Abstract
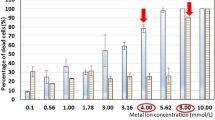
The obtained results demonstrated an influence of PEF on increase in accumulation of various ions in S. cerevisiae cells. Optimization of particular PEF parameters and ions concentrations in the medium caused twofold increase in accumulation of magnesium and zinc ions and 3.5-fold higher accumulation of calcium ions in the cells. In the case of ion couple, accumulation of magnesium and zinc was, respectively, 1.5-fold and twofold higher in comparison to the control cultures. Yeast cells biomass enriched with Mg2+, Zn2+, Ca2+ as well as Mg2+ and Zn2+ (simultaneously) may be an alternative for pharmacological supplementation applied in deficiency of these cations.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aronsson K, Rönner U, Borch E (2005) Inactivation of Escherichia coli, Listeria innocua and Saccharomyces cerevisiae in relation to membrane permeabilization and subsequent leakage of intracellular compounds due to pulsed electric field processing. Int J Food Microbiol 99:19–32
Blackwell KJ, Tobin JM, Avery SV (1997) Manganese uptake and toxicity in magnesium-supplemented and unsupplemented Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Appl Microbiol Biotech 47:180–184
Błażejak S, Duszkiewicz-Reinhard W, Gniewosz M, Mazurkiewicz B (2004) Distribution of magnesium in the Candida utilis ATCC 9950 yeast cells enriched in that element (in Polish). Acta Sci Pol Technol Aliment 3:95–110
Bonin S, Ślusarska M (2007) Influence of addition of magnesium and calcium salts to high-sugar musts on the process of wine fermentation and biomass growth (in Polish). Żywn Nauk Technol Ja 4:109–119
Cha JY, Cho YS (2009) Determination of optimal conditions for zinc hyperaccumulation by Saccharomyces cerevisiae FF-10. J Korean Soc Appl Biol Chem 52:227–233
Cho DH, Kim EY (2003) Characterization of Pb2 + biosorption from aqueous solution by Rhodotorula glutinis. Bioprocess Biosyst Eng 25:271–277
De Nicola R, Walker GM (2009) Accumulation and cellular distribution of zinc by brewing yeast. Enzym Microb Technol 44:2010–2016
Duszkiewicz-Reinhard W, Gniewosz M, Błażejak S, Bańkowski A (2002) Badania zdolności wiązania magnezu przez drożdże piekarskie Saccharomyces cerevisiae w hodowli stacjonarnej. Acta Sci Pol Technol Aliment 1:17–26
Gniewosz M, Błażejak S, Roman J, Duszkiewicz-Reinhard W (2006) A study on Saccharomyces cerevisiae and Candida utilis cell wall capacity for binding magnesium. Eur Food Res Technol 224:49–54
Korolczuk J, Mc Keag JR, Fernandez JC, Baron F, Grosset N, Jeantet R (2006) Effect of pulsed electric field processing parameters on Salmonella enteritidis inactivation. J Food Eng 75:11–20
Liu GJ, Martin DK, Gardner RC, Ryan PR (2002) Large Mg2+—dependent currents are associated with the increased expression of ALR1 in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Microbiol Lett 213:231–237
Lotan R, Berdicevsky I, Merzbach D, Grossowicz N (1976) Effect of calcium ions on growth and metabolism of Saccharomyces carlsbergensis. J Gen Microbiol 92:76–80
Mochaba F, O’Connor-Cox ESC, Axcell BC (1996a) Effects of yeast quality on the accumulation and release of metal causing beer instability. J Am Soc Brew Chem 54:164–171
Mochaba F, O’Connor-Cox ESC, Axcell BC (1996b) Metal ion concentration and release by a brewing yeast: characterization and implications. J Am Soc Brew Chem 54:155–163
Pankiewicz U, Jamroz J (2010) Effect of pulsed electric fields upon accumulation of magnesium in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Eur Food Res Technol 231:663–668
Pankiewicz U, Jamroz J (2011) Effect of pulsed electric fields upon accumulation of zinc in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Microbiol Biotechnol 21:646–651
Pankiewicz U, Jamroz J (2013) Application of pulsed electric field for enrichment of Saccharomyces cerevisiae cells with calcium ions. Ital J Food Sci 4:394–402
Pankiewicz U, Sujka M, Włodarczyk-Stasiak M, Mazurek A, Jamroz J (2014) Effect of pulse electric fields (PEF) on accumulation of magnesium and zinc ions in Saccharomyces cerevisiae cells. Food Chem 157:125–131
Pasternakiewicz A, Tuszyński T (1997) Effect of calcium, magnesium, cobalt (II), and zinc cations on the Saccharomyces cerevisiae growth. Pol J Food Nutr Sci 4:61–70
Shao Z, Sun F (2007) Intracellular sequestration of manganese and phosphorus in a metal-resistant fungus Cladosporium cladosporioides from deep-sea sediment. Extremophiles 11:435–443
Stehlik-Tomas V, Zetic VG, Stanzer D, Grba S, Vahcic N (2004) Zinc, copper and manganese enrichment in yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Food Technol Biotechnol 42:115–120
Torregrosa F, Esteve MD, Frigola A, Cortes C (2006) Ascorbic acid stability during refrigerated storage of orange-carrot juice treated by high pulsed electric field and comparison with pasteurized juice. J Food Eng 73:339–345
Tuszyński T, Pasternakiewicz A (2000) Bioaccumulation of metal ions by yeast cells of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Pol J Food Nutr Sci 4:31–39
Vinopal S, Ruml T, Kotrba P (2007) Biosorption of Cd2+ and Zn2+ by cell surface-engineered Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Int Biodeter Biodegr 60:96–102
Walker GM, Maynard AI (1996) Magnesium-limited growth of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Enzym Microbiol Technol 18:455–459
Williams RJP, Frausto da Silva JJR (2000) The distribution of elements in cells. Coord Chem Rev 200–202:247–348
Yamanaka M, Hara K, Kudo J (2005) Bactericidal actions of a silver ion solution on Escherichia coli, studied by energy-filtering Transmission Electron Microscopy and proteomic analysis. Appl Environ Microbiol 71:7589–7593
Yaseen M, Pedley K, Howell S (1982) Regulation of insulin secretion from islets of langerhans rendered permeable by electric discharge. Biochem J 206:81–87
Zimmermann U (1986) Electrical breakdown, electropermeabilization and electrofusion. Rev Physiol Biochem Pharmacol 105:175–256
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pankiewicz, U., Sujka, M. & Jamroz, J. Bioaccumulation of the Selected Metal Ions in Saccharomyces cerevisiae Cells Under Treatment of the Culture with Pulsed Electric Field (PEF). J Membrane Biol 248, 943–949 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00232-015-9844-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00232-015-9844-3