Abstract
Introduction
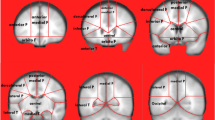
The aim of this study was to investigate whether the outline of the hippocampal body becomes rounded on coronal magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) as the volume of the hippocampal formation decreases in Alzheimer’s disease (AD).
Methods
Institutional review board approval of the study protocol was obtained, and all subjects provided informed consent for the mini-mental state examination (MMSE) and MRI. The MRI and MMSE were prospectively performed in all 103 subjects (27 men and 76 women; mean age ± standard deviation, 77.7 ± 7.8 years) who had AD or were concerned about having of dementia and who consulted our institute over 1 year. The subjects included 14 non-dementia cases (MMSE score ≥ 28) and 89 AD cases (MMSE score ≤ 27). The total volume of the bilateral hippocampal formation (VHF) was assessed with a tracing method, and the ratio of the VHF to the intracranial volume (RVHF) and the rounding ratio (RR) of the hippocampal body (mean ratio of its short dimension to the long dimension in the bilateral hippocampal body) were calculated. Using Spearman’s correlation coefficient, the correlations between RR and VHF and between RR and RVHF were assessed.
Results
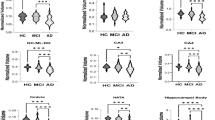
Correlation coefficients between RR and VHF and between RR and RVHF were −0.419 (p < 0.01) and −0.418 (p < 0.01), respectively. There was a significant negative correlation between RR and the volume of the hippocampal formation.
Conclusion
The outline of the body of the hippocampal formation becomes rounded on coronal images as its volume decreases in AD.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hyman BT, Van Hoesen GW, Damasio AR, Barnes CL (1984) Alzheimer’s disease: cell-specific pathology isolates the hippocampal formation. Science 225:1168–1170
Hyman BT, Van Hoesen GW (1990) Memory-related neural systems in Alzheimer’s disease: an anatomic study. Neurology 40:1721–1730
Van Hoesen GW, Hyman BT (1990) Hippocampal formation: anatomy and the patterns of pathology in Alzheimer’s disease. Prog Brain Res 83:445–457
Hyman BT, Kromer LJ, Van Hoesen GW (1987) Reinnervation of the hippocampal perforant pathway zone in Alzheimer’s disease. Ann Neurol 21:259–267
Hyman BT, Hoesen V, Kromer LJ, Damasio AR (1986) Perforant pathway changes and the memory impairment of Alzheimer’s disease. Ann Neurol 20:472–481
Price JL, Ko AI, Wade MJ, Tsou SK, Mckeel DW, Morris JC (2001) Neuron number in the entorhinal cortex, and CA1 in preclinical Alzheimer disease. Arch Neurol 58:1395–1402
Bobinski M, de Leon MJ, Tarnawski M et al (1998) Neuron and volume loss in CA1 of the hippocampal formation uniquely predicts duration and severity of Alzheimer disease. Brain Res 805:267–269
Ashburner J, Friston KJ (2000) Voxel-based morphometry—the methods. Neuroimage 11:805–821
Baron JC, Chételat G, Desgranges B et al (2001) In vivo mapping of gray matter loss with voxel-based morphometry in mild Alzheimer’s disease. Neuroimage 14:298–309
Chételat G, Landeau B, Eustache F et al (2005) Using voxel-based morphometry to map the structural changes associated with rapid conversion in MCI: a longitudinal MRI study. Neuroimage 27:934–946
Raji CA, Lopez OL, Kuller LH, Carmichael OT, Becker JT (2009) Age, Alzheimer disease, and brain structure. Neurology 73:1899–1905
Ohnishi T, Matsuda H, Tabira T, Asada T, Uno M (2001) Changes in brain morphology in Alzheimer disease and normal aging: is Alzheimer disease an exaggerated aging process? AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 22:1680–1685
Good CD, Johnsrude IS, Ashbuner J, Henson RN, Friston KJ, Frackowiak RS (2001) A voxel-based morphometric study of aging in 465 normal adult human brains. Neuroimage 14:21–36
Ishii K, Kawachi T, Sasaki H et al (2005) Voxel-based morphometry between early and late onset types of mild Alzheimer’s disease and assessing its diagnostic performance with Z score image. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 26:333–340
Adachi M, Kawanami T, Kawakatsu S, Shibata A, Ohshima F (2007) Rounding of the hippocampus in Alzheimer’s disease: a study by routine coronal magnetic resonance imaging. Radiat Med 25:224–228
Miller BL, Gearhart R (1999) Neuroimaging in the diagnosis of frontotemporal dementia. Dement Geriat Cogn Disord 10:71–74
Neary D, Snowden JS, Gustafson L et al (1998) Frontotemporal lobar degeneration: a consensus on clinical diagnostic criteria. Neurology 51:1546–1554
McKeith IG, Dickson DW, Lowe J et al (2005) Diagnosis and management of dementia with Lewy bodies: third report of the DLB consortium. Neurology 65:1863–1872
Kitagaki H, Mori E, Ishii K, Yamaji S, Hirono N, Imamura T (1998) CSF spaces in idiopathic normal pressure hydrocephalus; morphology and volumetry. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 19:1277–1284
Adachi M, Kawanami T, Ohshima F, Kato T (2006) Upper midbrain profile sign and cingulate sulcus sign: MRI findings on sagittal images in idiopathic normal pressure hydrocephalus, Alzheimer’s disease, and progressive supranuclear palsy. Radiat Med 24:568–572
Adachi M, Kawanami T, Ohshima H, Sugai Y, Hosoya T (2004) Morning glory sign: a particular MR finding in progressive supranuclear palsy. Magn Reson Med Sci 3:125–132
Oikawa H, Sasaki M, Tamakawa Y, Ehara S, Tohyama K (2002) The substantia nigra in Parkinson disease: proton density-weighted spin-echo and fast short inversion time inversion-recovery MR findings. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 23:1747–1756
Killiany RJ, Hyman BT, Gomez-Isla T, et al (2002) MRI measures of entorhinal cortex vs hippocampus in preclinical AD. Neurology 58:1188–1196
Adachi M, Kawakatsu S, Hosoya T et al (2003) Morphology of the inner structure of the hippocampal formation in Alzheimer disease. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 24:1575–1581
Jack CR, Petersen RC, Xu Y, O’Brien PC, Smith GE, Ivnik RJ et al (2000) Rates of hippocampal atrophy correlate with change in clinical status in aging and AD. Neurology 55:484–489
Bobinski M, Wegiel J, Tarnawski M et al (1997) Relationships between regional neuronal loss and neurofibrillary changes in the hippocampal formation and duration and severity of Alzheimer disease. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 56:414–420
Bobinski M, Wegiel J, Wisniewski HM et al (1996) Neurofibrillary pathology—correlation with hippocampal formation atrophy in Alzheimer disease. Neurobiol Aging 17:909–919
Hirata Y, Matsuda H, Nemoto K et al (2005) Voxel-based morphometry to discriminate early Alzheimer’s disease from controls. Neurosci Lett 382:269–274
Duara R, Loewenstein DA, Potter E et al (2008) Medial temporal lobe atrophy on MRI scans and the diagnosis of Alzheimer disease. Neurology 71:1986–1992
Urs R, Potter E, Barker W et al (2009) Visual rating system for assessing magnetic resonance images: a tool in the diagnosis of mild cognitive impairment and Alzheimer disease. J Comput Assist Tomogr 33:73–78
Conflict of interest
We declare that we have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Adachi, M., Kawakatsu, S., Sato, T. et al. Correlation between volume and morphological changes in the hippocampal formation in Alzheimer’s disease: rounding of the outline of the hippocampal body on coronal MR images. Neuroradiology 54, 1079–1087 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00234-012-1019-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00234-012-1019-7