Abstract
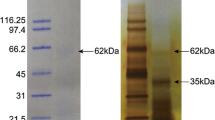
Aspein is one of the unusually acidic shell matrix proteins originally identified from the pearl oyster Pinctada fucata. Aspein is thought to play important roles in the shell formation, especially in calcite precipitation in the prismatic layer. In this study, we identified Aspein homologs from three closely related pterioid species: Pinctada maxima, Isognomon perna, and Pteria penguin. Our immunoassays showed that they are present in the calcitic prismatic layer but not in the aragonitic nacreous layer of the shells. Sequence comparison showed that the Ser-Glu-Pro and the Asp-Ala repeat motifs are conserved among these Aspein homologs, indicating that they are functionally important. All Aspein homologs examined share the Asp-rich D-domain, suggesting that this domain might have a very important function in calcium carbonate formation. However, sequence analyses showed a significantly high level of variation in the arrangement of Asp in the D-domain even among very closely related species. This observation suggests that specific arrangements of Asp are not required for the functions of the D-domain.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Albeck S, Aizenberg J, Addadi L, Weiner S (1993) Interactions of various skeletal intracrystalline components with calcite crystals. J Am Chem Soc 115:11691–11697
Berner RA (1975) The role of magnesium in the crystal growth of calcite and aragonite from sea water. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 39:489–504
Davis K, Dove P, Yoreo J (2000) The role of Mg2+ as an impurity in calcite growth. Science 290:1134–1137
Gotliv B, Kessler N, Sumerel JL, Morse DE, Tuross N, Addadi L, Weiner S (2005) Asprich: a novel aspartic acid-rich protein family from the prismatic shell matrix of the bibalve Atrina rigida. ChemBioChem 6:304–314
Jackson DJ, McDougall C, Woodcroft B, Moase P, Rose RA, Kube M, Reinhardt R, Rokhsar DS, Montagnani C, Joubert C, Piquemal D, Degnan BM (2010) Parallel evolution of nacre building gene sets in molluscs. Mol Biol Evol 27:591–608
Joubert C, Piquemal D, Marie B, Manchon L, Pierrat F, Zanella-Cléon I, Cochennec-Laureau N, Gueguen Y, Montagnani C (2010) Transcriptome and proteome analysis of Pinctada margaritifera calcifying mantle and shell: focus on biomineralization. BMC Genomics 11:613
Kitano Y (1962) The behavior of various inorganic ions in the separation of calcium carbonate from a bicarbonate solution. Bull Chem Soc 35:1973–1980
Marin F, Amous R, Guichard N, Stigter M, Hecher A, Luquet G, Westbroek P (2005) Caspartin and Calprismin, two proteins of the shell calcitic prisms of the Mediterranean fan mussel Pinna nobilis. J Biol Chem 275:20667–20675
McKnight DA, Fisher LW (2009) Molecular evolution of dentin phosphoprotein among toothed and toothless animals. BMC Evol Biol 9:299
McKnight DA, Suzanne HP, Hart TC, Hartsfield JK, Wilson A, Wright JT, Fisher LW (2008) A comprehensive analysis of normal variation and disease-causing mutations in the human DSPP gene. Hum Mutat 29:1392–1404
Miyazaki Y, Nishida T, Aoki H, Samata T (2010) Expression of genes responsible for biomineralization of Pinctada fucata during development. Comp Biochem Physiol B 155:241–248
Samata T, Ikeda D, Kazikawa A, Sato H, Nogawa C, Yamada D, Yamazaki R, Akiyama T (2008) A novel phosphorylated glycoprotein in the shell matrix of the oyster Crassostrea nippona. FEBS J 275:2977–2989
Sarashina I, Endo K (1998) Primary structure of a soluble matrix protein scallop shell implications for calcium carbonate biomineralization. Am Miner 83:1501–1515
Sarashina I, Endo K (2001) The complete primary structure of molluscan shell protein 1 (MSP-1), an acidic glycoprotein in the shell matrix of the scallop Patinopecten yessoensis. Mar Biotechnol 3:362–369
Song JA, Oh DY, Moon JS, Geum D, Kwon HB, Seong JY (2006) Involvement of the ser-glu-pro motif in ligand species-dependent desensitisation of the rat gonadotrophin-releasing hormone receptor. J Neuroendocrinol 10:757–766
Takeuchi T, Endo K (2006) Biphasic and dually coordinated expression of the genes encoding major shell matrix proteins in the pearl oyster Pinctada fucata. Mar Biotechnol 8:52–61
Takeuchi T, Sarashina I, Iijima M, Endo K (2008) In vitro regulation of CaCO3 crystal polymorphism by the highly acidic molluscan shell protein Aspein. FEBS Lett 582:591–596
Tëmkin I (2010) Molecular phylogeny of pearl oysters and their relatives (Mollusca, Bivalvia, Pterioidea). BMC Evol Biol 10:342
Tsukamoto D, Sarashina I, Endo K (2004) Structure and expression of an unusually acidic matrix protein of pearl oyster shells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 320:1175–1180
Wada K, Fujinuki T (1976) Biomineralization in bivalve molluscs with emphasis on the chemical composition of the extrapallial fluid. In: Watabe N, Wilbur KM (eds) Mechanisms of mineralization in the invertebrates and plants. University of South Carolina Press, Columbia, pp 175–190
Wang C, Yun O, Maiti K, Oh DY, Kim KK, Chae CH, Lee CJ, Seong JY, Kwon HB (2004) Position of Pro and Ser near Glu7.32 in the extracellular loop 3 of mammalian and nonmammalian gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) receptors is a critical determinant for differential ligand selectivity for mammalian GnRH and chicken GnRH-II. Mol Endocrinol 18:105–116
Weiner S (1979) Aspartic acid-rich proteins: major components of the soluble organic matrix of mollusk shells. Calcif Tissue Int 29:163–167
Weiner S, Hood L (1975) Soluble protein of the organic matrix of mollusk shells: a potential template for shell formation. Science 190:987–989
Acknowledgments
We thank Takenori Sasaki (The University Museum, The University of Tokyo) for identifying the specimens of I. perna. We also thank Tasaki and Co., Ltd. for providing P. fucata and P. penguin samples.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Isowa, Y., Sarashina, I., Setiamarga, D.H.E. et al. A Comparative Study of the Shell Matrix Protein Aspein in Pterioid Bivalves. J Mol Evol 75, 11–18 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00239-012-9514-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00239-012-9514-3