Abstract
Introduction
The aim of this work is to assess the usefulness of apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) value of the brain for diagnosis of patients with Gaucher’s disease type II and type III.
Methods
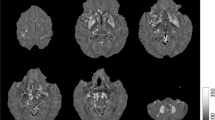
Prospective study was conducted upon 13 patients (nine boys and four girls aged 8 months–14 years: mean 6.1 years) with Gaucher’s disease type II and III and for age-matched control group (n = 13). Diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging using a single-shot echo-planar imaging with a diffusion-weighted factor b of 0, 500, and 1,000 s/mm2 was done for all patients and volunteers. The ADC value was calculated in ten regions of the brain parenchyma and correlated with genotyping.
Results
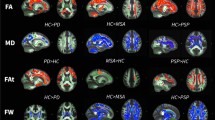
There was significantly lower ADC value of the cortical frontal (P = 0.003), cortical temporal (P = 0.04), frontal subcortical white matter (P = 0.02), corticospinal tract (P = 0.001), cerebellum (P = 0.001), medulla (P = 0.002), and midbrain (P = 0.02) between patients and volunteers. There was significant difference in the ADC value of the frontal and temporal gray matter (P = 0.04 and 0.05, respectively) between patients with heterozygous and homozygous gene mutation.
Conclusion
We concluded that ADC value is a new promising quantitative imaging parameter that can be used for the detection of brain abnormalities in patients with Gaucher’s disease type II and type III and has a correlation with genotyping.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Elstein D, Abrahamov A, Hadas-Halpern I, Zimran A (2001) Gaucher’s disease. Lancet 358:324–327
Sidransky E (2004) Gaucher disease: complexity in a “simple” disorder. Mol Genet Metab 83:6–15
Brady RO (2003) Gaucher’s disease: past, present and future. Bailliere’s Clin Haematol 10:621–634
Charrow J, Andersson HC, Kaplan P et al (2000) The Gaucher’s registry: demographics and disease characteristics of 1,698 patients with Gaucher’s disease. Arch Intern Med 160:2835–2843
Mehta A (2006) Epidemiology and natural history of Gaucher’s disease. Eur J Intern Med 17:S2–S5
Cherin P, Sedel F, Mignot C et al (2006) Neurological manifestations of type 1 Gaucher’s disease: is a revision of disease classification needed? Rev Neurol 162:1076–1083
Erikson A, Bembi B, Schiffmann R (1997) Neuronopathic forms of Gaucher’s disease. Bailliere’s Clin Haematol 10:711–723
Grewal R, Doppelt S, Thompson M, Katz D, Brady R, Barton N (1991) Neurologic complications of nonneuronopathic Gaucher’s disease. Arch Neurol 48:1271–1272
Vellodi A, Bembi B, de Villemeur T, Collin-Histed T, Erikson A, Mengel E et al (2001) Management of neuropathic Gaucher disease: a European consensus. J Inherit Metab Dis 24:319–327
Barranger JA, Rice EO, Swaney WP (1999) Gene transfer approaches to the lysosomal storage disorders. Neurochem Res 24:601–615
Pasmanik-Chor M, Madar-Shapiro L, Stein O, Aerts H, Gatt S, Horowitz M (1997) Expression of mutated glucocerebrosidasecerebrosidase alleles in human cells. Hum Mol Genet 6:887–895
Sibille E, Eng C, Kim S et al (1993) Phenotype/genotype correlations in Gaucher disease type I: clinical and therapeutic implications. Am J Hum Genet 52:1094–1101
Koprivica V, Stone DL, Park JK, Callahan M, Frisch A, Cohen IJ et al (2000) Analysis and classification of 304 mutant alleles in patients with type 1 and type 3 Gaucher disease. Am J Hum Genet 66:1777–1786
Hyerowitz R, Mizukami H, Richardson K, Finn L, Tivt C, Proia R (2004) Global gene expression in a type 2 Gaucher disease brain. Mol Genet Metab 83:288–296
Tayebi N, Stone D, Sidransky E (1999) Type 2 Gaucher disease: an expanding phenotype. Mol Genet Metab 68:209–219
Thoeny H, Keyzer F (2007) Extracranial applications of diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging. Eur Radiol 17:1385–1393
Aicardi J (1993) The inherited leukodystrophies: a clinical overview. J Inherit Metab Dis 16:733–743
Blaster S, Feigenbaum A (2004) A neuroimaging approach to inborn errors of metabolism. Neuroimaging Clin N Am 14:307–329
Meikle P, Hopwood J, Clague A (1999) Prevalence of lysosomal storage disorders. JAMA 281:249–254
Chang YC, Huang CC, Chen CY, Zimmerman RA (2000) MRI in acute neuropathic Gaucher’s disease. Neuroradiology 42:48–50
Lin DS, Lin SP, Liang DC, Ho CS, Wu MC (1999) Technetium-99 m-HmPAO brain SPECT in infantile Gaucher’s disease. Pediatr Neurol 20:66–69
Sakuragawa N, Sasaki M, Fueki N, Yoshikawa H (1991) Uncoupling of blood flow and oxygen metabolism in the cerebellum in type 3 Gaucher disease. Brain Dev 13:190–192
Mercimek-Mahmutoglu S, Gruber S, Rolfs A, Stadlbauer A, Woeber C, Kurnik P et al (2007) Neurological and brain MRS findings in patients with Gaucher disease type 1. Mol Genet Metab 91:390–395
Patay Z (2005) Diffusion-weighted MR imaging in leukodystrophies. Eur Radiol 15:2284–2303
Schneider JFL, Il’yasov KA, Boltshauser E, Hennig J, Martin E (2003) Diffusion tensor imaging in cases of adrenoleukodystrophy: preliminary experience as a marker for early demyelination. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 24:819–824
ter Rahe B, Majoie C, Akkerman E, den Heeten G, Poll-The B, Barth P (2004) Peroxisomal biogenesis disorder: comparison of conventional MR imaging with diffusion-weighted and diffusion-tensor imaging findings. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 25:1022–1027
Sener R (2003) Metachromatic leukodystrophy. Diffusion MR imaging and proton MR spectroscopy. Acta Radiol 44:440–443
Conradi N, Kyllerman M, Mansson J, Percy A, Svennerholm L (1991) Late-infantile Gaucher disease in a child with myoclonus and bulbar signs: neuropathological and neurochemical findings. Acta Neuropathol 82:152–157
Wong K, Sidransky E, Verma A et al (2004) Neuropathology provides clues to the pathophysiology of Gaucher disease. Mol Genet Metab 82:192–207
Kaye E, Ullman M, Wilson E, Barranger J (1986) Type 2 and type 3 Gaucher disease: a morphological and biochemical study. Ann Neurol 20:223–230
Lee R (ed) (1982) The pathology of Gaucher disease. Alan R Liss, New York, pp 177–217
Sener RN (2001) Diffusion MRI: apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) values in the normal brain and a classification of brain disorders based on ADC values. Comput Med Imaging Graph 25:299–326
Zhang L, Thomas K, Davidson M, Casey B, Heier L, Ulug A (2005) MR quantitation of volume and diffusion changes in the developing brain. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 26:45–49
Conflict of interest statement
We declare that we have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Abdel Razek, A.A.K., Abd El-Gaber, N., Abdalla, A. et al. Apparent diffusion coefficient vale of the brain in patients with Gaucher’s disease type II and type III. Neuroradiology 51, 773–779 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00234-009-0548-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00234-009-0548-1