Abstract
Purpose
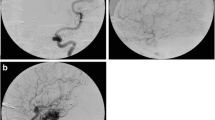
Embolization of arteriovenous malformations (AVMs) before radiosurgery has been reported to negatively impact the obliteration rate. This study aims to assess treatment outcomes in a series of 190 patients treated by Gamma Knife radiosurgery (GKRS) for previously embolized AVMs.
Methods
The institutional database of AVMs was retrospectively reviewed between January 2004 and March 2018. The clinical and radiological data of patients treated with GKRS for previously embolized AVMs were analyzed. Predicting factors of obliteration and hemorrhage following GKRS were assessed with univariate and multivariate regression analyses.
Results
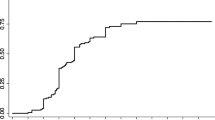
The mean AVM size was significantly reduced after embolization (p < 0.001). The obliteration rate was 78.4%. Multivariate analyses showed that a lower Spetzler-Martin grade (p = 0.035) and a higher marginal dose (p = 0.007) were associated with obliteration. Post-GKRS hemorrhages occurred in 14 patients (7.4%). A longer time between diagnosis and GKRS was the only factor associated with post-GKRS hemorrhages in multivariate analysis (p = 0.022). Complications related to the combined treatment were responsible for a new permanent neurological disability in 20 patients (10.5%), and a case of death (0.5%).
Conclusions
This study shows that the embolization of AVMs does not have a negative impact on the obliteration rate after radiosurgery. Embolization reduces the AVM size to a treatable volume by GKRS. However, the combined treatment results in an increased complication rate related to the addition of the risks of each treatment modality.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chen CJ, Ding D, Derdeyn CP et al (2020) Brain arteriovenous malformations: a review of natural history, pathobiology, and interventions. Neurology 95:917–927
Starke RM, Kano H, Ding D et al (2017) Stereotactic radiosurgery for cerebral arteriovenous malformations: evaluation of long-term outcomes in a multicenter cohort. J Neurosurg 126:36–44. https://doi.org/10.3171/2015.9.JNS151311
Pollock BE, Flickinger JC, Lunsford LD et al (1998) Factors associated with successful arteriovenous malformation radiosurgery. Neurosurgery 42:1239–1244. https://doi.org/10.1097/00006123-199806000-00020
Zaki Ghali MG, Kan P, Britz GW (2019) Curative embolization of arteriovenous malformations. World Neurosurg 129:467–486. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wneu.2019.01.166
Blackburn SL, Ashley WW, Rich KM et al (2011) Combined endovascular embolization and stereotactic radiosurgery in the treatment of large arteriovenous malformations: clinical article. J Neurosurg 114:1758–1767. https://doi.org/10.3171/2011.1.JNS10571
Kano H, Kondziolka D, Flickinger JC et al (2012) Aneurysms increase the risk of rebleeding after stereotactic radiosurgery for hemorrhagic arteriovenous malformations. Stroke 43:2586–2591. https://doi.org/10.1161/STROKEAHA.112.664045
Vollherbst DF, Chapot R, Bendszus M, Möhlenbruch MA (2022) Glue, onyx, squid or PHIL? Liquid embolic agents for the embolization of cerebral arteriovenous malformations and dural arteriovenous fistulas. Clin Neuroradiol 32:25–38. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00062-021-01066-6
Taylor CL, Dutton K, Rappard G et al (2004) Complications of preoperative embolization of cerebral arteriovenous malformations. J Neurosurg 100:810–812. https://doi.org/10.3171/jns.2004.100.5.0810
van Beijnum J, van der Worp HB, Buis DR et al (2011) Treatment of brain arteriovenous malformations: a systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA 306:2011–2019. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.2011.1632
Panagiotopoulos V, Gizewski E, Asgari S et al (2009) Embolization of intracranial arteriovenous malformations with ethylene-vinyl alcohol copolymer (Onyx). Am J Neuroradiol 30:99–106. https://doi.org/10.3174/ajnr.A1314
Huo X, Jiang Y, Lv X et al (2016) Gamma Knife surgical treatment for partially embolized cerebral arteriovenous malformations. J Neurosurg 124:767–776. https://doi.org/10.3171/2015.1.JNS142711
Xu F, Zhong J, Ray A et al (2014) Stereotactic radiosurgery with and without embolization for intracranial arteriovenous malformations: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Neurosurg Focus 37:E16. https://doi.org/10.3171/2014.6.FOCUS14178
Chen C-J, Ding D, Lee C-C et al (2021) Stereotactic radiosurgery with versus without embolization for brain arteriovenous malformations. Neurosurgery 88:313–321. https://doi.org/10.1093/neuros/nyaa418
Kashanian A, Sparks H, Kaprealian T, Pouratian N (2019) Assessing the volume of large cerebral arteriovenous malformations: can the ABC/2 formula reliably predict true volume? J Clin Neurosci 65:1–5. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jocn.2019.04.038
Pollock BE, Link MJ, Stafford SL et al (2016) Stereotactic radiosurgery for arteriovenous malformations: the effect of treatment period on patient outcomes. Neurosurgery 78:499–509. https://doi.org/10.1227/NEU.0000000000001085
Starke RM, Yen C-P, Ding D, Sheehan JP (2013) A practical grading scale for predicting outcome after radiosurgery for arteriovenous malformations: analysis of 1012 treated patients. J Neurosurg 119:981–987. https://doi.org/10.3171/2013.5.JNS1311
Yamamoto M, Kawabe T, Barfod BE (2013) Long-term side effects of radiosurgery for arteriovenous malformations. In: Niranjan A, Kano H, Lunsford LD (eds) Progress in Neurological Surgery. S. Karger AG, pp 97–106
Kano H, Kondziolka D, Flickinger JC et al (2012) Stereotactic radiosurgery for arteriovenous malformations after embolization: a case-control study. J Neurosurg 117:265–275. https://doi.org/10.3171/2012.4.JNS111935
Russell D, Peck T, Ding D et al (2018) Stereotactic radiosurgery alone or combined with embolization for brain arteriovenous malformations: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Neurosurg 128:1338–1348. https://doi.org/10.3171/2016.11.JNS162382
Buell TJ, Ding D, Starke RM et al (2014) Embolization-induced angiogenesis in cerebral arteriovenous malformations. J Clin Neurosci Off J Neurosurg Soc Australas 21:1866–1871. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jocn.2014.04.010
Natarajan SK, Ghodke B, Britz GW et al (2008) Multimodality treatment of brain arteriovenous malformations with microsurgery after embolization with onyx: single-center experience and technical nuances. Neurosurgery 62:1213–1226. https://doi.org/10.1227/01.neu.0000333293.74986.e5
Rao VR, Mandalam KR, Gupta AK et al (1989) Dissolution of isobutyl 2-cyanoacrylate on long-term follow-up. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 10:135–141
Andrade-Souza YM, Ramani M, Beachey DJ et al (2008) Liquid embolisation material reduces the delivered radiation dose: a physical experiment. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 150:161–164. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00701-007-1482-9 (discussion 164)
Kwon Y, Jeon SR, Kim JH et al (2000) Analysis of the causes of treatment failure in gamma knife radiosurgery for intracranial arteriovenous malformations. J Neurosurg 93(Suppl 3):104–106. https://doi.org/10.3171/jns.2000.93.supplement
Bing F, Doucet R, Lacroix F et al (2012) Liquid embolization material reduces the delivered radiation dose: clinical myth or reality? AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 33:320–322. https://doi.org/10.3174/ajnr.A2943
Chen C-J, Ding D, Lee C-C et al (2021) Embolization of brain arteriovenous malformations with versus without onyx before stereotactic radiosurgery. Neurosurgery 88:366–374. https://doi.org/10.1093/neuros/nyaa370
Oermann EK, Ding D, Yen C-P et al (2015) Effect of prior embolization on cerebral arteriovenous malformation radiosurgery outcomes: a case-control study. Neurosurgery 77:406–417. https://doi.org/10.1227/NEU.0000000000000772 (discussion 417)
Mohr JP, Parides MK, Stapf C et al (2014) Medical management with or without interventional therapy for unruptured brain arteriovenous malformations (ARUBA): a multicentre, non-blinded, randomised trial. Lancet 383:614–621. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(13)62302-8
Al-Shahi Salman R, White PM, Counsell CE et al (2014) Outcome after conservative management or intervention for unruptured brain arteriovenous malformations. JAMA 311:1661. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.2014.3200
Wu EM, El Ahmadieh TY, McDougall CM et al (2020) Embolization of brain arteriovenous malformations with intent to cure: a systematic review. J Neurosurg 132:388–399. https://doi.org/10.3171/2018.10.JNS181791
Nerva JD, Mantovani A, Barber J et al (2015) Treatment outcomes of unruptured arteriovenous malformations with a subgroup analysis of ARUBA (A Randomized Trial of Unruptured Brain Arteriovenous Malformations)-eligible patients. Neurosurgery 76:563–570. https://doi.org/10.1227/NEU.0000000000000663
Rutledge WC, Abla AA, Nelson J et al (2014) Treatment and outcomes of ARUBA-eligible patients with unruptured brain arteriovenous malformations at a single institution. Neurosurg Focus 37:E8. https://doi.org/10.3171/2014.7.FOCUS14242
Pollock BE, Flickinger JC (2008) Modification of the radiosurgery-based arteriovenous malformation grading system. Neurosurgery 63:239–243. https://doi.org/10.1227/01.NEU.0000315861.24920.92 (discussion 243)
Hartmann A, Stapf C, Hofmeister C et al (2000) Determinants of neurological outcome after surgery for brain arteriovenous malformation. Stroke 31:2361–2364. https://doi.org/10.1161/01.str.31.10.2361
Friedman WA, Bova FJ, Bollampally S, Bradshaw P (2003) Analysis of factors predictive of success or complications in arteriovenous malformation radiosurgery. Neurosurgery 52:296–307. https://doi.org/10.1227/01.neu.0000043692.51385.91 (discussion 307-308)
Hirschmann D, Goebl P, Witte FH et al (2020) Evaluation of the radiosurgical treatment of cerebral arteriovenous malformations: a retrospective single-center analysis of three decades. J Neurointerventional Surg 12:401–406. https://doi.org/10.1136/neurintsurg-2019-015332
Saatci I, Geyik S, Yavuz K, Cekirge HS (2011) Endovascular treatment of brain arteriovenous malformations with prolonged intranidal Onyx injection technique: long-term results in 350 consecutive patients with completed endovascular treatment course. J Neurosurg 115:78–88. https://doi.org/10.3171/2011.2.JNS09830
Koltz MT, Polifka AJ, Saltos A et al (2013) Long-term outcome of Gamma Knife stereotactic radiosurgery for arteriovenous malformations graded by the Spetzler-Martin classification. J Neurosurg 118:74–83. https://doi.org/10.3171/2012.9.JNS112329
Roark C, Vadlamudi V, Chaudhary N et al (2018) ABC/2 Method Does not Accurately Predict Cerebral Arteriovenous Malformation Volume. Neurosurgery 82:220–225. https://doi.org/10.1093/neuros/nyx139
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. Material preparation, data collection and analysis were performed by Mehdi Yahia-Cherif, Chifra Fenton, Florence Lefranc and Boris Lubicz. The first draft of themanuscript was written by Mehdi Yahia-Cherif and all authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Ethics approval
The study obtained institutional ethics committee approval. Ethics committee ULB-Erasme.
Number: P2022/078.
Consent to participate
This retrospective study was approved by the institutional ethics committee approval, and patients’ consents were waived.
Consent for publication
This retrospective study was approved by the institutional ethics committee approval, and patients’ consents were waived.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Yahia-Cherif, M., Fenton, C., Bonnet, T. et al. Embolization before Gamma Knife radiosurgery for cerebral arteriovenous malformations does not negatively impact its obliteration rate: a series of 190 patients. Neuroradiology 65, 391–399 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00234-022-03066-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00234-022-03066-w