Abstract
Introduction
Thrombosis of the cerebral veins and sinus are common causes of stroke. Animal models help us to understand the underlying pathophysiology of this condition. Therefore, the purpose of our study was to evaluate a well-established model for sinus sagittalis (SSS) thrombosis using micro- and nanocomputed tomography (CT) imaging.
Methods
SSS thrombosis was performed in four rats. After contrast perfusion, brains were isolated and scanned using micro-CT at (8 µm)³ voxel size to generate 3D images of the cerebral vasculature. For more detailed information on vascular perfusion territories, nano-CT imaging was performed to investigate the boundary layer of contrast-enhanced vessels and the occluded veins. The venous and arterial vascular volume fraction and gray scale measurements were obtained in the SSS thrombosis group and compared to controls. The significance of differences in vascular volume fraction and gray scale measurements was tested with analysis of variance. Results were complemented with histology.
Results
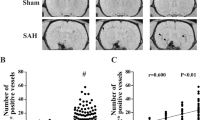
Micro-CT proved to accurately visualize and differentiate vascular occlusion territories performed in the SSS thrombosis model. Moreover, 3D micro-CT provided quantitative information on arterial and venous vascular volume fraction. Micro-CT imaging enables a total 3D visualization of complications (ventricle rupture) in the SSS thrombosis model. We established gray scale measurements by which focal cerebral ischemia could be radiographically categorized (p < 0.001).
Conclusions
Using nano-CT, the interface of contrast-perfused and occluded veins can be visualized. Micro-CT is feasible for analysis and differentiation of perfusion territories in an animal model of focal cerebral ischemia.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Stolz E, Trittmacher S, Rahimi A, Gerriets T, Rottger C, Siekmann R, Kaps M (2004) Influence of recanalization on outcome in dural sinus thrombosis: a prospective study. Stroke 35:544–547
Stolz E, Gerriets T, Bodeker RH, Hugens-Penzel M, Kaps M (2002) Intracranial venous hemodynamics is a factor related to a favorable outcome in cerebral venous thrombosis. Stroke 33:1645–1650
Rottger C, Bachmann G, Gerriets T, Kaps M, Kuchelmeister K, Schachenmayr W, Walberer M, Wessels T, Stolz E (2005) A new model of reversible sinus sagittalis superior thrombosis in the rat: magnetic resonance imaging changes. Neurosurgery 57:573–580
Srivastava AK, Kalita J, Haris M, Gupta RK, Misra UK (2009) Radiological and histological changes following cerebral venous sinus thrombosis in a rat model (epub ahead of print) (Record Supplied By Publisher). Neurosci Res
Langheinrich AC, Bohle RM, Greschus S, Hackstein N, Walker G, Von Gerlach S, Rau WS, Holschermann H (2004) Atherosclerotic lesions at micro CT: feasibility for analysis of coronary artery wall in autopsy specimens. Radiology 231:675–681
Langheinrich AC, Michniewicz A, Bohle RM, Ritman EL (2007) Vasa vasorum neovascularization and lesion distribution among different vascular beds in ApoE-/-/LDL-/- double knockout mice. Atherosclerosis 191:73–81
Langheinrich AC, Leithauser B, Greschus S, Von Gerlach S, Breithecker A, Matthias FR, Rau WS, Bohle RM (2004) Acute rat lung injury: feasibility of assessment with micro-CT. Radiology 233:165–171
Gerriets T, Stolz E, Walberer M, Muller C, Kluge A, Bachmann A, Fisher M, Kaps M, Bachmann G (2004) Noninvasive quantification of brain edema and the space-occupying effect in rat stroke models using magnetic resonance imaging. Stroke 35:566–571
Walberer M, Stolz E, Muller C, Friedrich C, Rottger C, Blaes F, Kaps M, Fisher M, Bachmann G, Gerriets T (2006) Experimental stroke: ischaemic lesion volume and oedema formation differ among rat strains (a comparison between Wistar and Sprague-Dawley rats using MRI). Lab Anim 40:1–8
Rottger C, Madlener K, Heil M, Gerriets T, Walberer M, Wessels T, Bachmann G, Kaps M, Stolz E (2005) Is heparin treatment the optimal management for cerebral venous thrombosis? Effect of abciximab, recombinant tissue plasminogen activator, and enoxaparin in experimentally induced superior sagittal sinus thrombosis. Stroke 36:841–846
Reese T, Bochelen D, Sauter A, Beckmann N, Rudin M (1999) Magnetic resonance angiography of the rat cerebrovascular system without the use of contrast agents. NMR Biomed 12:189–196
Gerriets T, Stolz E, Walberer M, Muller C, Rottger C, Kluge A, Kaps M, Fisher M, Bachmann G (2004) Complications and pitfalls in rat stroke models for middle cerebral artery occlusion: a comparison between the suture and the macrosphere model using magnetic resonance angiography. Stroke 35:2372–2377
Beckmann N (2000) High resolution magnetic resonance angiography non-invasively reveals mouse strain differences in the cerebrovascular anatomy in vivo. Magn Reson Med 44:252–258
Rother J, Waggie K, van Bruggen N, de Crespigny AJ, Moseley ME (1996) Experimental cerebral venous thrombosis: evaluation using magnetic resonance imaging. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 16:1353–1361
McDannold N, Vykhodtseva N, Jolesz FA, Hynynen K (2004) MRI investigation of the threshold for thermally induced blood-brain barrier disruption and brain tissue damage in the rabbit brain. Magn Reson Med 51:913–923
Vernooij MW, Ikram MA, Tanghe HL, Vincent AJ, Hofman A, Krestin GP, Niessen WJ, Breteler MM, Van der LA (2007) Incidental findings on brain MRI in the general population. N Engl J Med 357:1821–1828
De Vita E, Thomas DL, Roberts S, Parkes HG, Turner R, Kinchesh P, Shmueli K, Yousry TA, Ordidge RJ (2003) High resolution MRI of the brain at 4.7 Tesla using fast spin echo imaging. Br J Radiol 76:631–637
Bernstein MA, Huston J, Lin C, Gibbs GF, Felmlee JP (2001) High-resolution intracranial and cervical MRA at 3.0T: technical considerations and initial experience. Magn Reson Med 46:955–962
Pfeuffer J, Adriany G, Shmuel A, Yacoub E, Van De Moortele PF, Hu X, Ugurbil K (2002) Perfusion-based high-resolution functional imaging in the human brain at 7 tesla. Magn Reson Med 47:903–911
Glover PM, Bowtell RW, Brown GD, Mansfield P (1994) A microscope slide probe for high resolution imaging at 11.7 Tesla. Magn Reson Med 31:423–428
Stracke CP, Spuentrup E, Katoh M, Gunther RW, Spangenberg P (2006) New experimental model of sinus and cortical vein thrombosis in pigs for MR imaging studies. Neuroradiology 48:721–729
Stracke CP, Katoh M, Wiethoff AJ, Parsons EC, Spangenberg P, Spuntrup E (2007) Molecular MRI of cerebral venous sinus thrombosis using a new fibrin-specific MR contrast agent. Stroke 38:1476–1481
Langheinrich AC, Michniewicz A, Sedding DG, Walker G, Beighley PE, Rau WS, Bohle RM, Ritman EL (2006) Correlation of vasa vasorum neovascularization and plaque progression in aortas of apolipoprotein E(-/-)/low-density lipoprotein(-/-) double knockout mice. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 26:347–352
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank G. Martels, Justus-Liebig University, Giessen, Germany, for technical assistance. The investigation was supported in part from the Faculty of Human Medicine of the Justus-Liebig University, Giessen, Germany, and the DFG (German Research Foundation) under contract number INST 162/291-1 FUGG. We also thank the Pitzer-Foundation for technical support.
Conflict of interest statement
We declare that we have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Alexander C. Langheinrich, Mesut Yeniguen, and Anne Ostendorf contributed equally to the study
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Langheinrich, A.C., Yeniguen, M., Ostendorf, A. et al. In vitro evaluation of the sinus sagittalis superior thrombosis model in the rat using 3D micro- and nanocomputed tomography. Neuroradiology 52, 815–821 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00234-009-0617-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00234-009-0617-5