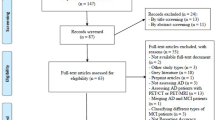
Abstract
Purpose
Advanced machine learning (ML) algorithms can assist rapid medical image recognition and realize automatic, efficient, noninvasive, and convenient diagnosis. We aim to further evaluate the diagnostic performance of ML to distinguish patients with probable Alzheimer’s disease (AD) from normal older adults based on structural magnetic resonance imaging (MRI).
Methods
The Medline, Embase, and Cochrane Library databases were searched for relevant literature published up until July 2021. We used the Quality Assessment of Diagnostic Accuracy Studies-2 (QUADAS-2) tool and Checklist for Artificial Intelligence in Medical Imaging (CLAIM) to evaluate all included studies’ quality and potential bias. Random-effects models were used to calculate pooled sensitivity and specificity, and the Deeks’ test was used to assess publication bias.
Results
We included 24 models based on different brain features extracted by ML algorithms in 19 papers. The pooled sensitivity, specificity, positive likelihood ratio, negative likelihood ratio, diagnostic odds ratio, and area under the summary receiver operating characteristic curve for ML in detecting AD were 0.85 (95%CI 0.81–0.89), 0.88 (95%CI 0.84–0.91), 7.15 (95%CI 5.40–9.47), 0.17 (95%CI 0.12–0.22), 43.34 (95%CI 26.89–69.84), and 0.93 (95%CI 0.91–0.95).
Conclusion
ML using structural MRI data performed well in diagnosing probable AD patients and normal elderly. However, more high-quality, large-scale prospective studies are needed to further enhance the reliability and generalizability of ML for clinical applications before it can be introduced into clinical practice.




Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
Data is available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
Ballard C, Gauthier S, Corbett A, Brayne C, Aarsland D, Jones E (2011) Alzheimer’s disease. Lancet 377(9770):1019–1031. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0140-6736(10)61349-9
(2021) 2021 Alzheimer's disease facts and figures. Alzheimers Dement 17(3): 327–406. https://doi.org/10.1002/alz.12328
World failing to address dementia challenge. https://www.who.int/news/item/02-09-2021-world-failing-to-address-dementia-challenge. Accessed 9 Sept 2021
WHO’s Global Health Estimates. https://www.who.int/data/gho/data/themes/mortality-and-global-health-estimates. Accessed 9 Sept 2021
(2016) The need for early detection and treatment in Alzheimer's disease. EBioMedicine 9: 1–2. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ebiom.2016.07.001
Bobinski M, de Leon MJ, Wegiel J, Desanti S, Convit A, Saint Louis LA et al (2000) The histological validation of post mortem magnetic resonance imaging-determined hippocampal volume in Alzheimer’s disease. Neuroscience 95(3):721–725. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0306-4522(99)00476-5
Whitwell JL, Dickson DW, Murray ME, Weigand SD, Tosakulwong N, Senjem ML et al (2012) Neuroimaging correlates of pathologically defined subtypes of Alzheimer’s disease: a case-control study. Lancet Neurol 11(10):868–877. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1474-4422(12)70200-4
Downs M, Turner S, Bryans M, Wilcock J, Keady J, Levin E et al (2006) Effectiveness of educational interventions in improving detection and management of dementia in primary care: cluster randomised controlled study. BMJ 332(7543):692–696. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.332.7543.692
Pellegrini E, Ballerini L, Hernandez M, Chappell FM, González-Castro V, Anblagan D et al (2018) Machine learning of neuroimaging for assisted diagnosis of cognitive impairment and dementia: a systematic review. Alzheimers Dement (Amst) 10:519–535. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dadm.2018.07.004
Yuan Y, Gu ZX, Wei WS (2009) Fluorodeoxyglucose-positron-emission tomography, single-photon emission tomography, and structural MR imaging for prediction of rapid conversion to Alzheimer disease in patients with mild cognitive impairment: a meta-analysis. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 30(2):404–410. https://doi.org/10.3174/ajnr.A1357
Liberati A, Altman DG, Tetzlaff J, Mulrow C, Gøtzsche PC, Ioannidis JP et al (2009) The PRISMA statement for reporting systematic reviews and meta-analyses of studies that evaluate health care interventions: explanation and elaboration. Ann Intern Med 151(4):W65-94. https://doi.org/10.7326/0003-4819-151-4-200908180-00136
Bossuyt PM, Reitsma JB, Bruns DE, Gatsonis CA, Glasziou PP, Irwig L et al (2015) STARD 2015: an updated list of essential items for reporting diagnostic accuracy studies. BMJ 351:h5527. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.h5527
Whiting PF, Rutjes AW, Westwood ME, Mallett S, Deeks JJ, Reitsma JB et al (2011) QUADAS-2: a revised tool for the quality assessment of diagnostic accuracy studies. Ann Intern Med 155(8):529–536. https://doi.org/10.7326/0003-4819-155-8-201110180-00009
Mongan J, Moy L, Kahn CE Jr (2020) Checklist for Artificial Intelligence in Medical Imaging (CLAIM): a guide for authors and reviewers. Radiol Artif Intell 2(2):e200029. https://doi.org/10.1148/ryai.2020200029
Alabed S, Maiter A, Salehi M, Mahmood A, Daniel S, Jenkins S et al (2022) Quality of reporting in AI cardiac MRI segmentation studies - a systematic review and recommendations for future studies. Front Cardiovasc Med 9:956811. https://doi.org/10.3389/fcvm.2022.956811
Deeks JJ, Macaskill P, Irwig L (2005) The performance of tests of publication bias and other sample size effects in systematic reviews of diagnostic test accuracy was assessed. J Clin Epidemiol 58(9):882–893. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclinepi.2005.01.016
Zamora J, Abraira V, Muriel A, Khan K, Coomarasamy A (2006) Meta-DiSc: a software for meta-analysis of test accuracy data. BMC Med Res Methodol 6:31. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2288-6-31
Vemuri P, Gunter JL, Senjem ML, Whitwell JL, Kantarci K, Knopman DS et al (2008) Alzheimer’s disease diagnosis in individual subjects using structural MR images: validation studies. Neuroimage 39(3):1186–1197. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2007.09.073
Gerardin E, Chételat G, Chupin M, Cuingnet R, Desgranges B, Kim HS et al (2009) Multidimensional classification of hippocampal shape features discriminates Alzheimer’s disease and mild cognitive impairment from normal aging. Neuroimage 47(4):1476–1486. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2009.05.036
Magnin B, Mesrob L, Kinkingnéhun S, Pélégrini-Issac M, Colliot O, Sarazin M et al (2009) Support vector machine-based classification of Alzheimer’s disease from whole-brain anatomical MRI. Neuroradiology 51(2):73–83. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00234-008-0463-x
Oliveira PP Jr, Nitrini R, Busatto G, Buchpiguel C, Sato JR, Amaro E Jr (2010) Use of SVM methods with surface-based cortical and volumetric subcortical measurements to detect Alzheimer’s disease. J Alzheimers Dis 19(4):1263–1272. https://doi.org/10.3233/jad-2010-1322
Plant C, Teipel SJ, Oswald A, Böhm C, Meindl T, Mourao-Miranda J et al (2010) Automated detection of brain atrophy patterns based on MRI for the prediction of Alzheimer’s disease. Neuroimage 50(1):162–174. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2009.11.046
Diciotti S, Ginestroni A, Bessi V, Giannelli M, Tessa C, Bracco L et al (2012) Identification of mild Alzheimer’s disease through automated classification of structural MRI features. Annu Int Conf IEEE Eng Med Biol Soc 2012:428–431. https://doi.org/10.1109/embc.2012.6345959
Polat F, Demirel SO, Kitis O, Simsek F, Haznedaroglu DI, Coburn K et al (2012) Computer based classification of MR scans in first time applicant Alzheimer patients. Curr Alzheimer Res 9(7):789–794. https://doi.org/10.2174/156720512802455359
Aguilar C, Westman E, Muehlboeck JS, Mecocci P, Vellas B, Tsolaki M et al (2013) Different multivariate techniques for automated classification of MRI data in Alzheimer’s disease and mild cognitive impairment. Psychiatry Res 212(2):89–98. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pscychresns.2012.11.005
Vandenberghe R, Nelissen N, Salmon E, Ivanoiu A, Hasselbalch S, Andersen A et al (2013) Binary classification of 18F-flutemetamol PET using machine learning: comparison with visual reads and structural MRI. Neuroimage 64:517–525. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2012.09.015
Zhou Q, Goryawala M, Cabrerizo M, Barker W, Duara R, Adjouadi M (2014) Significance of normalization on anatomical MRI measures in predicting Alzheimer's disease. Sci World J 2014. https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/541802
Rondina JM, Ferreira LK, de Souza Duran FL, Kubo R, Ono CR, Leite CC et al (2018) Selecting the most relevant brain regions to discriminate Alzheimer’s disease patients from healthy controls using multiple kernel learning: a comparison across functional and structural imaging modalities and atlases. Neuroimage Clin 17:628–641. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nicl.2017.10.026
Lazli L, Boukadoum M, Ait Mohamed O (2019) Computer-aided diagnosis system of Alzheimer's disease based on multimodal fusion: tissue quantification based on the hybrid fuzzy-genetic-possibilistic model and discriminative classification based on the SVDD model. Brain Sci 9(10). https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci9100289
Aderghal K, Afdel K, Benois-Pineau J, Catheline G (2020) Improving Alzheimer’s stage categorization with convolutional neural network using transfer learning and different magnetic resonance imaging modalities. Heliyon 6(12):e05652. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2020.e05652
Jin D, Zhou B, Han Y, Ren J, Han T, Liu B et al (2020) Generalizable, reproducible, and neuroscientifically interpretable imaging biomarkers for Alzheimer’s disease. Adv Sci (Weinh) 7(14):2000675. https://doi.org/10.1002/advs.202000675
Lorenzi RM, Palesi F, Castellazzi G, Vitali P, Anzalone N, Bernini S et al (2020) Unsuspected involvement of spinal cord in Alzheimer disease. Front Cell Neurosci 14. https://doi.org/10.3389/fncel.2020.00006
Pan Y, Liu M, Lian C, Xia Y, Shen D (2020) Spatially-constrained fisher representation for brain disease identification with incomplete multi-modal neuroimages. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 39(9):2965–2975. https://doi.org/10.1109/TMI.2020.2983085
Qiu S, Joshi PS, Miller MI, Xue C, Zhou X, Karjadi C et al (2020) Development and validation of an interpretable deep learning framework for Alzheimer’s disease classification. Brain 143(6):1920–1933. https://doi.org/10.1093/brain/awaa137
Toshkhujaev S, Lee KH, Choi KY, Lee JJ, Kwon GR, Gupta Y et al (2020) Classification of Alzheimer’s disease and mild cognitive impairment based on cortical and subcortical features from MRI T1 brain images utilizing four different types of datasets. J Healthc Eng 2020:3743171. https://doi.org/10.1155/2020/3743171
Yee E, Ma D, Popuri K, Wang L, Beg MF (2021) Construction of MRI-based Alzheimer’s disease score based on efficient 3D convolutional neural network: comprehensive validation on 7,902 images from a multi-center dataset. J Alzheimers Dis 79(1):47–58. https://doi.org/10.3233/jad-200830
McKhann G, Drachman D, Folstein M, Katzman R, Price D, Stadlan EM (1984) Clinical diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease: report of the NINCDS-ADRDA Work Group under the auspices of Department of Health and Human Services Task Force on Alzheimer’s Disease. Neurology 34(7):939–944. https://doi.org/10.1212/wnl.34.7.939
Park HY, Park CR, Suh CH, Shim WH, Kim SJ (2021) Diagnostic performance of the medial temporal lobe atrophy scale in patients with Alzheimer’s disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur Radiol 31(12):9060–9072. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-021-08227-8
Mo JA, Lim JH, Sul AR, Lee M, Youn YC, Kim HJ (2015) Cerebrospinal fluid β-amyloid1-42 levels in the differential diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease–systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS One 10(2):e0116802. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0116802
Mitchell AJ (2009) A meta-analysis of the accuracy of the mini-mental state examination in the detection of dementia and mild cognitive impairment. J Psychiatr Res 43(4):411–431. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpsychires.2008.04.014
Bloudek LM, Spackman DE, Blankenburg M, Sullivan SD (2011) Review and meta-analysis of biomarkers and diagnostic imaging in Alzheimer’s disease. J Alzheimers Dis 26(4):627–645. https://doi.org/10.3233/jad-2011-110458
Cuocolo R, Cipullo MB, Stanzione A, Romeo V, Green R, Cantoni V et al (2020) Machine learning for the identification of clinically significant prostate cancer on MRI: a meta-analysis. Eur Radiol 30(12):6877–6887. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-020-07027-w
van Kempen EJ, Post M, Mannil M, Kusters B, Ter Laan M, Meijer FJA et al (2021) Accuracy of machine learning algorithms for the classification of molecular features of gliomas on MRI: a systematic literature review and meta-analysis. Cancers (Basel) 13(11). https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13112606
Fleuren LM, Klausch TLT, Zwager CL, Schoonmade LJ, Guo T, Roggeveen LF et al (2020) Machine learning for the prediction of sepsis: a systematic review and meta-analysis of diagnostic test accuracy. Intensive Care Med 46(3):383–400. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00134-019-05872-y
Cho SJ, Sunwoo L, Baik SH, Bae YJ, Choi BS, Kim JH (2021) Brain metastasis detection using machine learning: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Neuro Oncol 23(2):214–225. https://doi.org/10.1093/neuonc/noaa232
Schwarz CG (2021) Uses of human MR and PET imaging in research of neurodegenerative brain diseases. Neurotherapeutics. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13311-021-01030-9
Atri A (2019) The Alzheimer’s disease clinical spectrum: diagnosis and management. Med Clin North Am 103(2):263–293. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mcna.2018.10.009
McKhann GM, Knopman DS, Chertkow H, Hyman BT, Jack CR Jr, Kawas CH et al (2011) The diagnosis of dementia due to Alzheimer’s disease: recommendations from the National Institute on Aging-Alzheimer’s Association workgroups on diagnostic guidelines for Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimers Dement 7(3):263–269. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jalz.2011.03.005
Pichot P (1986) [DSM-III: the 3d edition of the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders from the American Psychiatric Association]. Rev Neurol (Paris) 142(5):489–499
Knopman DS, DeKosky ST, Cummings JL, Chui H, Corey-Bloom J, Relkin N et al (2001) Practice parameter: diagnosis of dementia (an evidence-based review). Report of the Quality Standards Subcommittee of the American Academy of Neurology. Neurology 56(9):1143–1153. https://doi.org/10.1212/wnl.56.9.1143
Gauthier S, Leuzy A, Racine E, Rosa-Neto P (2013) Diagnosis and management of Alzheimer’s disease: past, present and future ethical issues. Prog Neurobiol 110:102–113. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pneurobio.2013.01.003
Cerullo E, Quinn TJ, McCleery J, Vounzoulaki E, Cooper NJ, Sutton AJ (2021) Interrater agreement in dementia diagnosis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Int J Geriatr Psychiatry 36(8):1127–1147. https://doi.org/10.1002/gps.5499
Jack CR Jr, Petersen RC, O’Brien PC, Tangalos EG (1992) MR-based hippocampal volumetry in the diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease. Neurology 42(1):183–188. https://doi.org/10.1212/wnl.42.1.183
Killiany RJ, Moss MB, Albert MS, Sandor T, Tieman J, Jolesz F (1993) Temporal lobe regions on magnetic resonance imaging identify patients with early Alzheimer’s disease. Arch Neurol 50(9):949–954. https://doi.org/10.1001/archneur.1993.00540090052010
Chetelat G, Baron JC (2003) Early diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease: contribution of structural neuroimaging. Neuroimage 18(2):525–541. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1053-8119(02)00026-5
Jack CR Jr (2011) Alliance for aging research AD biomarkers work group: structural MRI. Neurobiol Aging 32 Suppl 1(0 1):S48-57. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2011.09.011
Pini L, Pievani M, Bocchetta M, Altomare D, Bosco P, Cavedo E et al (2016) Brain atrophy in Alzheimer’s disease and aging. Ageing Res Rev 30:25–48. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arr.2016.01.002
Grimm O, Pohlack S, Cacciaglia R, Winkelmann T, Plichta MM, Demirakca T et al (2015) Amygdalar and hippocampal volume: a comparison between manual segmentation, Freesurfer and VBM. J Neurosci Methods 253:254–261. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jneumeth.2015.05.024
Mulder ER, de Jong RA, Knol DL, van Schijndel RA, Cover KS, Visser PJ et al (2014) Hippocampal volume change measurement: quantitative assessment of the reproducibility of expert manual outlining and the automated methods FreeSurfer and FIRST. Neuroimage 92:169–181. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2014.01.058
Wenger E, Mårtensson J, Noack H, Bodammer NC, Kühn S, Schaefer S et al (2014) Comparing manual and automatic segmentation of hippocampal volumes: reliability and validity issues in younger and older brains. Hum Brain Mapp 35(8):4236–4248. https://doi.org/10.1002/hbm.22473
Kim DW, Jang HY, Kim KW, Shin Y, Park SH (2019) Design characteristics of studies reporting the performance of artificial intelligence algorithms for diagnostic analysis of medical images: results from recently published papers. Korean J Radiol 20(3):405–410. https://doi.org/10.3348/kjr.2019.0025
Bizopoulos P, Koutsouris D (2019) Deep learning in cardiology. IEEE Rev Biomed Eng 12:168–193. https://doi.org/10.1109/rbme.2018.2885714
Liu X, Faes L, Kale AU, Wagner SK, Fu DJ, Bruynseels A et al (2019) A comparison of deep learning performance against health-care professionals in detecting diseases from medical imaging: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Digit Health 1(6):e271–e297. https://doi.org/10.1016/s2589-7500(19)30123-2
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Jiayi Hu: conception and design, data analysis and interpretation, drafting and revision of the manuscript. Yashan Wang: data analysis and interpretation, drafting and revision of the manuscript. Dingjie Guo: conception and design, data analysis and interpretation. Zihan Qu: data analysis and interpretation. Chuanying Sui: data analysis and interpretation. Guangliang He: contributed to the discussion. Song Wang: contributed to the discussion. Xiaofei Chen: contributed to the discussion. Chunpeng Wang: data analysis and interpretation, revised the manuscript. Xin Liu: conception and design, revised the manuscript, approval of the final version of the manuscript. All the authors have read and approved the publication of this manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
We declare that we have no conflict of interest.
Research involving human participants and/or animals
None.
Informed consent
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Hu, J., Wang, Y., Guo, D. et al. Diagnostic performance of magnetic resonance imaging–based machine learning in Alzheimer’s disease detection: a meta-analysis. Neuroradiology 65, 513–527 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00234-022-03098-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00234-022-03098-2