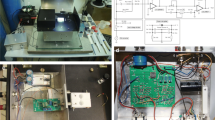
Abstract
We present a system for measuring planar lipid bilayer properties. The system is composed of a control unit, an output stage, an LCR meter, pumps for filling reservoirs, a bath with temperature regulation and a measurement chamber with four electrodes. The planar lipid bilayer is automatically formed using a folding method on apertures of different sizes. The automatization is assured by two syringes, which are clamped in actuators. Actuators are driven and controlled by a control unit via RS-232 communication. The temperature of the planar lipid bilayer can be regulated between 15 and 55 °C. The regulation is assured by insertion of the measurement chamber into the temperature-regulated bath. Different shapes of voltage- or current-clamp signals can be applied to the planar lipid bilayer. By measuring the response of the planar lipid bilayer to the applied signal, the capacitance and breakdown voltage of the planar lipid bilayer can be determined. The cutoff frequencies of the system output stage for voltage- and current-clamp methods are 11 and 17 kHz, respectively.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Antonov VF, Anosov AA, Norik VP et al (2003) Electrical capacitance of lipid bilayer membranes of hydrogenated egg lecithin at the temperature phase transition. Eur Biophys J 32:55–59
Basu R, De S, Ghosh D, Nandy P (2001) Nonlinear conduction in bilayer lipid membranes—effect of temperature. Phys A 292:146–152
Benz R, Fröhlich O, Läuger P, Montal M (1975) Electrical capacity of black lipid films and of lipid bilayers made from monolayers. Biochim Biophys Acta 394:323–334
Boheim G, Hanke W, Eibl H (1980) Lipid phase transition in planar bilayer membrane and its effect on carrier- and pore-mediated ion transport. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 77:3403–3407
Chen C, Smye SW, Robinson MP, Evans JA (2006) Membrane electroporation theories: a review. Med Biol Eng Comput 44:5–14
Coronado R, Latorre R (1983) Phospholipid bilayers made from monolayers on patch-clamp pipettes. Biophys J 43:231–236
Daud AI, DeConti RC, Andrews S et al (2008) Phase I trial of interleukin-12 plasmid electroporation in patients with metastatic melanoma. J Clin Oncol 26:5896–5903
Davalos RV, Mir LM, Rubinsky B (2005) Tissue ablation with irreversible electroporation. Ann Biomed Eng 33:223–231
Denet AR, Vanbever R, Préat V (2004) Skin electroporation for transdermal and topical delivery. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 56:659–674
Funakoshi K, Suzuki H, Takeuchi S (2006) Lipid bilayer formation by contacting monolayers in a microfluidic device for membrane protein analysis. Anal Chem 78:8169–8174
Golberg A, Fischer J, Rubinsky B (2010) The use of irreversible electroporation in food preservation. In: Rubinsky B (ed) Irreversible electroporation. Springer, Berlin, pp 273–312
Huang C, Wheeldon L, Thompson TE (1964) The properties of lipid bilayer membranes separating two aqueous phases: formation of a membrane of simple composition. J Mol Biol 8:148–160
Kalinowski S, Figaszewski Z (1995) A 4-electrode potentiostat–galvanostat for studies of bilayer lipid membranes. Meas Sci Technol 6:1050–1055
Katsaras J, Gutberlet T (2010) Lipid bilayers: structure and interactions. Springer, Berlin
Kotnik T, Bobanovic F, Miklavcic D (1997) Sensitivity of transmembrane voltage induced by applied electric fields—a theoretical analysis. Bioelectrochem Bioenerg 43:285–291
Kramar P, Miklavcic D, Lebar AM (2007) Determination of the lipid bilayer breakdown voltage by means of linear rising signal. Bioelectrochemistry 70:23–27
Kramar P, Miklavcic D, Kotulska M, Lebar AM (2010) Voltage- and current-clamp methods for determination of planar lipid bilayer properties. Academic Press, San Diego, pp 29–69
Levine ZA, Vernier PT (2010) Life cycle of an electropore: field-dependent and field-independent steps in pore creation and annihilation. J Membr Biol 236:27–36
Luckey M (2008) Membrane structural biology: with biochemical and biophysical foundations. Cambridge University Press, New York
Maor E, Ivorra A, Rubinsky B (2009) Nonthermal irreversible electroporation: novel technology for vascular smooth muscle cell ablation. PLoS One 4:e4757
Meier W, Graff A, Diederich A, Winterhalter M (2000) Stabilization of planar lipid membranes: a stratified layer approach. Phys Chem Chem Phys 2:4559–4562
Mekid H, Mir LM (2000) In vivo cell electrofusion. Biochim Biophys Acta 1524:118–130
Montal M, Mueller P (1972) Formation of bimolecular membranes from lipid monolayers and a study of their electrical properties. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 69:3561–3566
Mueller P, Rudin DO, Tien HT, Wescott WC (1963) Methods for the formation of single bimolecular lipid membranes in aqueous solution. J Phys Chem 67:534–535
Naumowicz M, Petelska A, Figaszewski Z (2003) Capacitance and resistance of the bilayer lipid membrane formed of phosphatidylcholine and cholesterol. Cell Mol Biol Lett 8:5–8
Ogura A, Matsuda J, Yanagimachi R (1994) Birth of normal young after electrofusion of mouse oocytes with round spermatids. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 91:7460–7462
Ottova A, Tien H (2002) The 40th anniversary of bilayer lipid membrane research. Bioelectrochemistry 56:171–173
Ouagari KE, Teissié J, Benoist H (1995) Glycophorin A protects K562 cells from natural killer cell attack. J Biol Chem 270:26970–26975
Prausnitz MR (1999) A practical assessment of transdermal drug delivery by skin electroporation. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 35:61–76
Punnamaraju S, Steckl AJ (2010) Voltage control of droplet interface bilayer lipid membrane dimensions. Langmuir 27:618–626
Sersa G, Miklavcic D, Cemazar M et al (2008) Electrochemotherapy in treatment of tumours. Eur J Surg Oncol 34:232–240
Tarek M (2005) Membrane electroporation: a molecular dynamics simulation. Biophys J 88:4045–4053
Teissié J (1998) Transfer of foreign receptors to living cell surfaces: the bioelectrochemical approach. Bioelectrochem Bioenerg 46:115–120
Tekle E, Astumian RD, Friauf WA, Chock PB (2001) Asymmetric pore distribution and loss of membrane lipid in electroporated DOPC vesicles. Biophys J 81:960–968
Tieleman DP, Leontiadou H, Mark AE, Marrink S-J (2003) Simulation of pore formation in lipid bilayers by mechanical stress and electric fields. J Am Chem Soc 125:6382–6383
Tokumasu F, Jin AJ, Dvorak JA (2002) Lipid membrane phase behaviour elucidated in real time by controlled environment atomic force microscopy. J Electron Microsc (Tokyo) 51:1–9
Vernhes MC, Benichou A, Pernin P et al (2002) Elimination of free-living amoebae in fresh water with pulsed electric fields. Water Res 36:3429–3438
Weaver JC, Chizmadzhev YA (1996) Theory of electroporation: a review. Bioelectrochem Bioenerg 41:135–160
White SH (1974) Temperature-dependent structural changes in planar bilayer membranes: solvent “freeze-out”. Biochim Biophys Acta 356:8–16
White SH (1978) Formation of “solvent-free” black lipid bilayer membranes from glyceryl mono oleate dispersed in squalene. Biophys J 23:337–347
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Slovenian Research Agency. The research was conducted in the scope of the EBAM European Associated Laboratory.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Polak, A., Mulej, B. & Kramar, P. System for Measuring Planar Lipid Bilayer Properties. J Membrane Biol 245, 625–632 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00232-012-9476-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00232-012-9476-9