Abstract
Introduction
The purpose of our study was to determine the diagnostic role of diffusion-weighted imaging (DWI) in the differentiating of malignant and benign thyroid nodules by using fine needle aspiration biopsy cytology criteria as a reference standard. The apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) values of the normal-looking thyroid parenchyma were also evaluated both in normal patients and in patients with nodules.
Methods
Between March 2007 and February 2008, 76 consecutive patients with ultrasound-diagnosed thyroid nodules and 20 healthy subjects underwent diffusion-weighted MR imaging by using single-shot spin echo, echo planar imaging. A total of 93 nodules were included in the study using the following b factors 100, 200, and 300 mm2/s. ADC values of thyroid nodules and normal area in all subjects were calculated and compared using suitable statistical analysis.
Results
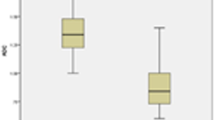
Mean ADC values for malignant and benign nodules were \(0.96 \pm 0.65 \times 10^{ - 3} \) and \(3.06 \pm 0.71 \times 10^{ - 3} {{{\text{mm}}^2 } \mathord{\left/ {\vphantom {{{\text{mm}}^2 } {\text{s}}}} \right. \kern-\nulldelimiterspace} {\text{s}}}\) for b-100 factor, \(0.56 \pm 0.43 \times 10^{ - 3} \) and \(1.80 \pm 0.60 \times 10^{ - 3} {{{\text{mm}}^2 } \mathord{\left/ {\vphantom {{{\text{mm}}^2 } \operatorname{s} }} \right. \kern-\nulldelimiterspace} \operatorname{s} }\) for b-200, and \(0.30 \pm 0.20 \times 10^{ - 3} \) and \(1.15 \pm 0.43 \times 10^{ - 3} {{{\text{mm}}^2 } \mathord{\left/ {\vphantom {{{\text{mm}}^2 } \operatorname{s} }} \right. \kern-\nulldelimiterspace} \operatorname{s} }\), for b-300, respectively. Mean ADC values of malignant nodules were lower than benign nodules. There were significant differences in ADC values between benign and malignant nodules. ADC values among normal-appearing thyroid parenchyma of patients and normal-appearing thyroid parenchyma of healthy subjects were insignificant at all b factors.
Conclusion
Benign nodules have higher ADC values than malignant ones. DWI may be helpful in differentiating malign and benign thyroid nodules.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cooper DS, Doherty GM, Haugen BR, Kloos RT, Lee SL, Mandel SJ, Mazzaferri EL, McIver B, Sherman SI, Tuttle RM (2006) Management guidelines for patients with thyroid nodules and differentiated thyroid cancer. Thyroid 16:109–142
Hegedüs L (2004) Clinical practice. The thyroid nodule. N Engl J Med 351:1764–1771
Werk EE Jr, Vernon BM, Gonzalez JJ, Ungaro PC, McCoy RC (1984) Cancer in thyroid nodules. A community hospital survey. Arch Intern Med 144:474–476
Maeda M, Kato H, Sakuma H, Maier SE, Takeda K (2005) Usefulness of the apparent diffusion coefficient in line scan diffusion-weighted imaging for distinguishing between squamous cell carcinomas and malignant lymphomas of the head and neck. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 26:1186–1192
Le Bihan D, Breton E, Lallemand D, Aubin ML, Vignaud J, Laval-Jeantet M (1988) Separation of diffusion and perfusion in intravoxel incoherent motion MR imaging. Radiology 168:497–505
Warach S, Chien D, Li W, Ronthal M, Edelman RR (1992) Fast magnetic resonance diffusion-weighted imaging of acute human stroke. Neurology 42:1717–1723
Bozgeyik Z, Kocakoc E, Sonmezgoz F (2008) Diffusion-weighted MR imaging findings of kidneys in patients with early phase of obstruction. Eur J Radiol doi:10.1016/j.ejrad.2008.01.013
Wang J, Takashima S, Takayama F, Kawakami S, Saito A, Matsushita T, Momose M, Ishiyama T (2001) Head and neck lesions: characterization with diffusion-weighted echo-planar MR imaging. Radiology 220:621–630
Eida S, Sumi M, Sakihama N, Takahashi H, Nakamura T (2007) Apparent diffusion coefficient mapping of salivary gland tumors: prediction of the benignancy and malignancy. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 28:116–121
King AD, Ahuja AT, Yeung DK, Fong DK, Lee YY, Lei KI, Tse GM (2007) Malignant cervical lymphadenopathy: diagnostic accuracy of diffusion-weighted MR imaging. Radiology 245:806–813
Razek AA, Sadek AG, Kombar OR, Elmahdy TE, Nada N (2008) Role of apparent diffusion coefficient values in differentiation between malignant and benign solitary thyroid nodules. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 29:563
Vander JB, Gaston EA, Dawber TR (1968) The significance of nontoxic thyroid nodules. Final report of a 15-year study of the incidence of thyroid malignancy. Ann Intern Med 69:537–540
Wong CK, Wheeler MH (2000) Thyroid nodules: rational management. World J Surg 24:934–941
Brander A, Viikinkoski P, Nickels J, Kivisaari L (1991) Thyroid gland: US screening in a random adult population. Radiology 181:683–687
Mortensen JD, Woolner LB, Bennett WA (1955) Gross and microscopic findings in clinically normal thyroid glands. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 15:1270–1280
Solbiati L, Osti V, Cova L, Tonolini M (2001) Ultrasound of thyroid, parathyroid glands and neck lymph nodes. Eur Radiol 11:2411–2424
Tee YY, Lowe AJ, Brand CA, Judson RT (2007) Fine-needle aspiration may miss a third of all malignancy in palpable thyroid nodules: a comprehensive literature review. Ann Surg 246:714–720
Baur A, Huber A, Arbogast S, Dürr HR, Zysk S, Wendtner C, Deimling M, Reiser M (2001) Diffusion-weighted imaging of tumor recurrencies and posttherapeutical soft-tissue changes in humans. Eur Radiol 11:828–833
Ward R, Caruthers S, Yablon C, Blake M, DiMasi M, Eustace S (2000) Analysis of diffusion changes in posttraumatic bone marrow using navigator-corrected diffusion gradients. AJR Am J Roentgenol 174:731–734
Koh DM, Collins DJ (2007) Diffusion-weighted MRI in the body: applications and challenges in oncology. AJR Am J Roentgenol 188:1622–1635
Abdel Razek AA, Soliman NY, Elkhamary S, Alsharaway MK, Tawfik A (2006) Role of diffusion-weighted MR imaging in cervical lymphadenopathy. Eur Radiol 16:1468–1477
King AD, Ahuja AT, Yeung DK, Fong DK, Lee YY, Lei KI, Tse GM (2007) Malignant cervical lymphadenopathy: diagnostic accuracy of diffusion-weighted MR imaging. Radiology 245:806–813
Tezuka M, Murata Y, Ishida R, Ohashi I, Hirata Y, Shibuya H (2003) MR imaging of the thyroid: correlation between apparent diffusion coefficient and thyroid gland scintigraphy. J Magn Reson Imaging 17:163–169
Oertel YC, Oertel JE (1998) Diagnosis of malignant epithelial thyroid lesions: fine needle aspiration and histopathologic correlations. Ann Diagn Pathol 2:377–400
Anderson JR (2001) Tumours. I. General features, types and examples. In: Anderson JR (ed) Muir’s textbook of pathology, 20th edn. Edward Arnold, London, pp 12.1–12.49
Conflict of interest statement
We declare that we have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bozgeyik, Z., Coskun, S., Dagli, A.F. et al. Diffusion-weighted MR imaging of thyroid nodules. Neuroradiology 51, 193–198 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00234-008-0494-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00234-008-0494-3