Abstract
Introduction
The German Society of Ultrasound in Medicine (known by its acronym DEGUM) recently proposed a novel multi-parametric ultrasound approach for comprehensive and accurate assessment of extracranial internal carotid artery (ICA) steno-occlusive disease. We determined the agreement between duplex ultrasonography (DUS) interpreted by the DEGUM criteria and CT angiography (CTA) for grading of extracranial ICA steno-occlusive disease.
Methods
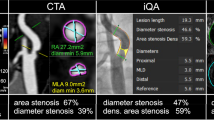
Consecutive patients with acute cerebral ischemia underwent DUS and CTA. Internal carotid artery stenosis was graded according to the DEGUM-recommended criteria for DUS. Independent readers manually performed North American Symptomatic Carotid Endarterectomy Trial-type measurements on axial CTA source images. Both modalities were compared using Spearman’s correlation and Bland-Altman analyses.
Results
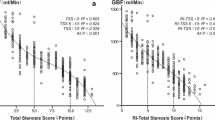
A total of 303 acute cerebral ischemia patients (mean age, 72 ± 12 years; 58 % men; median baseline National Institutes of Health Stroke Scale score, 4 [interquartile range 7]) provided 593 DUS and CTA vessel pairs for comparison. There was a positive correlation between DUS and CTA (r s = 0.783, p < 0.001) with mean difference in degree of stenosis measurement of 3.57 %. Bland-Altman analysis further revealed widely varying differences (95 % limits of agreement −29.26 to 22.84) between the two modalities.
Conclusion
Although the novel DEGUM criteria showed overall good agreement between DUS and CTA across all stenosis ranges, potential for wide incongruence with CTA underscores the need for local laboratory validation to avoid false screening results.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Grau AJ, Weimar C, Buggle F, Heinrich A, Goertler M, Neumaier S et al (2001) Risk factors, outcome, and treatment in subtypes of ischemic stroke: the German stroke data bank. Stroke 32:2559–2566
Petty GW, Brown RD Jr, Whisnant JP, Sicks JD, O’Fallon WM, Wiebers DO (1999) Ischemic stroke subtypes: a population-based study of incidence and risk factors. Stroke 30:2513–2516
Rothwell PM, Eliasziw M, Gutnikov SA, Fox AJ, Taylor DW, Mayberg MR et al (2003) Analysis of pooled data from the randomized controlled trials of endarterectomy for symptomatic carotid stenosis. Lancet 361:107–116
European Carotid Surgery Trialists’ Collaborative Group (1998) Randomised trial of endarterectomy for recently symptomatic carotid stenosis: final results of the MRC European Carotid Surgery Trial (ECST). Lancet 351:1379–1387
Barnett HJ, Taylor DW, Eliasziw M, Fox AJ, Ferguson GG, Haynes RB et al (1998) Benefit of carotid endarterectomy in patients with symptomatic moderate or severe stenosis. North American Symptomatic Carotid Endarterectomy Trial Collaborators. N Engl J Med 339:1415–1425
Halliday A, Mansfield A, Marro J, Peto C, Peto R, Potter J et al (2004) Prevention of disabling and fatal strokes by successful carotid endarterectomy in patients without recent neurological symptoms: randomised controlled trial. Lancet 363:1491–1502
Dawkins AA, Evans AL, Wattam J, Romanowski CA, Connolly DJ, Hodgson TJ et al (2007) Complications of cerebral angiography: a prospective analysis of 2,924 consecutive procedures. Neuroradiology 49:753–759
Brott TG, Halperin JL, Abbara S, Bacharach JM, Barr JD, Bush RL et al (2011) ASA/ACCF/AHA/AANN/AANS/ACR/ASNR/CNS/SAIP/SCAI/SIR/SNIS/SVM/SVS guideline on the management of patients with extracranial carotid and vertebral artery disease: executive summary. Circulation 124:489–532
U-King-Im JM, Young V, Gillard JH (2009) Carotid-artery imaging in the diagnosis and management of patients at risk of stroke. Lancet Neurol 8:569–580
Zavanone C, Ragone E, Samson Y (2012) Concordance rates of Doppler ultrasound and CT angiography in the grading of carotid artery stenosis: a systematic literature review. J Neurol 259:1015–1018
van Prehn J, Muhs BE, Pramanik B, Ollenschleger M, Rockman CB, Cayne NS et al (2008) Multidimensional characterization of carotid artery stenosis using CT imaging: a comparison with ultrasound grading and peak flow measurement. Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg 36:267–72
Müller M, Agten CA, Österreich M, Hoffmann M (2015) Assessing internal carotid artery stenosis with a semiautomated computed tomography angiography tool and duplex ultrasound. J Vasc Surg 61:1449–1456
Silvennoinen HM, Ikonen S, Soinne L, Railo M, Valanne L (2007) CT angiographic analysis of carotid artery stenosis: comparison of manual assessment, semiautomatic vessel analysis, and digital subtraction angiography. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 28:97–103
Bartlett ES, Walters TD, Symons SP, Fox AJ (2006) Quantification of carotid stenosis on CT angiography. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 27:13–19
Grant EG, Benson CB, Moneta GL, Alexandrov AV, Baker JD, Bluth EI et al (2003) Carotid artery stenosis: gray-scale and Doppler US diagnosis—Society of Radiologists in Ultrasound Consensus Conference. Radiology 229:340–346
Beach KW, Bergelin RO, Leotta DF, Primozich JF, Sevareid PM, Stutzman ET et al (2010) Standardized ultrasound evaluation of carotid stenosis for clinical trials: University of Washington Ultrasound Reading Center. Cardiovasc Ultrasound 8:39
Arning C, Widder B, von Reutern GM, Stiegler H, Görtler M (2010) Revision of DEGUM ultrasound criteria for grading internal carotid artery stenoses and transfer to NASCET measurement. Ultraschall Med 31:251–257
Klingelhöfer J (2014) Ultrasonography of carotid stenosis. Int J Clin Neurosci Ment Health 1:S04
von Reutern GM, Goertler MW, Bornstein NM, Del Sette M, Evans DH, Hetzel A et al (2012) Grading carotid stenosis using ultrasonic methods. Stroke 43:916–921
Intersocietal Accreditation Commission. https://www.google.de/url?sa=t&rct=j&q=&esrc=s&source=web&cd=1&cad=rja&uact=8&ved=0CCEQFjAAahUKEwjzs_enif7GAhWDn3IKHc7oAdc&url=http%3A%2F%2Fintersocietal.org%2Fvascular%2F&ei=jZa3VbO5E4O_ygPO0Ye4DQ&usg=AFQjCNGWqrmnZUue1_U4BI_sovUlnxeiEg. Accessed 28 July 2015
Bland JM, Altman DG (1986) Statistical methods for assessing agreement between two methods of clinical measurement. Lancet i:307–310.
Cohen J (1988) Statistical power analysis for the behavioral sciences, 2nd edn. L. Erlbaum Associates, Hillsdale
Barlinn K, Alexandrov AV (2011) Vascular imaging in stroke: comparative analysis. Neurotherapeutics 8:340–348
Patel SG, Collie DA, Wardlaw JM (2002) Outcome, observer reliability, and patient preferences if CTA, MRA, or Doppler ultrasound were used, individually or together, instead of digital subtraction angiography before carotid endarterectomy. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 73:21–28
Wardlaw JM, Chappell FM, Best JJ, Wartolowska K, Berry E (2006) Non-invasive imaging compared with intra-arterial angiography in the diagnosis of symptomatic carotid stenosis: a meta-analysis. Lancet 367:1503–1512
Chappell FM, Wardlaw JM, Young GR, Gillard JH, Roditi GH, Yip B et al (2009) Carotid artery stenosis: accuracy of noninvasive tests—individual patient data meta-analysis. Radiology 251:493–502
Alexandrov AV, Needleman L (2012) Carotid artery stenosis: making complex assessments of a simple problem or simplifying approach to a complex disease? Stroke 43:627–628
Koga M, Kimura K, Minematsu K, Yamaguchi T (2001) Diagnosis of internal carotid artery stenosis greater than 70% with power Doppler duplex sonography. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 22:413–417
Neschis DG, Lexta FJ, Davis JT, Carpenter JP (2001) Duplex criteria for determination of 50 % or greater carotid stenosis. J Ultrasound Med 20:207–215
Hirt LS (2014) Progression rate and ipsilateral neurological events in asymptomatic carotid stenosis. Stroke 45:702–706
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
We declare that all human and animal studies have been approved by the ethics committee of the Technische Universität Dresden (#111032014) and have therefore been performed in accordance with the ethical standards laid down in the 1964 Declaration of Helsinki and its later amendments. Due to the retrospective nature of this study, informed consent was waived.
Conflict of Interest
We declare that we have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Barlinn, K., Floegel, T., Kitzler, H.H. et al. Multi-parametric ultrasound criteria for internal carotid artery disease—comparison with CT angiography. Neuroradiology 58, 845–851 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00234-016-1706-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00234-016-1706-x