Abstract
Introduction
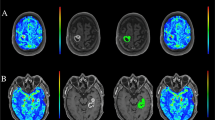
Hemangioblastoma and metastatic tumors are the major differential diagnoses for the posterior fossa tumors in adults. Our purpose was to evaluate the efficacy of ASL in differentiating hemangioblastomas from metastatic brain tumors.
Methods
A total of 19 patients including 5 with a hemangioblastomas and 14 with metastatic tumors (7 from lung cancer, 4 from breast cancer, 1 from RCC, 1 from gastric cancer, and 1 from unknown origin) were enrolled in this study. ASL was performed using a pulsed ASL method at a 3-T unit. aTBF was measured as a mean absolute blood flow value within a region of interest drawn in the tumor. In addition, rTBF was obtained by normalizing the aTBF by a blood flow measured in the normal-appearing cortical gray matter. The aTBF and rTBF values were compared between hemangioblastomas and metastatic tumors using Student’s t test.
Results
Both the aTBF and rTBF values were significantly higher in hemangioblastomas (mean aTBF ± SD = 437 ± 274 mL/100 g/min, mean rTBF ± SD = 7.96 ± 3.12) in comparison with metastatic brain tumors (mean aTBF ± SD = 125 ± 134 mL/100 g/min, mean rTBF ± SD = 2.98 ± 3.91; p < 0.05, respectively). However, a metastasis from RCC showed very high aTBF (559 mL/100 g/min) and rTBF (16.2).
Conclusion
Our results demonstrated that ASL provides useful information to differentiate between hemangioblastomas and metastatic brain tumors. Metastasis from RCC may mimic hemangioblastoma on ASL blood flow measurement.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chaudhry AP, Montes M, Cohn GA (1978) Ultrastructure of cerebellar hemangioblastoma. Cancer 42:1834–1850
Catapano D, Muscarella LA, Guarnieri V et al (2005) Hemangioblastomas of central nervous system: molecular genetic analysis and clinical management. Neurosurgery 56:1215–1221
Yoshida S, Takahashi H (2009) Cerebellar metastases in patients with cancer. Surg Neurol 71:184–187
Kanner AA, Suh JH, Siomin VE et al (2003) Posterior fossa metastases: aggressive treatment improves survival. Stereotact Funct Neurosurg 81:18–23
Soffietti R, Rudā R, Mutani R (2002) Management of brain metastases. J Neurol 249:1357–1369
Chaskis C, Stadnik T, Michotte A et al (2006) Prognostic value of perfusion-weighted imaging in brain glioma: a prospective study. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 148:277–285
Warmuth C, Gunther M, Zimmer C (2003) Quantification of blood flow in brain tumors: comparison of arterial spin labeling and dynamic susceptibility-weighted contrast-enhanced MR imaging. Radiology 228:523–532
Järnum H, Steffensen EG, Knutsson L et al (2010) MRI of brain tumours: a comparative study of pseudo-continuous arterial spin labelling and dynamic susceptibility contrast imaging. Neuroradiology 52:307–317
Detre JA, Alsop DC, Vives LR et al (1998) Noninvasive MRI evaluation of cerebral blood flow in cerebrovascular disease. Neurology 50:633–641
Chalela JA, Alsop DC, Gonzalez-Atavales JB et al (2000) Magnetic resonance perfusion imaging in acute ischemic stroke using continuous arterial spin labeling. Stroke 31:680–687
Alsop DC, Detre JA, Grossman M (2000) Assessment of cerebral blood flow in Alzheimer’s disease by spin-labeled magnetic resonance imaging. Ann Neurol 47:93–100
Yoshiura T, Hiwatashi A, Noguchi T et al (2009) Arterial spin labelling at 3-T MR imaging for detection of individuals with Alzheimer’s disease. Eur Radiol 19:2819–2825
Chawla S, Wang S, Wolf RL et al (2007) Arterial spin-labeling and MR spectroscopy in the differentiation of gliomas. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 28:1683–1689
Kim HS, Kim SY (2007) A prospective study on the added value of pulsed arterial spin-labeling and apparent diffusion coefficients in the grading of gliomas. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 28:1693–1699
Noguchi T, Yoshiura T, Hiwatashi A et al (2008) Perfusion imaging of brain tumors using arterial spin-labeling: correlation with histopathologic vascular density. Am J Neuroradiol 29:688–693
Tourdias T, Rodrigo S, Oppenheim C et al (2008) Pulsed arterial spin labeling applications in brain tumors: practical review. Neuroradiol 35:79–89
Petersen ET, Lim T, Golay X (2006) Model-free arterial spin labeling quantification approach for perfusion MRI. Magn Reson Med 55:219–232
Look DC, Locker DR (1970) Time saving in measurement of NMR and EPR relaxation times. Rev Sci Instrum 41:250–251
Lehmann P, Monet P, de Marco G et al (2010) A comparative study of perfusion measurement in brain tumours at 3 Tesla MR: arterial spin labeling versus dynamic susceptibility contrast-enhanced MRI. Eur Neurol 64:21–26
Loeber RT, Sherwood AR, Renshaw PF et al (1999) Differences in cerebellar blood volume in schizophrenia and bipolar disorder. Schizophr Res 37:81–89
Löbel U, Sedlacik J, Reddick WE et al (2011) Quantitative diffusion-weighted and dynamic susceptibility-weighted contrast-enhanced perfusion MR imaging analysis of T2 hypointense lesion components in pediatric intrinsic pontine glioma. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 32:315–322
Kimura H, Takeuchi H, Koshimoto Y et al (2006) Perfusion imaging of meningioma by using continuous arterial spin-labeling: comparison with dynamic susceptibility-weighted contrast-enhanced MR images and histopathologic features. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 27:85–93
Pedrosa I, Alsop DC, Rofsky NM (2009) Magnetic resonance imaging as a biomarker in renal cell carcinoma. Cancer 115(10 Suppl):2334–2345
Pfefferbaum A, Chanraud S, Pitel AL et al (2010) Volumetric cerebral perfusion imaging in healthy adults: regional distribution, laterality, and repeatability of pulsed continuous arterial spin labeling (PCASL). Psychiat Res 182:266–273
Clelland CA, Treip CS (1989) Histological differentiation of metastatic renal carcinoma in the cerebellum from cerebellar haemangioblastoma in von Hippel-Lindau's disease. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 52:162–166
Kitaoka K, Abe H, Aida T et al (1990) Follow-up study on metastatic cerebellar tumor surgery—characteristic problems of surgical treatment. Neurol Med Chir (Tokyo) 30:591–598
Conflict of interest
We declare that we have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yamashita, K., Yoshiura, T., Hiwatashi, A. et al. Arterial spin labeling of hemangioblastoma: differentiation from metastatic brain tumors based on quantitative blood flow measurement. Neuroradiology 54, 809–813 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00234-011-0977-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00234-011-0977-5