Abstract
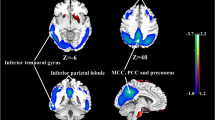
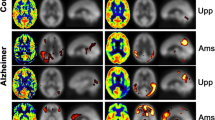
The purpose of this study was to determine whether arterial spin labelling (ASL) at 3-T MR imaging can be used to discriminate individuals with Alzheimer’s disease (AD) from cognitively normal subjects. Twenty AD patients and 23 cognitively normal control subjects were studied using ASL on a 3-T MR imager. Absolute regional cerebral blood flow (rCBF) maps were calculated. In addition, normalized rCBF maps were obtained using CBF in the sensorimotor cortex for normalization. A voxel-wise comparison of these rCBF maps between the AD and control groups was performed using the two-sample t test. Individuals with AD were discriminated from control subjects based on mean rCBF values within a region-of-interest defined by the t test, and the discriminating performance was evaluated by the receiver operating characteristic (ROC) analysis. Comparisons of both absolute and normalized rCBF maps revealed areas of significant hypoperfusion caused by the effects of AD in the bilateral precunei and posterior cingulate gyri. ROC analyses resulted in area under the curve (AUC) values of 0.861 to 0.877 for absolute and 0.910 to 0.932 for normalized rCBF. Our results suggest that ASL at 3-T MR imaging can be used to help discriminate individuals with AD from normal subjects.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hirata Y, Matsuda H, Nemoto K et al (2005) Voxel-based morphometry to discriminate early Alzheimer’s disease from controls. Neurosci Lett 382:269–274
Matsuda H (2007) Role of neuroimaging in Alzheimer’s disease, with emphasis on brain perfusion SPECT. J Nucl Med 48:1289–1300
Minoshima S, Giordani B, Berent S et al (1997) Metabolic reduction in the posterior cingulate cortex in very early Alzheimer’s disease. Ann Neurol 42:85–94
Detre JA, Leigh JS, Williams DS et al (1992) Perfusion imaging. Magn Reson Med 23:37–45
Petersen E, Zimine I, Ho Y-C et al (2006) Non-invasive measurement of perfusion: a critical review of arterial spin labelling techniques. Br J Radiol 79:688–701
McKhann G, Drachman D, Folstein M et al (1984) Clinical diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease: report of the NINCDS-ADRDA Work Group under the auspices of Department of Health and Human Services Task Force on Alzheimer’s Disease. Neurology 34:939–944
American Psychiatric Association (1994) Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders: DSM-IV, 4th edn. American Psychiatric Association, Washington
Román GC, Tatemichi TK, Erkinjuntti T et al (1993) Vascular dementia: diagnostic criteria for research studies. Report of the NINDS-AIREN International Workshop. Neurology 43:250–260
Folstein MF, Folstein SE, McHugh PR (1975) “Mini-Mental State”: a practical method for grading the cognitive state of patients for the clinician. J Psychiatr Res 12:189–198
Zung WW (1965) A self-rating depression scale. Arch Gen Psychiatry 12:63–70
Petersen ET, Lim T, Golay X (2006) Model-free arterial spin labeling quantification approach for perfusion MRI. Magn Reson Med 55:219–232
Gowland P, Mansfield P (1993) Accurate measurement of T1 in vivo in less than 3 seconds using echo-planar imaging. Magn Reson Med 30:351–354
Lu H, Clingman C, Golay X et al (2004) Determining the longitudinal relaxation time (T1) of blood at 3.0 Tesla. Magn Reson Med 52:679–682
Herscovitch P, Raichle ME (1985) What is the correct value for the brain–blood partition coefficient for water? J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 5:65–69
Brun A, Gustafson L (1976) Distribution of cerebral degeneration in Alzheimer’s disease. A clinico-pathological study. Arch Psychiat Nervenkr 223:15–33
Braak H, Braak E (1991) Neuropathological staging of Alzheimer-related changes. Acta Neuropathol 82:239–259
Alsop DC, Detre JA, Grossman M (2000) Assessment of cerebral blood flow in Alzheimer’s disease by spin-labeled magnetic resonance imaging. Ann Neurol 47:93–100
Johnson NA, Jahng G-H, Welner MW et al (2005) Pattern of cerebral hypoperfusion in Alzheimer disease and mild cognitive impairment measured with arterial spin-labeling MR imaging: initial experience. Radiology 234:851–859
Kogure D, Matsuda H, Ohnishi T et al (2000) Longitudinal evaluation of early Alzheimer’s disease using brain perfusion SPECT. J Nucl Med 41:1155–1162
Ishii K, Sasaki M, Yamaji S et al (1997) Demonstration of decreased posterior cingulate perfusion in mild Alzheimer’s disease by means of H2 15O positron emission tomography. Eur J Nucl Med 24:670–673
Greicius MD, Srivastava G, Reiss AL et al (2004) Default-mode network activity distinguishes Alzheimer’s disease from healthy aging: evidence from functional MRI. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101:4637–4642
Asllani I, Habeck C, Scarmeas N et al (2008) Multivariate and univariate analysis of continuous arterial spin labeling perfusion MRI in Alzheimer’s disease. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 28:725–736
Petersen ET, Golay X (2008) The QUASAR reproducibility study. Is arterial spin labeling ready for prime time? Preliminary results from the QUASAR reproducibility study. In: Proceeding of the 16th meeting of the International Society for Magnetic Resonance in Medicine. Toronto, Canada. International Society for Magnetic Resonance in Medicine, p 191
Latchaw RE, Yonas H, Hunter GJ et al (2003) Guideline and recommendations for perfusion imaging in cerebral ischemia: a scientific statement for healthcare professionals by the writing group on perfusion imaging, from the council on cardiovascular radiology of the American Heart Association. Stroke 34:1084–1104
Ishii K, Sasaki M, Matsui M et al (2000) A diagnostic method for suspected Alzheimer’s disease using H(2)15O positron emission tomography perfusion Z score. Neuroradiology 42:787–794
Ishii K, Kawachi T, Sasaki H et al (2005) Voxel-based morphometric comparison between early- and late-onset mild Alzheimer’s disease and assessment of diagnostic performance of Z score images. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 25:333–340
Kawachi T, Ishii K, Sakamoto S et al (2006) Comparison of the diagnostic performance of FDG-PET and VBM-MRI in very mild Alzheimer’s disease. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 33:801–809
Harris GJ, Lewis RF, Satlin A et al (1996) Dynamic susceptibility contrast MRI of regional cerebral blood volume in Alzheimer’s disease. Am J Psychiatry 153:721–724
Jahng G-H, Song E, Zhu X-P et al (2005) Human brain: reliability and reproducibility of pulsed arterial spin-labeling perfusion MR imaging. Radiology 234:909–916
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yoshiura, T., Hiwatashi, A., Noguchi, T. et al. Arterial spin labelling at 3-T MR imaging for detection of individuals with Alzheimer’s disease. Eur Radiol 19, 2819–2825 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-009-1511-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-009-1511-6