Abstract
Background
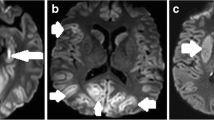
In clinical practice, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is commonly used to assess the severity of a cardiac arrest patient’s cerebral injury, utilizing treating neurologists’ imaging interpretation. We sought to determine whether clinical interpretation of diffusion-weighted imaging (DWI) helps to determine poor outcome in comatose cardiac arrest patients.
Methods
We analyzed 80 consecutive MRIs from patients in coma following cardiac arrest. Each study was graded as “normal” or “abnormal restricted diffusion” in pre-specified brain regions by two blinded stroke neurologists. Poor outcome was defined as a modified Rankin Scale (mRS) score >4 at 3 months. Formal interpretations of neuroimaging by non-blinded neuroradiologists were compared with the blinded reviews by the stroke neurologists.
Results
DWI abnormalities were highly sensitive (98.5 %) but only modestly specific (46.2 %) for predicting poor neurological outcome. Inter-observer reliability was moderate (kappa = 0.49 ± 0.32), with 91 % agreement between study observers, and no significant differences in study observers’ interpretations (p = 0.125). There were, however, significant differences between the study observers and the clinical neuroradiologists in identifying studies showing evidence of global hypoxic-ischemic injury (p = 0.001).
Conclusions
The qualitative evaluation of imaging abnormalities by stroke physicians in comatose cardiac arrest patients is a highly sensitive method of predicting poor outcome, but with limited specificity.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wijdicks EF, Hijdra A, Young GB, Bassetti CL, Wiebe S. Practice parameter: prediction of outcome in comatose survivors after cardiopulmonary resuscitation (an evidence-based review): report of the Quality Standards Subcommittee of the American Academy of Neurology. Neurology. 2006;67:203–10.
Hjort N, Christensen S, Sølling C, Ashkanian M, Wu O, Røhl L, Gyldensted C, Andersen G, Østergaard L. Ischemic injury detected by diffusion imaging 11 minutes after stroke. Ann Neurol. 2005;58:462–5.
Pierpaoli C, Alger JR, Righini A, et al. High temporal resolution diffusion MRI of global cerebral ischemia and reperfusion. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 1996;16:892–905.
Fischer M, Bockhorst K, Hoehn-Berlage M, et al. Imaging of the apparent diffusion coefficient for the evaluation of cerebral metabolic recovery after cardiac arrest. Magn Reson Imaging. 1995;13:781–90.
Wijman CA, Mlynash M, Caulfield AF, Hsia AW, Eyngorn I, Bammer R, Fischbein N, Albers GW, Moseley M. Prognostic value of brain diffusion-weighted imaging after cardiac arrest. Ann Neurol. 2009;65:394–402.
Wijdicks EF, Campeau NG, Miller GM. MR imaging in comatose survivors of cardiac resuscitation. Am J Neuroradiol. 2001;22:1561–5.
Wu O, Sorensen AG, Benner T, Singhal AB, Furie KL, Greer DM. Comatose patients with cardiac arrest: predicting clinical outcome with diffusion-weighted MR imaging. Radiology. 2009;252:173–81.
Els T, Kassubek J, Kubalek R, Klisch J. Diffusion-weighted MRI during early global cerebral hypoxia: a predictor for clinical outcome? Acta Neurol Scand. 2004;110:361–7.
McKinney AM, Teksam M, Felice R, et al. Diffusion-weighted imaging in the setting of diffuse cortical laminar necrosis and hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2004;25:1659–65.
Arbelaez A, Castillo M, Mukherji SK. Diffusion-weighted MR imaging of global cerebral anoxia. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 1999;20:999–1007.
Kawahara H, Takeda Y, Tanaka A, Nagano O, Katayama H, Hirakawa M, Hiraki Y. Does diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging enable detection of early ischemic change following transient cerebral ischemia? J Neurol Sci. 2000;181:73–81.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Greer, D., Scripko, P., Bartscher, J. et al. Clinical MRI Interpretation for Outcome Prediction in Cardiac Arrest. Neurocrit Care 17, 240–244 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12028-012-9716-y
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12028-012-9716-y