Abstract
Introduction
Professional boxing can lead to chronic traumatic encephalopathy, a variant of traumatic brain injury (TBI). Its occurrence in amateur boxers is a matter of debate since amateur boxing is considered to be less harmful due to more strict regulations. However, several studies using different methodological approaches have revealed subtle signs of TBI even in amateurs. Diffusion tensor imaging (DTI) is sensitive to microscopic white matter changes and has been proven useful in TBI when routine MR imaging often is unrevealing.
Methods
DTI, with tract-based spatial statistics (TBSS) together with neuropsychological examination of executive functions and memory, was used to investigate a collective of 31 male amateur boxers and 31 age-matched controls as well as a subgroup of 19 individuals, respectively, who were additionally matched for intellectual performance (IQ).
Results
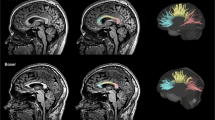
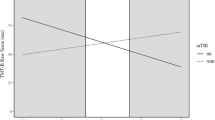
All participants had normal findings in neurological examination and conventional MR. Amateur boxers did not show deficits in neuropsychological tests when their IQ was taken into account. Fractional anisotropy was significantly reduced, while diffusivity measures were increased along central white matter tracts in the boxers group. These changes were in part associated with the number of fights.
Conclusions
TBSS revealed widespread white matter disturbance partially related to the individual fighting history in amateur boxers. These findings closely resemble those in patients with accidental TBI and indicate similar histological changes in amateur boxers.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adamson C, Yuan W, Babcock L et al (2013) Diffusion tensor imaging detects white matter abnormalities and associated cognitive deficits in chronic adolescent TBI. Brain Inj 27:454–463
Aoki Y, Inokuchi R, Gunshin M et al (2012) Diffusion tensor imaging studies of mild traumatic brain injury: a meta-analysis. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 83:870–876
Arfanakis K, Haughton VM, Carew JD et al (2002) Diffusion tensor MR imaging in diffuse axonal injury. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 23:794–802
Bazarian JJ, Zhu T, Zhong J et al (2014) Persistent, long-term cerebral white matter changes after sports-related repetitive head impacts. PLoS One 9, e94734
Beaulieu C (2002) The basis of anisotropic water diffusion in the nervous system—a technical review. NMR Biomed 15:435–455
Behrens TE, Berg HJ, Jbabdi S et al (2007) Probabilistic diffusion tractography with multiple fibre orientations: what can we gain? Neuroimage 34:144–155
Behrens TE, Woolrich MW, Jenkinson M et al (2003) Characterization and propagation of uncertainty in diffusion-weighted MR imaging. Magn Reson Med 50:1077–1088
Belanger HG, Spiegel E, Vanderploeg RD (2010) Neuropsychological performance following a history of multiple self-reported concussions: a meta-analysis. J Int Neuropsychol Soc 16:262–267
Bender AR, Prindle JJ, Brandmaier AM et al. (2015) White matter and memory in healthy adults: coupled changes over two years. Neuroimage
Benson RR, Meda SA, Vasudevan S et al (2007) Global white matter analysis of diffusion tensor images is predictive of injury severity in traumatic brain injury. J Neurotrauma 24:446–459
Brooks N, Kupshik G, Wilson L et al (1987) A neuropsychological study of active amateur boxers. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 50:997–1000
Butler RJ, Forsythe WI, Beverly DW et al (1993) A prospective controlled investigation of the cognitive effects of amateur boxing. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 56:1055–1061
Casson IR, Siegel O, Sham R et al (1984) Brain damage in modern boxers. Jama 251:2663–2667
Chamard E, Lassonde M, Henry L et al (2013) Neurometabolic and microstructural alterations following a sports-related concussion in female athletes. Brain Inj 27:1038–1046
Chamard E, Lefebvre G, Lassonde M et al. (2015) Long-Term Abnormalities in the Corpus Callosum of Female Concussed Athletes. J Neurotrauma
Chappell MH, Brown JA, Dalrymple-Alford JC et al (2008) Multivariate analysis of diffusion tensor imaging data improves the detection of microstructural damage in young professional boxers. Magn Reson Imaging 26:1398–1405
Chappell MH, Ulug AM, Zhang L et al (2006) Distribution of microstructural damage in the brains of professional boxers: a diffusion MRI study. J Magn Reson Imaging 24:537–542
Cheng AL, Batool S, Mccreary CR et al (2013) Susceptibility-weighted imaging is more reliable than T2*-weighted gradient-recalled echo MRI for detecting microbleeds. Stroke 44:2782–2786
Chiang MC, Barysheva M, Toga AW et al (2011) BDNF gene effects on brain circuitry replicated in 455 twins. Neuroimage 55:448–454
Corsellis JA, Brierley JB (1959) Observations on the pathology of insidious dementia following head injury. J Ment Sci 105:714–720
Cubon VA, Putukian M, Boyer C et al (2011) A diffusion tensor imaging study on the white matter skeleton in individuals with sports-related concussion. J Neurotrauma 28:189–201
Dekosky ST, Blennow K, Ikonomovic MD et al (2013) Acute and chronic traumatic encephalopathies: pathogenesis and biomarkers. Nat Rev Neurol 9:192–200
Douaud G, Jbabdi S, Behrens TE et al (2011) DTI measures in crossing-fibre areas: increased diffusion anisotropy reveals early white matter alteration in MCI and mild Alzheimer’s disease. Neuroimage 55:880–890
Drew RH, Templer DI, Schuyler BA et al (1986) Neuropsychological deficits in active licensed professional boxers. J Clin Psychol 42:520–525
Forstl H, Haass C, Hemmer B et al (2010) Boxing-acute complications and late sequelae: from concussion to dementia. Dtsch Arztebl Int 107:835–839
Gavett BE, Cantu RC, Shenton M et al (2011) Clinical appraisal of chronic traumatic encephalopathy: current perspectives and future directions. Curr Opin Neurol 24:525–531
Guo LF, Wang G, Zhu XY et al (2013) Comparison of ESWAN, SWI-SPGR, and 2D T2*-weighted GRE sequence for depicting cerebral microbleeds. Clin Neuroradiol 23:121–127
Hahnel S, Stippich C, Weber I et al (2008) Prevalence of cerebral microhemorrhages in amateur boxers as detected by 3T MR imaging. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 29:388–391
Hasiloglu ZI, Albayram S, Selcuk H et al (2011) Cerebral microhemorrhages detected by susceptibility-weighted imaging in amateur boxers. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 32:99–102
Heilbronner RL, Bush SS, Ravdin LD et al (2009) Neuropsychological consequences of boxing and recommendations to improve safety: a National Academy of Neuropsychology education paper. Arch Clin Neuropsychol 24:11–19
Heilbronner RL, Henry GK, Carson-Brewer M (1991) Neuropsychologic test performance in amateur boxers. Am J Sports Med 19:376–380
Hellyer PJ, Leech R, Ham TE et al (2013) Individual prediction of white matter injury following traumatic brain injury. Ann Neurol 73:489–499
Helmstaedter C, Lendt M, Lux S (2001) Verbaler Lern- und Merkfähigkeitstest. Beltz, Göttingen
Holzgraefe M, Lemme W, Funke W et al (1992) The significance of diagnostic imaging in acute and chronic brain damage in boxing. A prospective study in amateur boxing using magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). Int J Sports Med 13:616–620
Huisman TA, Schwamm LH, Schaefer PW et al (2004) Diffusion tensor imaging as potential biomarker of white matter injury in diffuse axonal injury. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 25:370–376
Inglese M, Makani S, Johnson G et al (2005) Diffuse axonal injury in mild traumatic brain injury: a diffusion tensor imaging study. J Neurosurg 103:298–303
Jako P (2002) Safety measures in amateur boxing. Br J Sports Med 36:394–395
Jordan BD, Zimmerman RD (1988) Magnetic resonance imaging in amateur boxers. Arch Neurol 45:1207–1208
Kaste M, Kuurne T, Vilkki J et al (1982) Is chronic brain damage in boxing a hazard of the past? Lancet 2:1186–1188
Kinnunen KM, Greenwood R, Powell JH et al (2011) White matter damage and cognitive impairment after traumatic brain injury. Brain 134:449–463
Koenis MM, Brouwer RM, Van Den Heuvel MP et al (2015) Development of the brain’s structural network efficiency in early adolescence: a longitudinal DTI twin study. Hum Brain Mapp 36:4938–4953
Koerte IK, Kaufmann D, Hartl E et al. (2012) A prospective study of physician-observed concussion during a varsity university hockey season: white matter integrity in ice hockey players. Part 3 of 4. Neurosurgical focus 33:E3: 1–7
Kourtidou P, Mccauley SR, Bigler ED et al (2013) Centrum semiovale and corpus callosum integrity in relation to information processing speed in patients with severe traumatic brain injury. J Head Trauma Rehabil 28:433–441
Kraus MF, Susmaras T, Caughlin BP et al (2007) White matter integrity and cognition in chronic traumatic brain injury: a diffusion tensor imaging study. Brain 130:2508–2519
Lipton ML, Gellella E, Lo C et al (2008) Multifocal white matter ultrastructural abnormalities in mild traumatic brain injury with cognitive disability: a voxel-wise analysis of diffusion tensor imaging. J Neurotrauma 25:1335–1342
Liu G, Ghimire P, Pang H et al. (2015) Improved sensitivity of 3.0 Tesla susceptibility-weighted imaging in detecting traumatic bleeds and its use in predicting outcomes in patients with mild traumatic brain injury. Acta Radiol (Stockholm, Sweden: 1987) 56:1256–1263
Loosemore M, Knowles CH, Whyte GP (2007) Amateur boxing and risk of chronic traumatic brain injury: systematic review of observational studies. BMJ 335:809
Mckee AC, Cantu RC, Nowinski CJ et al (2009) Chronic traumatic encephalopathy in athletes: progressive tauopathy after repetitive head injury. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 68:709–735
Mclatchie G, Brooks N, Galbraith S et al (1987) Clinical neurological examination, neuropsychology, electroencephalography and computed tomographic head scanning in active amateur boxers. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 50:96–99
Medana IM, Esiri MM (2003) Axonal damage: a key predictor of outcome in human CNS diseases. Brain 126:515–530
Messe A, Caplain S, Paradot G et al (2011) Diffusion tensor imaging and white matter lesions at the subacute stage in mild traumatic brain injury with persistent neurobehavioral impairment. Hum Brain Mapp 32:999–1011
Moriarity J, Collie A, Olson D et al (2004) A prospective controlled study of cognitive function during an amateur boxing tournament. Neurology 62:1497–1502
Moriarity JM, Pietrzak RH, Kutcher JS et al (2012) Unrecognised ringside concussive injury in amateur boxers. Br J Sports Med 46:1011–1015
Murugavel M, Cubon V, Putukian M et al (2014) A longitudinal diffusion tensor imaging study assessing white matter fiber tracts after sports-related concussion. J Neurotrauma 31:1860–1871
Navas-Sanchez FJ, Aleman-Gomez Y, Sanchez-Gonzalez J et al (2014) White matter microstructure correlates of mathematical giftedness and intelligence quotient. Hum Brain Mapp 35:2619–2631
Nichols TE, Holmes AP (2002) Nonparametric permutation tests for functional neuroimaging: a primer with examples. Hum Brain Mapp 15:1–25
Perianez JA, Rios-Lago M, Rodriguez-Sanchez JM et al (2007) Trail making test in traumatic brain injury, schizophrenia, and normal ageing: sample comparisons and normative data. Arch Clin Neuropsychol 22:433–447
Reitan RM (1955) The relation of the trail making test to organic brain damage. J Consult Psychol 19:393–394
Roberts GW, Allsop D, Bruton C (1990) The occult aftermath of boxing. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 53:373–378
Shams S, Martola J, Cavallin L et al (2015) SWI or T2*: which MRI sequence to use in the detection of cerebral microbleeds? The Karolinska Imaging Dementia Study. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 36:1089–1095
Sharp DJ, Ham TE (2011) Investigating white matter injury after mild traumatic brain injury. Curr Opin Neurol 24:558–563
Shin W, Mahmoud SY, Sakaie K et al (2014) Diffusion measures indicate fight exposure-related damage to cerebral white matter in boxers and mixed martial arts fighters. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 35:285–290
Smith SM (2002) Fast robust automated brain extraction. Hum Brain Mapp 17:143–155
Smith SM, Jenkinson M, Johansen-Berg H et al (2006) Tract-based spatial statistics: voxelwise analysis of multi-subject diffusion data. Neuroimage 31:1487–1505
Smith SM, Jenkinson M, Woolrich MW et al (2004) Advances in functional and structural MR image analysis and implementation as FSL. Neuroimage 23(Suppl 1):S208–S219
Smith SM, Nichols TE (2009) Threshold-free cluster enhancement: addressing problems of smoothing, threshold dependence and localisation in cluster inference. Neuroimage 44:83–98
Stewart WF, Gordon B, Selnes O et al (1994) Prospective study of central nervous system function in amateur boxers in the United States. Am J Epidemiol 139:573–588
Stiller JW, Yu SS, Brenner LA et al (2014) Sparring and neurological function in professional boxers. Frontiers in public health 2:69
Stojsih S, Boitano M, Wilhelm M et al (2010) A prospective study of punch biomechanics and cognitive function for amateur boxers. Br J Sports Med 44:725–730
Tewes U (1994) HAWIE-R: Hamburg-Wechsler-Intelligenztest für Erwachsene. Revision 1991. Huber, Bern, Göttingen, Toronto, Seattle
Wilde EA, Hunter JV, Li X et al. (2015) Chronic effects of boxing: diffusion tensor imaging and cognitive findings. J Neurotrauma
Wolf D, Fischer FU, Fesenbeckh J et al (2014) Structural integrity of the corpus callosum predicts long-term transfer of fluid intelligence-related training gains in normal aging. Hum Brain Mapp 35:309–318
Zhang L, Heier LA, Zimmerman RD et al (2006) Diffusion anisotropy changes in the brains of professional boxers. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 27:2000–2004
Zhang L, Ravdin LD, Relkin N et al (2003) Increased diffusion in the brain of professional boxers: a preclinical sign of traumatic brain injury? AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 24:52–57
Zimmermann P, Fimm B (2002) A test battery for attentional performance. In: Leclerq M, Zimmermann P (eds) Applied neuropsychology of attention: theory, diagnosis and rehabilitation. Psychology Press, p 110–151
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
We declare that all human and animal studies have been approved by the ethics committee of the University of Heidelberg and have therefore been performed in accordance with the ethical standards laid down in the 1964 Declaration of Helsinki and its later amendments. We declare that all patients gave informed consent prior to inclusion in this study.
Conflict of interest
We declare that we have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Herweh, C., Hess, K., Meyding-Lamadé, U. et al. Reduced white matter integrity in amateur boxers. Neuroradiology 58, 911–920 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00234-016-1705-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00234-016-1705-y