Abstract.
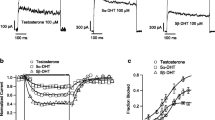
17β-estradiol propionate was found to reduce the gap junctional communication in a concentration range similar to that of testosterone propionate, in primary cultures of rat Sertoli cells and cardiac myocytes. Uncoupling was reversible on washing out and occurred without concomitant rise in the intracellular calcium concentration.
Esterification was a prerequisite for the activity of extracellularly applied steroid compounds (for example, testosterone was ineffective even at external concentrations up to 100 μm, whereas its intracellular application at 1 μm totally interrupted intercellular communication), but their uncoupling efficiency did not depend on the nature of the ester chain nor on its position on the steroid nucleus. The derivatives of two other androgen hormones (derivatives of the androstane nucleus) were also efficient as junctional uncouplers. Among five steroid molecules belonging to the pregnane family, only one (pregnanediol diacetate) interrupted the junctional communication. Neither cholic acid nor cholesteryl acetate or ouabain showed this effect. Altogether, no correlation with the presence or position of double bonds nor with the trans- or cis-fusion of the A and B rings could be recognized.
These results suggest that this reversible, nondeleterious uncoupling effect of steroids is independent of the shape of the molecules and is more probably related to their size and liposolubility, that condition their insertion into the lipid bilayer. Their incorporation into the membrane could disturb the activity of the membrane proteins by a physical mechanism.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 10 April 1995/Revised: 27 October 1995
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hervé, J., Pluciennik, F., Verrecchia, F. et al. Influence of the Molecular Structure of Steroids on Their Ability to Interrupt Gap Junctional Communication. J. Membrane Biol. 149, 179–187 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/s002329900018
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s002329900018