Abstract
Introduction
Diagnosis of cerebral sinus vein thrombosis is still a challenge for imaging. MRI and MRA play a major role in sinus imaging. For further development of MR techniques, MR-compatible animal models are required. The aim of this study was to develop an animal model for sinus thrombosis and additional cortical vein thrombosis with a clot of human blood for MR imaging studies.
Methods
A combined surgical and interventional approach was carried out in 13 pigs. After minimal invasive surgical access to the anterior superior sagittal sinus and cortical vein, thrombosis with human blood was induced using an interventional catheter approach. MR imaging was performed prior to and after thrombus induction.
Results
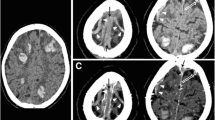
Sinus thrombosis was induced in 12 of 13 animals. Three animals suffered acute subdural haemorrhage; one of these animals died during the intervention, and one died after thrombus induction. MR imaging of the thrombosed sinus could easily be performed without significant artefacts in 11 of 13 animals.
Conclusion
This new model of sinus and cortical vein thrombosis with a clot of human blood allows artefact-free imaging studies on MR.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Renowden S (2004) Cerebral venous sinus thrombosis. Eur Radiol 14(2):215–226
Towbin A (1973) The syndrome of latent cerebral sinus venous thrombosis: its frequency and relation to age and congestive heart failure. Stroke 4:419–430
Ferro JM, Canhao P, Stam J, Mousser MG, Barinagarrementeria F; ISCVT Investigators (2004) Prognosis of cerebral vein and dural sinus thrombosis. Stroke 35(3):664–667
Stam J (2005) Thrombosis of the cerebral veins and sinuses. N Engl J Med 352:1791–1798
Sheehy NP, Bole GE, Meaney JF (2005) Normal anterior spinal arteries within the cervical region: high-spatial-resolution contrast-enhanced three dimensional MR angiography. Radiology 236(2):637–641
Ley S, Fink C, Zaporozhan J, Borst MM, Meyer FJ, Puderbach M, Eichinger M, Plathow C, Grunig E, Kreitner KF, Kauczor HU (2005) Value of high spatial and high temporal resolution magnetic resonance angiography for differentiation between idiopathic and thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension: initial results. Eur Radiol 15(11):2256–2263
Ziveh S, Strecker R, Berlis A, Weber J, Klisch J, Mader I (2005) Dynamic 3D MR angiography of intra- and extracranial vascular malformations at 3 T: a technical note. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 26(3):630–634
Ruehm SG, Zimny K, Debatin JF (2001) Direct contrast-enhanced 3D MR venography. Eur Radiol 11(1):102–112
Lovblad KO, Schneider J, Bassetti C, El-Koussy M, Guzman R, Heid O, Remonda L, Schroth G (2002) Fast contrast-enhanced MR whole-brain venography. Neuroradiology 44(8):681–688
Sparing R, Harrer JU, Spuentrup E, Krings T (2004) MR-imaging of thrombus in extra- and intracranial arteries employing balanced fast-field echo MRI. Neuroradiology 46(12):973–977
Kelly J, Hunt BJ, Moody A (2003) Magnetic resonance direct thrombus imaging: a novel technique for imaging venous thromboemboli. Thromb Haemost 89(5):773–782
Moody AR, Pollock JG, O’Connor AR, Bagnall M (1998) Lower limb deep venous thrombosis: direct MR imaging of the thrombus. Radiology 209(2):349–355
Moody AR, Liddicoat A, Krarup K (1997) Magnetic resonance pulmonary angiography and direct imaging of embolus for detection of pulmonary emboli. Invest Radiol 32(8):431–440
Botnar RM, Buecker A, Wiethoff AJ, Parsons EC, Katoh M, Katsimaglis G, Weisskoff RM, Lauffer RB, Graham PB, Gunther RW, Manning WJ, Spuentrup E (2004) In vivo magnetic resonance imaging of coronary thrombosis using a fibrin-binding molecular magnetic resonance agent. Circulation 110:1463–1466
Flacke S, Fischer S, Scott MJ, Fuhrhop RJ, Allen JS, McLean M, Winter P, Sicard GA, Gaffney PJ, Wickline SA, Lanza GM (2001) Novel MRI contrast agent for molecular imaging of fibrin: implications for detecting vulnerable plaques. Circulation 104(11):1280–1285
Yu X, Song Sk, Chen J, Scott MJ, Fuhrhop RJ, Hall CS, Gaffney PJ, Wickline SA, Lanza GM (2000) High-resolution MRI characterization of human thrombus using a novel fibrin-targeted paramagnetic nanoparticle contrast agent. Magn Reson Med 44(6):867–872
Fries G, Wallenfang T, Kempski O, Hennen J, Velthaus M, Perneczky A (1990) Brain oedema and intracranial pressure in superior sagittal sinus balloon occlusion. An experimental study in pigs. Acta Neurochir Suppl (Wien) 51:231–232
Fries G, Wallenfang T, Hennen J, Velthaus M, Heimann A, Schild H, Perneczky A, Kempki O (1992) Occlusion of the pig superior sagittal sinus, bridging and cortical veins: multistep evolution of sinus-vein thrombosis. J Neurosurg 77(1):127–133
Ito K, Tsugane R, Ikeda A, Suzuki Y, Sato K (1997) Cerebral hemodynamics and histological changes following acute cerebral venous occlusion in cats. Tokai J Exp Clin Med 22(3):83–93
Ueda K, Nakase H, Miyamoto K, Otsuka H, Sakaki T (2000) Impact of anatomical difference of the cerebral venous system on microcirculation in a gerbil superior sagittal sinus occlusion model. Acta Neurochir 142(1):75–82
Rother J, Waggie K, van Bruggen N, de Crespigny AJ, Moseley ME (1996) Experimental cerebral venous thrombosis: evaluation using magnetic resonance imaging. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 16(6):1353–1361
Rottger C, Bachmann G, Gerriets T, Kaps M, Kuchelmeister K, Schachenmayr W, Walberer M, Wessels T, Stolz E (2005) A new model for reversible sinus sagittalis superior thrombosis in the rat: magnetic resonance imaging changes. Neurosurgery 57(3):573–578
Schaller B, Graf R, Wienhard K, Heiss WD (2003) A new animal model of cerebral venous infarction: ligation of the posterior part of the superior sagittal sinus in the cat. Swiss Med Wkly 133(29–39):412–418
Sarwar M, Virapongse C, Carbo P (1985) Experimental production of superior sagittal sinus vein thrombosis in the dog. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 6(1):19–22
Acknowledgement
This study was supported in part by the German Research Council (SP634/2-1).
Conflict of interest statement
We declare that we have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Stracke, C.P., Spuentrup, E., Katoh, M. et al. New experimental model of sinus and cortical vein thrombosis in pigs for MR imaging studies. Neuroradiology 48, 721–729 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00234-006-0125-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00234-006-0125-9