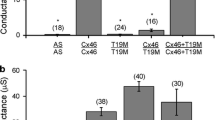
Abstract
The cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator (CFTR) is a chloride (Cl−) channel known to influence the function of other channels, including connexin channels. To further study potential functional interactions between CFTR and gap junction channels, we have co-expressed CFTR and connexin45 (Cx45) in Xenopus oocytes and monitored junctional conductance and voltage sensitivity by dual voltage clamp electrophysiology. In single oocytes expressing CFTR, an increase in cAMP caused by forskolin application induced a Cl− current and increased membrane conductance; application of diphenylamine carboxylic acid (CFTR blocker) readily blocked the Cl− current. With co-expression of CFTR and Cx45, application of forskolin to paired oocytes induced a typical outward current and increased junctional conductance (Gj). In addition, the presence of CFTR reduced the transjunctional voltage sensitivity of Cx45 channels without affecting the kinetics of junctional current inactivation. The drop in voltage sensitivity was further enhanced by forskolin application. The data indicate that CFTR influences cell-to-cell coupling mediated by Cx45 channels.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
L.C. Barrio T. Suchyna T. Bargiello L.X. Xu R.S. Roginski M.V.L. Bennett B.J. Nicholson (1991) ArticleTitleGap junctions formed by connexins 26 and 32 alone and in combination are differently affected by applied voltage Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 88 8410–8414
C.E. Bear F. Duguay A.L. Naismith N. Kartner J.W. Hanrahan J.R. Riordan (1991) ArticleTitleCl− channel activity in Xenopus oocytes expressing the cystic fibrosis gene J Biol. Chem. 268 19142–19145
F.F. Bukauskas A. Bukauskiene V.K. Verselis M.V.L. Bennett (2002) ArticleTitleCoupling asymmetry of heterotypic connexin 45/connexin 43-EGFP gap junctions: Properties of fast and slow gating mechanisms Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 99 7113–7118
F.F. Bukauskas C. Peracchia (1997) ArticleTitleTwo distinct gating mechanisms in gap junction channels: CO2-sensitive and voltage-sensitive Biophys. J. 72 2137–2142
M. Chanson I. Scerri S. Suter (1999) ArticleTitleDefective regulation of gap junction coupling in cystic fibrosis pancreatic duct cells J. Clin. Invest. 103 1677–1684
J. Cheng W.B. Guggino (1998) ArticleTitleMolecular cloning and characterization of a novel PDZ domain containing protein that interact with CFTR Pediatr. Pulmonol. 26 IssueIDSuppl–17 213
J. Cheng H. Wang W.B. Guggino (2004) ArticleTitleModulation of mature cystic fibrosis transmembrane regulator protein by the PDZ domain protein CAL J. Biol. Chem. 279 1892–1898
S.A. Cunningham R.T. Worrell D.J. Benos R.A. Frizzell (1992) ArticleTitlecAMP-stimulated ion currents in Xenopus oocytes expressing CFTR cRNA Am. J. Physiol. 262 C783–C788
A. DiStefano M. Wittner E. Schlatter H. Lang H. Englert R. Greger (1985) ArticleTitleDiphenylamine-2-carboxylate, a blocker of the Cl–conductive pathway in Cl− transporting epithelia Pfluegers Arch. 405 S95–S100
M.L. Drumm D.J. Wilkinson L.S. Smit R.T. Worrell T.V. Strong R.A. Frizzell D.C. Dawson F.S. Collins (1991) ArticleTitleChloride conductance expressed by delta F508 and other CFTRs in Xenopus oocytes Science 254 1797–1799
S. Elenes A.D. Martinez M. Delmar E.G. Beyer A.P. Moreno (2001) ArticleTitleHeterotypic docking of Cx43 and Cx45 connexons blocks fast voltage gating of Cx43 Biophys. J. 81 1406–1418
D. Gadsby A.C. Nairn (1999) ArticleTitleControl of CFTR channel gating by phosphorylation and nucleotide hydrolysis Physiol. Rev. 79 77–107
R. Greger R. Schreiber M. Mall A. Wissner A. Hopf M. Briel M. Bleich R. Warth K. Kunzelmann (2001) ArticleTitleCystic fibrosis and CFTR Pfluegers Arch. 443 S3–S7
P.M. Haggie B.A. Stanton A.S. Verkman (2004) ArticleTitleIncreased diffusional mobility of CFTR at the plasma membrane after deletion of its C-terminal PDZ binding motif J. Biol. Chem. 279 5494–5500
A.L. Harris (2001) ArticleTitleEmerging issues of connexin channels: Biophysics fills the gap Quart. Rev. Biophys. 34 325–472
PJ. Kausalya M. Reichert W. Hunziker (2001) ArticleTitleConnexin45 directly binds to ZO-1 and localizes to the tight junction region in epithelial MDCK cells FEES Lett. 505 92–96
K. Kunzelmann (2001) ArticleTitleCFTR: interacting with everything? News Physiol Sci. 16 167–170
J.G. Laing R.N. Manley-Markowski M. Koval R. Civitelli T.H. Steinberg (2001) ArticleTitleConnexin45 interacts with zonula occludens-1 in osteoblastic cells Cell. Comm. Adhes. 8 208–212
A. Lazrak C. Peracchia (1993) ArticleTitleGap junction gating sensitivity to physiological internal calcium regardless of pH in Novikoff hepatoma cells Biophys. J. 65 2002–2012
C. Peracchia (1990a) ArticleTitleIncrease in gap junction resistance with acidification in crayfish septate axons is closely related to changes in intracellular calcium but not hydrogen ion concentration J. Membrane Biol. 113 75–92
C. Peracchia (1990b) ArticleTitleEffects of caffeine and ryanodine on low pHi-induced changes in gap junction conductance and calcium concentration in crayfish septate axons J. Membrane Biol. 117 79–89
Peracchia, C. 2004. Chemical gating of gap junction channels. Roles of calcium, pH and calmodulin. In: The Connexins. J.C. Hervé, editor Biochim. Biophys. Acta (Biomembranes) 1662:61–80
C. Peracchia X. Wang L. Li L.L. Peracchia (1996) ArticleTitleInhibition of calmodulin expression prevents low-pH-induced gap junction uncoupling in Xenopus oocytes Pfluegers Arch. 431 379–387
C. Peracchia X.G. Wang L.L. Peracchia (1999) ArticleTitleIs the chemical gate of connexins voltage sensitive? Behavior of Cx32 wild-type and mutant channels Am. J. Physiol. 276 C1361–C1373
C. Peracchia X.G. Wang L.L. Peracchia (2000) ArticleTitleSlow gating of gap junction channels and calmodulin J. Membrane Biol. 78 55–70
C. Peracchia K.C. Young X.G. Wang L.L. Peracchia (2003) ArticleTitleIs the voltage gate of connexins CO2-sensitive? Cx45 channels and inhibition of calmodulin expression J. Membrane Biol. 195 53–62
D. Reczek M. Berryman A. Bretscher (1997) ArticleTitleIdentification of EBP50: a PDZ-containing phosphoprotein that associates with members of the ezrin-radixin-moesin family J. Cell. Biol. 139 169–179
M.M. Reddy P.M. Quinton (2002) ArticleTitleEffect of anion transport blockers on CFTR in human sweat duct J Membrane Biol. 189 15–25
B.D. Schultz A.K. Singh D.C. Devor R.J. Bridges (1999) ArticleTitlePharmacology of CFTR chloride channel activity Physiol. Rev. 79 S109–S144
E.M. Schwiebert M.E. Egan T.H. Hwang S.B. Fulmer S.S. Alien G.R. Cutting W.B. Guggino (1995) ArticleTitleCFTR regulates outwardly rectifying chloride channels through an autocrine mechanism involving ATP Cell 81 1063–1073
D.N. Sheppard M.J. Welsh (1999) ArticleTitleStructure and function of the CFTR chloride channel Physiol. Rev. 79 S23–S45
D.C. Spray A.L. Harris M.V.L. Bennett (1981) ArticleTitleEquilibrium properties of a voltage-dependent junctional conductance J. Gen. Physiol. 77 77–93
M.J. Stutts C.M. Canessa J.C. Olsen M. Hamrick J.A. Cohn B.C. Rossier R.C. Boucher (1995) ArticleTitleCFTR as a cAMP-dependent regulator of sodium channels Science 269 847–850
M. Sugita Y. Yue J.K. Foskett (1998) ArticleTitleCFTR Cl− channel and CFTR-associated ATP channel: distinct pores regulated by common gates EMBO J. 17 898–908
S. Wang M. Li (2001) ArticleTitleMolecular studies of CFTR interacting proteins Pfluegers Arch. 443 S62–S64
S. Wang H. Yue R.B. Derin W.B. Guggino M. Li (2000) ArticleTitleAccessory protein facilitated CFTR-CFTR interaction, a molecular mechanism to potentiate the chloride channel activity Cell 103 169–179
D. Yoo O. Olsen V. Raghuram J.K. Foskett P.A. Welling (2004) ArticleTitleAssembly and trafficking of a multiprotein ROMK (Kir 1.1) chan- nel complex by PDZ interactions J. Biol Chem. 279 6863–6873
Z.R. Zhang S. Zeltwanger N.A. McCarty (2000) ArticleTitleDirect comparison of NPPB and DPC as probes of CFTR expressed in Xenopus oocytes J. Membrane Biol. 175 35–52
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by the National Institutes of Health, grant GM20113. The authors thank Dr. D.C. Devor (University of Pittsburgh) for the generous gift of human CFTR cDNA, Mr. Joey T. Chen for preparing CFTR cRNA, and Ms. Lillian M. Peracchia for technical assistance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kotsias, B., Peracchia, C. Functional Interaction Between CFTR and Cx45 Gap Junction Channels Expressed in Oocytes. J Membrane Biol 203, 143–150 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00232-005-0739-6
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00232-005-0739-6