Abstract
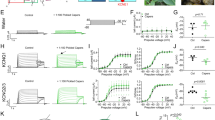
Phytochemicals are ubiquitous in naturally occurring dietary elements that exhibits diverse pharmacological properties over various pathological disorders, including cancer. Voltage gated K+ (KV) channel in the plasma membrane contributes to wide range of cellular processes including cancer progression. Therefore, modulation of KV channel is being considered as a novel potential target for cancer therapy. The whole cell patch clamp technique was used to record the modulatory effect of chrysin, naringenin, caffeic acid, gallic acid, and zingerone on delayed rectifier potassium current (IK) in human prostate cancer cells LNCaP and PC-3. Among the tested compounds, zingerone blocked IK in a concentration-dependent manner in LNCaP cells and estimated the IC50 value of 141 μM and Emax was 81.3%. Further analysis of KV channel activation kinetics showed that zingerone induces a positive shift in the activation curve in LNCaP cells, whereas the inhibitory effect of gallic acid on IK was significantly less potent than the inhibition caused by zingerone. However, chrysin, naringenin, and caffeic acid did not modulate the KV channel conductance in LNCaP or PC-3 cells. Our findings confirmed that not all the tested phytochemicals to be effective modulators of IK and suggested that IK inhibitory effect of zingerone and gallic acid may be responsible for their anticancer effects in prostate cancer cells.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdul M, Hoosein N (2002) Expression and activity of potassium ion channels in human prostate cancer. Cancer Lett 186(1):99–105
Abdul M, Hoosein N (2006) Reduced Kv1.3 potassium channel expression in human prostate cancer. J Membr Biol 214(2):99–102
Anantharaju PG, Gowda PC, Vimalambike MG, Madhunapantula SV (2016) An overview on the role of dietary phenolics for the treatment of cancers. Nutr J 15:99
Bae WY, Choi JS, Kim JE, Park C, Jeong JW (2016) Zingerone suppresses angiogenesis via inhibition of matrix metalloproteinases during tumor development. Oncotarget 7(30):47232–47241
Calderone V, Chericoni S, Martinelli C, Testai L, Nardi A, Morelli I, Breschi MC, Martinotti E (2004) Vasorelaxing effects of flavonoids: investigation on the possible involvement of potassium channels. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol 370(4):290–298
Castle NA (1992) Differential inhibition of potassium currents in rat ventricular myocytes by capsaicin. Cardiovasc Res 26(11):1137–1144
Comes N, Bielanska J, Vallejo-Gracia A, Serrano-Albarrás A, Marruecos L, Gómez D, Soler C, Condom E, Ramón Y, Cajal S, Hernández-Losa J, Ferreres JC, Felipe A (2013) The voltage-dependent K(+) channels Kv1.3 and Kv1.5 in human cancer. Front Physiol 4(283):1–13
Fraser SP, Grimes JA, Djamgoz MB (2000) Effects of voltage-gated ion channel modulators on rat prostatic cancer cell proliferation: comparison of strongly and weakly metastatic cell lines. Prostate 44(1):61–76
Fraser SP, Peters A, Fleming-Jones S, Mukhey D, Djamgoz MB (2014) Resveratrol: inhibitory effects on metastatic cell behaviors and voltage-gated Na+ channel activity in rat prostate cancer in vitro. Nutr Cancer 66(6):1047–1058
George K, Thomas NS, Malathi R (2019) Piperine blocks voltage gated K+ current and inhibits proliferation in androgen sensitive and insensitive human prostate cancer cell lines. Arch Biochem Biophys 667:36–48
Haddad AQ, Venkateswaran V, Viswanathan L, Teahan SJ, Fleshner NE, Klotz LH (2006) Novel antiproliferative flavonoids induce cell cycle arrest in human prostate cancer cell lines. Prostate Cancer Prostatic Dis 9(1):68–76
Heidarian E, Keloushadi M, Ghatreh-Samani K, Valipour P (2016) The reduction of IL-6 gene expression, pAKT, pERK1/2, pSTAT3 signaling pathways and invasion activity by gallic acid in prostate cancer PC3 cells. Biomed Pharmacother 84:264–269
Huang X, Jan LY (2014) Targeting potassium channels in cancer. J Cell Biol 206(2):151–162
Karna P, Chagani S, Gundala SR, Rida PC, Asif G, Sharma V, Gupta MV, Aneja R (2012) Benefits of whole ginger extract in prostate cancer. Br J Nutr 107(4):473–484
Kim JH, Hong EK, Choi HS, Oh SJ, Kim KM, Uhm DY, Kim SJ (2002) K+ channel currents in rat ventral prostate epithelial cells. Prostate 51(3):201–210
Kim Y, Kim WJ, Cha EJ (2011) Quercetin-induced growth inhibition in human bladder cancer cells is associated with an increase in Ca-activated K channels. Korean J Physiol Pharmacol 15(5):279–283
Lang F, Stournaras C (2014) Ion channels in cancer: future perspectives and clinical potential. Philos Trans R Soc B 369(1638):20130108
Laniado ME, Fraser SP, Djamgoz MB (2001) Voltage-gated K(+) channel activity in human prostate cancer cell lines of markedly different metastatic potential: distinguishing characteristics of PC-3 and LNCaP cells. Prostate 46(4):262–274
Lim W, Park S, Bazer FW, Song G (2017) Naringenin-induced apoptotic cell death in prostate cancer cells is mediated via the PI3K/AKT and MAPK signaling pathways. J Cell Biochem 118(5):1118–1131
Liu L, Simon SA (1996) Similarities and differences in the currents activated by capsaicin, piperine, and zingerone in rat trigeminal ganglion cells. J Neurophysiol 76(3):1858–1869
Magyar J, Szentandrássy N, Bányász T, Fülöp L, Varró A, Nánási PP (2004) Effects of terpenoid phenol derivatives on calcium current in canine and human ventricular cardiomyocytes. Eur J Pharmacol 487(1–3):29–36
Morales P, Haza AI (2012) Selective apoptotic effects of piceatannol and myricetin in human cancer cells. J Appl Toxicol 32(12):986–993
Ohya S, Kimura K, Niwa S, Ohno A, Kojima Y, Sasaki S, Kohri K, Imaizumi Y (2009) Malignancy grade-dependent expression of K+-channel subtypes in human prostate cancer. J Pharmacol Sci 109(1):148–151
Ouadid-Ahidouch H, Ahidouch A (2013) K+ channels and cell cycle progression in tumor cells. Front Physiol 4:220–228
Ouyang DY, Zeng LH, Pan H, Xu LH, Wang Y, Liu KP, He XH (2013) Piperine inhibits the proliferation of human prostate cancer cells via induction of cell cycle arrest and autophagy. Food Chem Toxicol 60:424–430
Prevarskaya N, Skryma R, Bidaux G, Flourakis M, Shuba Y (2007) Ion channels in death and differentiation of prostate cancer cells. Cell Death Differ 14(7):1295–1304
Protić D, Beleslin-Čokić B, Spremović-Rađenović S, Radunović N, Heinle H, Šćepanović R, Gojković Bukarica L (2014) The Different effects of resveratrol and naringenin on isolated human umbilical vein: the role of ATP-sensitive K+ channels. Phytother Res 28(9):1412–1418
Rao BN, Rao BS (2010) Antagonistic effects of Zingerone, a phenolic alkanone against radiation-induced cytotoxicity, genotoxicity, apoptosis and oxidative stress in Chinese hamster lung fibroblast cells growing in vitro. Mutagenesis 25(6):577–587
Reddivari L, Vanamala J, Safe SH, Miller JC Jr (2010) The bioactive compounds alpha-chaconine and gallic acid in potato extracts decrease survival and induce apoptosis in LNCaP and PC3 prostate cancer cells. Nutr Cancer 62(5):601–610
Russell LH Jr, Mazzio E, Badisa RB, Zhu ZP, Agharahimi M, Oriaku ET, Goodman CB (2012) Autoxidation of gallic acid induces ROS-dependent death in human prostate cancer LNCaP cells. Anticancer Res 32(5):1595–1602
Rybalchenko V, Prevarskaya N, Van Coppenolle F, Legrand G, Lemonnier L, Le Bourhis X, Skryma R (2001) Verapamil inhibits proliferation of LNCaP human prostate cancer cells influencing K+ channel gating. Mol Pharmacol 59(6):1376–1387
Ryu S, Lim W, Bazer FW, Song G (2017) Chrysin induces death of prostate cancer cells by inducing ROS and ER stress. J Cell Physiol 232(12):3786–3797
Sak K (2014) Cytotoxicity of dietary flavonoids on different human cancer types. Pharmacogn Rev 8(16):122–146
Samarghandian S, Afshari JT, Davoodi S (2011) Chrysin reduces proliferation and induces apoptosis in the human prostate cancer cell line PC-3. Clinics (Sao Paulo) 66(6):1073–1079
Scholz EP, Zitron E, Kiesecker C, Lück S, Thomas D, Kathöfer S, Kreye VA, Katus HA, Kiehn J, Schoels W, Karle CA (2005) Inhibition of cardiac HERG channels by grapefruit flavonoid naringenin: implications for the influence of dietary compounds on cardiac repolarisation. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol 371(6):516–525
Schönherr R (2005) Clinical relevance of ion channels for diagnosis and therapy of cancer. J Membr Biol 205(3):175–184
Singh AN, Baruah MM, Sharma N (2017) Structure based docking studies towards exploring potential anti-androgen activity of selected phytochemicals against prostate cancer. Sci Rep 7(1):1955
Skryma RN, Prevarskaya NB, Dufy-Barbe L, Odessa MF, Audin J, Dufy B (1997) Potassium conductance in the androgen-sensitive prostate cancer cell line, LNCaP: involvement in cell proliferation. Prostate 33(2):112–122
Teisseyre A, Duarte N, Ferreira MJ, Michalak K (2009) Influence of the multidrug transporter inhibitors on the activity of KV1.3 voltage-gated potassium channels. J Physiol Pharmacol 60(1):69–76
Teisseyre A, Palko-Labuz A, Uryga A, Michalak K (2018) The influence of 6-prenylnaringenin and selected non-prenylated flavonoids on the activity of Kv1.3 channels in human jurkat T cells. J Membr Biol 251(5–6):695–704
Theyer G, Schirmbock M, Thalhammer T, Sherwood ER, Baumgartner G, Hamilton G (1993) Role of the MDR-1-encoded multiple drug resistance phenotype in prostate cancer cell lines. J Urol 150(5 pt 1):1544–1547
Weng CJ, Yen GC (2012) Chemopreventive effects of dietary phytochemicals against cancer invasion and metastasis: phenolic acids, monophenol, polyphenol, and their derivatives. Cancer Treat Rev 38(1):76–87
Yue HY, Jiang CY, Fujita T, Kumamoto E (2013) Zingerone enhances glutamatergic spontaneous excitatory transmission by activating TRPA1 but not TRPV1 channels in the adult rat substantia gelatinosa. J Neurophysiol 110(3):658–671
Zhang X, Li H, Zhang H, Liu Y, Huo L, Jia Z, Xue Y, Sun X, Zhang W (2017) Inhibition of transmembrane member 16A calcium-activated chloride channels by natural flavonoids contributes to flavonoid anticancer effects. Br J Pharmacol 174(14):2334–2345
Acknowledgements
We gratefully acknowledge the funding support from University Grant Commission, New Delhi for providing Grant in the form of Basic Scientific Research fellowship for meritorious students (SRF) (No. F.7-376/2012(BSR)).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Ethical Approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
George, K., Thomas, N.S. & Malathi, R. Modulatory Effect of Selected Dietary Phytochemicals on Delayed Rectifier K+ Current in Human Prostate Cancer Cells. J Membrane Biol 252, 195–206 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00232-019-00070-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00232-019-00070-9