Abstract
Purpose
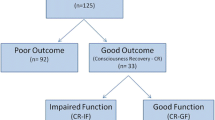
The aim of this study is to compare a qualitative and a quantitative assessment of brain diffusion-weighted imaging (DWI) in predicting outcome of comatose patients after cardiac arrest (CA).
Methods
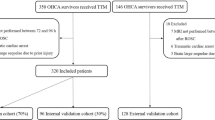
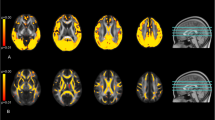
Two observers used a scoring template to analyze the DWI of 75 patients. A total of 13 regions were scored from 0 to 3 (0 = normal, 1 = probably normal, 2 = probably abnormal, 3 = definitely abnormal). The total cerebral cortex (TCC), the total deep grey nuclei (TDGN), the total brain stem, the total cerebellum, and the total brain score were calculated. Intra- and inter-observer variability were tested. The mean whole brain apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) values and percentage of voxels below a specific ADC value cut-off were calculated. The data were correlated with clinical outcome (cerebral performance category score after 180 days, dichotomized in a score 1–2 with favorable outcome and score 3–5 with unfavorable outcome) using ROC analysis.
Results
Intra-observer variability was excellent for the TCC score (ICC 0.95 and 0.86) and the TDGN score (ICC 0.89 and 0.75). Inter-observer variability was good to excellent for total cerebral cortex score and total deep grey nuclei score in both the first (ICC 0.78 and 0.69) and third (ICC 0.86 and 0.83) image assessment. TCC and TDGN score show the best correlation with clinical outcome (highest AUC values 0.87 and 0.87). Quantitative parameters did not show good correlation with clinical outcome (AUC values 0.57 and 0.60).
Conclusion
A qualitative assessment of brain DWI using a scoring template provides useful data regarding patient outcome while quantitative data appeared less reliable.



Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ADC:
-
Apparent diffusion coefficient
- AUC:
-
Area under the curve
- CA:
-
Cardiac arrest
- CPC:
-
Cerebral performance category
- DWI:
-
Diffusion-weighted imaging
- FLAIR:
-
Fluid-attenuated inversion recovery
- ICC:
-
Intra-class correlation coefficient
- MWB:
-
Mean whole brain
- PV650:
-
Percentage of voxels with an ADC value of less than 0.650 × 10−3 mm2/s
- ROC:
-
Receiver operator curve
- RS:
-
Spearman’s rank correlation
- TB:
-
Total brain
- TBS:
-
Total brainstem
- TC:
-
Total cerebellum
- TCC:
-
Total cerebral cortex
- TDGN:
-
Total deep grey nuclei
- WML:
-
White matter lesions
References
Gräsner JT, Bossaert L (2013) Epidemiology and management of cardiac arrest: what registries are revealing. Best Pract Res Clin Anaesthesiol 27:293–306
Rossetti AO, Rabinstein AA, Oddo M (2016) Neurological prognostication of outcome in patients in coma after cardiac arrest. Lancet Neurol 15:597–609
Wijdicks EFM, Campeau NG, Miller GM (2001) MR Imaging in comatose survivors of cardiac resuscitation. Am J Neuroradiol 22:1561–1565
Wijman CAC, Mlynash M, Caulfield AF et al (2009) Prognostic value of brain diffusion- after weighted imaging cardiac arrest. Ann Neurol 65:394–402
Choi SP, Park KN, Park HK et al (2010) Diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging for predicting the clinical outcome of comatose survivors after cardiac arrest: A cohort study. Crit Care 14:1–11
Mlynash M, Campbell DM, Leproust EM, Fischbein NJ, Bammer R, Eyngorn I, Hsia AW, Moseley M, Wijman CAC (2010) Temporal and spatial profile of brain diffusion-weighted MRI after cardiac arrest. Stroke 41:1665–1672
Greer D, Scripko P, Bartscher J, Sims J, Camargo E, Singhal A, Parides M, Furie K (2012) Clinical MRI interpretation for outcome prediction in cardiac arrest. Neurocrit Care 17:240–244
Luyt CE, Galanaud D, Perlbarg V, Vanhaudenhuyse A, Stevens RD, Gupta R, Besancenot H, Krainik A, Audibert G, Combes A, Chastre J, Benali H, Laureys S, Puybasset L, Neuro Imaging for Coma Emergence and Recovery Consortium (2012) Diffusion tensor imaging to predict long-term outcome after cardiac arrest: A bicentric pilot study. Anesthesiology 117:1311–1321
Youn CS, Park KN, Kim JY, Callaway CW, Choi SP, Rittenberger JC, Kim SH, Oh SH, Kim YM (2015) Repeated diffusion weighted imaging in comatose cardiac arrest patients with therapeutic hypothermia. Resuscitation 96:1–8
Hirsch KG, Mlynash M, Jansen S, Persoon S, Eyngorn I, Krasnokutsky MV, Wijman CAC, Fischbein NJ (2015) Prognostic value of a qualitative brain MRI scoring system after cardiac arrest. J Neuroimaging 25:430–437
Hirsch KG, Mlynash M, Eyngorn I, Pirsaheli R, Okada A, Komshian S, Chen C, Mayer SA, Meschia JF, Bernstein RA, Wu O, Greer DM, Wijman CA, Albers GW (2016) Multi-center study of diffusion-weighted imaging in coma after cardiac arrest. Neurocrit Care 24:82–89
Velly L, Perlbarg V, Boulier T, Adam N, Delphine S, Luyt CE, Battisti V, Torkomian G, Arbelot C, Chabanne R, Jean B, di Perri C, Laureys S, Citerio G, Vargiolu A, Rohaut B, Bruder N, Girard N, Silva S, Cottenceau V, Tourdias T, Coulon O, Riou B, Naccache L, Gupta R, Benali H, Galanaud D, Puybasset L, Constantin JM, Chastre J, Amour J, Vezinet C, Rouby JJ, Raux M, Langeron O, Degos V, Bolgert F, Weiss N, Similowski T, Demoule A, Duguet A, Tollard E, Veber B, Lotterie JA, SANCHEZ-PENA P, Génestal M, Patassini M (2018) Use of brain diffusion tensor imaging for the prediction of long-term neurological outcomes in patients after cardiac arrest: a multicentre, international, prospective, observational, cohort study. Lancet Neurol 17:317–326
Moon HK, Jang J, Park KN et al (2018) Quantitative analysis of relative volume of low apparent diffusion coefficient value can predict neurologic outcome after cardiac arrest. Resuscitation 126:36–42
Sair HI, Hannawi Y, Li S, Kornbluth J, Demertzi A, di Perri C, Chabanne R, Jean B, Benali H, Perlbarg V, Pekar J, Luyt CE, Galanaud D, Velly L, Puybasset L, Laureys S, Caffo B, Stevens RD, For the Neuroimaging for Coma Emergence and Recovery (NICER) Consortium (2018) Early functional connectome integrity and 1-year recovery in comatose survivors of cardiac arrest. Radiology 287:247–255
Quintard H, Velly L, Boussen S, Chiosi X, Amoretti ME, Cervantes E, Ichai C (2019) Value of assessment of multivoxel proton chemical shift imaging to predict long term outcome in patients after out-of-hospital cardiac arrest: A preliminary prospective observational study. Resuscitation 134:136–144
Ameloot K, De Deyne C, Ferdinande B et al (2017) Mean arterial pressure of 65 mm Hg versus 85-100 mm Hg in comatose survivors after cardiac arrest: Rationale and study design of the Neuroprotect post-cardiac arrest trial. Am Heart J 191:91–98
Ameloot K, De Deyne C, Eertmans W et al (2019) Early goal-directed haemodynamic optimization of cerebral oxygenation in comatose survivors after cardiac arrest: the Neuroprotect post-cardiac arrest trial. Eur Heart J 40:1804–1814
Raina KD, Callaway C, Rittenberger JC, Holm MB (2008) Neurologiccal and functional status following cardiac arrest: method and tool utility. Resuscitation 79:249–256
Funding
No funding was received for this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in the studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki Declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Sarah Cappelle is joint first author of the paper.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vanden Berghe, S., Cappelle, S., De Keyzer, F. et al. Qualitative and quantitative analysis of diffusion-weighted brain MR imaging in comatose survivors after cardiac arrest. Neuroradiology 62, 1361–1369 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00234-020-02460-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00234-020-02460-6