Summary
Objective. To test a new hypothesis that the glue/contrast admixture used for embolisation reduces the dose delivered to AVMs using an experimental model.
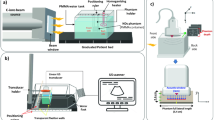
Method. A model was created using a block of “solid water” (6 × 5 × 2 cm) with twelve wells of different depths. Different concentrations of the glue admixture (Embucrilate + Lipiodol) were used. The model was irradiated using a 5MV beam with a clinical LINAC system and the dose was checked upstream and downstream. Dose was measured using Kodak XV film, a Vidar 16 bit film scanner and software for therapeutic film dosimetry measurements (RIT software).
Results. The radiation dose varied with the distance beyond the glue solid water interface. For distances of 0, 2 and 5 mm to the film, the mean reduction was 13.65% (SD = 2.94), 6.87% (SD = 1.95) and 1.75% (SD = 1.14), respectively. There was also correlation with the Lipiodol concentration in the mixture. The maximum reductions for 80, 50 and 20% Lipiodol concentrations were 16.1% (SD = 1.32), 14.85% (SD = 0.98) and 10% (SD = 1.21), respectively. There was no correlation between the glue depth and the dose delivered.
Conclusion. The hypothesis that the glue mixture used for embolisation reduces the radiation dose delivered was experimentally confirmed with this study.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
YM Andrade-Souza M Ramani D Scora MN Tsao K terBrugge ML Schwartz (2007) ArticleTitleEmbolization before radiosurgery reduces the obliteration rate of arteriovenous malformations Neurosurgery 60 443–451 Occurrence Handle17327788 Occurrence Handle10.1227/01.NEU.0000255347.25959.D0
JC Flickinger D Kondziolka AH Maitz LD Lunsford (2002) ArticleTitleAn analysis of the dose-response for arteriovenous malformation radiosurgery and other factors affecting obliteration Radiother Oncol 63 347–354 Occurrence Handle12142099 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0167-8140(02)00103-2
JC Flickinger BE Pollock D Kondziolka LD Lunsford (1996) ArticleTitleA dose-response analysis of arteriovenous malformation obliteration after radiosurgery Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 36 873–879 Occurrence Handle8960516 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:ByiC3MbosVE%3D
P Gallina L Merienne JF Meder M Schlienger D Lefkopoulos JJ Merland (1998) ArticleTitleFailure in radiosurgery treatment of cerebral arteriovenous malformations Neurosurgery 42 996–1002 Occurrence Handle9588543 Occurrence Handle10.1097/00006123-199805000-00024 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaK1c3ksl2mtQ%3D%3D
B Karlsson I Lax M Soderman (1998) ArticleTitleCan the probability for obliteration after radiosurgery for arteriovenous malformations be accurately predicted? Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 43 313–319
Y Kwon SR Jeon JH Kim JK Lee DS Ra DJ Lee BD Kwun (2000) ArticleTitleAnalysis of the causes of treatment failure in gamma knife radiosurgery for intracranial arteriovenous malformations J Neurosurg 93 IssueIDSuppl 3 104–106 Occurrence Handle11143225
JA Mathis JD Barr JA Horton CA Jungreis LD Lunsford DS Kondziolka D Vincent S Pentheny (1995) ArticleTitleThe efficacy of particulate embolization combined with stereotactic radiosurgery for treatment of large arteriovenous malformations of the brain Am J Neuroradiol 16 299–306 Occurrence Handle7726076 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:ByqB2czhtlI%3D
L Miyawaki C Dowd W Wara B Goldsmith N Albright P Gutin V Halbach G Hieshima R Higashida B Lulu L Pitts M Schell V Smith K Weaver C Wilson D Larson (1999) ArticleTitleFive year results of LINAC radiosurgery for arteriovenous malformations: outcome for large AVMS Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 44 1089–1106 Occurrence Handle10421543 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaK1Mzksl2isw%3D%3D
A Niroomand-Rad R Razavi S Thobejane KW Harter (1996) ArticleTitleRadiation dose perturbation at tissue-titanium dental interfaces in head and neck cancer patients Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 34 475–480 Occurrence Handle8567351 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:BymC2MfnvVQ%3D
BE Pollock JC Flickinger LD Lunsford A Maitz D Kondziolka (1998) ArticleTitleFactors associated with successful arteriovenous malformation radiosurgery Neurosurgery 42 1239–1244 Occurrence Handle9632181 Occurrence Handle10.1097/00006123-199806000-00020 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaK1c3ptl2ksg%3D%3D
BE Pollock D Kondziolka LD Lunsford D Bissonette JC Flickinger (1996) ArticleTitleRepeat stereotactic radiosurgery of arteriovenous malformations: factors associated with incomplete obliteration Neurosurgery 38 318–324 Occurrence Handle8869059 Occurrence Handle10.1097/00006123-199602000-00016 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:ByiD383mvF0%3D
M Schlienger D Atlan D Lefkopoulos L Merienne E Touboul O Missir F Nataf H Mammar K Platoni P Grandjean JN Foulquier J Huart C Oppenheim JF Meder E Houdart JJ Merland (2000) ArticleTitleLinac radiosurgery for cerebral arteriovenous malformations: results in 169 patients Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 46 1135–1142 Occurrence Handle10725623 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DC%2BD3c7ptFOlsg%3D%3D
M Schwartz K Sixel C Young A Kemeny D Forster L Walton E Franssen (1997) ArticleTitlePrediction of obliteration of arteriovenous malformations after radiosurgery: the obliteration prediction index Can J Neurol Sci 24 106–109 Occurrence Handle9164685 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:ByiA3cjkvFA%3D
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Correspondence: Michael L. Schwartz, Sunnybrook Health Sciences Centre, Division of Neurosurgery – Suite A1 29, 2075 Bayview Avenue, Toronto, ON, M4N 3M5 Canada.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Andrade-Souza, Y., Ramani, M., Beachey, D. et al. Liquid embolisation material reduces the delivered radiation dose: a physical experiment. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 150, 161–164 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00701-007-1482-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00701-007-1482-9