059
Hanson LM, Obradovich S, Mouniargi J, Farrell AP (2006) The role of adrenergic stimulation in maintaining maximum cardiac performance in rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) during hypoxia, hyperkalemia and acidosis at 10°C. J Exp Biol 209(13):2442–2451. https://doi.org/10.1242/jeb.02237
Hastings KEM, Koppe RI, Marmor E, Bader D, Shimada Y, Toyota N (1991) Structure and developmental expression of troponin I isoforms: cDNA clone analysis of avian cardiac troponin I mRNA. J Biol Chem 266(29):19659–19665
Huang QQ, Jin J-P (1999) Preserved close linkage between the genes encoding troponin I and troponin T, reflecting an evolution of adapter proteins coupling the Ca2+ signaling of contractility. J Mol Evol 49(6):780–788. https://doi.org/10.1007/PL00006600
Jin J-P (1996) Alternative RNA splicing-generated cardiac troponin T isoform switching: a non-heart-restricted genetic programming synchronized in developing cardiac and skeletal muscles. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 225(3):883–889. https://doi.org/10.1006/bbrc.1996.1267
Jin JP, Yang FW, Yu ZB, Ruse CI, Bond M, Chen A (2001) The highly conserved COOH terminus of troponin I forms a Ca2+-modulated allosteric domain in the troponin complex. Biochemistry 40(8):2623–2631. https://doi.org/10.1021/bi002423j
Jin JP, Zhang Z, Bautista JA (2008) Isoform diversity, regulation, and functional adaptation of troponin and calponin. Crit Rev Eukaryot Gene Expr 18(2):93–124. https://doi.org/10.1615/critreveukargeneexpr.v18.i2.10
Katrukha IA (2013) Human cardiac troponin complex: structure and functions. Biochemistry 78(13):1447–1465. https://doi.org/10.1134/S0006297913130063
Kawasaki T, Saito K, Deguchi T, Fujimori K, Tadokoro M, Yuba S, Ohgushi H, Kawarabayasi Y (2008) Pharmacological characterization of isoproterenol-treated medaka fish. Pharmacol Res 58(5–6):348–355. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phrs.2008.09.011
Kentish JC, McCloskey DT, Layland J, Palmer S, Leiden JM, Martin AF, Solaro RJ (2001) Phosphorylation of troponin i by protein kinase A accelerates relaxation and crossbridge cycle kinetics in mouse ventricular muscle. Circ Res 88(10):1059–1065. https://doi.org/10.1161/hh1001.091640
Kirkpatrick KP, Robertson AS, Klaiman JM, Gillis TE (2011) The influence of trout cardiac troponin I and PKA phosphorylation on the Ca2+ affinity of the cardiac troponin complex. J Exp Biol 214(12):1981–1988. https://doi.org/10.1242/jeb.052860
Kranias EG, Solaro RJ (1982) Phosphorylation of troponin I and phospholamban during catecholamine stimulation of rabbit heart. Nature 298:182–184. https://doi.org/10.1038/298182a0
Martin AF (1981) Turnover of cardiac troponin subunits. Kinetic evidence for a precursor pool of troponin-I. J Biol Chem 256(2):964–968
McConnell BK, Popovic Z, Mal N, Lee K, Bautista J, Forudi F, Schwartzman R, Jin JP, Penn M, Bond M (2009) Disruption of protein kinase A interaction with A-kinase-anchoring proteins in the heart in vivo: effects on cardiac contractility, protein kinase A phosphorylation, and troponin I proteolysis. J Biol Chem 284(3):1583–1592. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M806321200
Mendonça PC, Gamperl AK (2009) Nervous and humoral control of cardiac performance in the winter flounder (Pleuronectes americanus). J Exp Biol 212(7):934–944. https://doi.org/10.1242/jeb.027680
Meyer A, Schloissnig S, Franchini P, Du K, Woltering JM, Irisarri I, Wong WY, Nowoshilow S, Kneitz S, Kawaguchi A, Fabrizius A, Xiong P, Dechaud C, Spaink HP, Volff JN, Simakov O, Burmester T, Tanaka EM, Schartl M (2021) Giant lungfish genome elucidates the conquest of land by vertebrates. Nature 590(7845):284–289. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-021-03198-8
Ogut O, Jin J-P (1998) Developmentally regulated, alternative RNA splicing-generated pectoral muscle-specific troponin T isoforms and role of the NH2-terminal hypervariable region in the tolerance to acidosis. J Biol Chem 273:27858–27866
OOta S, Saitou N, (1999) Phylogenetic relationship of muscle tissues deduced from superimposition of gene trees. Mol Biol Evol 16(6):856–867. https://doi.org/10.1093/oxfordjournals.molbev.a026170
Rao VS, Korte FS, Razumova MV, Feest ER, Hsu H, Irving TC, Regnier M, Martyn DA (2013) N-terminal phosphorylation of cardiac troponin-I reduces length-dependent calcium sensitivity of contraction in cardiac muscle. J Physiol 591(2):475–490. https://doi.org/10.1113/jphysiol.2012.241604
Reid SG, Bernier NJ, Perry SF (1998) The adrenergic stress response in fish: control of catecholamine storage and release. Comp Biochem Physiol C Toxicol Pharmacol 120(1):1–27. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0742-8413(98)00037-1
Shaffer JF, Gillis TE (2010) Evolution of the regulatory control of vertebrate striated muscle: the roles of troponin I and myosin binding protein-C. Physiol Gen 42(3):406–419. https://doi.org/10.1152/physiolgenomics.00055.2010
Sheikh F, Lyon RC, Chen J (2015) Functions of myosin light chain-2 (MYL2) in cardiac muscle and disease. Gene 569:14–20
Sheng J-J, Jin J-P (2014) Gene regulation, alternative splicing, and posttranslational modification of troponin subunits in cardiac development and adaptation: a focused review. Front Physiol 5(165):1–16. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphys.2014.00165
Sheng JJ, Jin JP (2016) TNNI1, TNNI2 and TNNI3: evolution, regulation, and protein structure-function relationships. Gene 576(1 Pt 3):385–394. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gene.2015.10.052
Solaro RJ, Moir AJG, Perry SV (1976) Phosphorylation of troponin I and the inotropic effect of adrenaline in the perfused rabbit heart. Nature 262:615–617. https://doi.org/10.1038/262615a0
Steele SL, Yang X, Debiais-Thibaud M, Schwerte T, Pelster B, Ekker M, Tiberi M, Perry SF (2011) In vivo and in vitro assessment of cardiac-adrenergic receptors in larval zebrafish (Danio rerio). J Exp Biol 214(9):1445–1457. https://doi.org/10.1242/jeb.052803
Steinmetz PRH, Kraus JEM, Larroux C, Hammel JU, Amon-Hassenzahl A, Houliston E, Wörheide G, Nickel M, Degnan BM, Technau U (2012) Independent evolution of striated muscles in cnidarians and bilaterians. Nature 487:231–234. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature11180
Wang Z, Nishimura Y, Shimada Y, Umemoto N, Hirano M, Zang L, Oka T, Sakamoto C, Kuroyanagi J, Tanaka T (2009) Zebrafish β-adrenergic receptor mRNA expression and control of pigmentation. Gene 446(1):18–27. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gene.2009.06.005
Wang K, Wang J, Zhu C, Yang L, Ren Y, Ruan J, Fan G, Hu J, Xu W, Bi X et al (2021) African lungfish genome sheds light on the vertebrate water-to-land transition. Cell 184(5):1362-1376.e18. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2021.01.047
Warkman AS, Atkinson BG (2004) Amphibian cardiac troponin I gene’s organization, developmental expression, and regulatory properties are different from its mammalian homologue. Dev Dyn 229(2):275–288. https://doi.org/10.1002/dvdy.10434
Wei B, Wei H, Jin JP (2015) Dysferlin deficiency blunts β-adrenergic-dependent lusitropic function of mouse heart. J Physiol 593:5127–5144
Wilkinson JM, Grand RJA (1978) Comparison of amino acid sequence of troponin I from different striated muscles. Nature 271:31–35. https://doi.org/10.1038/271031a0
Yaguchi S, Yaguchi J, Tanaka H (2017) Troponin-I is present as an essential component of muscles in echinoderm larvae. Sci Rep 7:1–8. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep43563
Yu ZB, Zhang LF, Jin JP (2001) A proteolytic NH2-terminal truncation of cardiac troponin I that is up-regulated in simulated microgravity. J Biol Chem 276(19):15753–15760. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M011048200
Zhang XH, Chiang VL (1996) Single-stranded DNA ligation by T4 RNA ligase for PCR cloning of 5’-noncoding fragments and coding sequence of a specific gene. Nucleic Acids Res 24(5):990–991. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/24.5.990
Zhang R, Zhao JJ, Potter JD (1995) Phosphorylation of both serine residues in cardiac troponin I is required to decrease the Ca2+ affinity of cardiac troponin C. J Biol Chem 270(51):30773–30780. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.270.51.30773
Zhu M, Yu X (2002) A primitive fish close to the common ancestor of tetrapods and lungfish. Nature 418:767–770. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature00871
Acknowledgements
We thank Dr. Irene Salinas and Dr. Ottavia Benedicenti for providing lungfish hearts.
Funding
This research was supported by grants from the National Institutes of Health, HL127691, JianPing Jin, HL138007, JianPing Jin
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
MR: performed experiments, analyzed data, drafted, and edited manuscript, approved final version for submission; HZF: performed experiments, analyzed data, drafted manuscript, approved final version for submission; JPJ: conceived the research project, drafted and edited manuscript, approved final version for submission.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Communicated by Belinda Chang.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rasmussen, M., Feng, HZ. & Jin, JP. Evolution of the N-Terminal Regulation of Cardiac Troponin I for Heart Function of Tetrapods: Lungfish Presents an Example of the Emergence of Novel Submolecular Structure to Lead the Capacity of Adaptation. J Mol Evol 90, 30–43 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00239-021-10039-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00239-021-10039-9