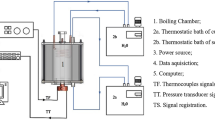
Abstract
An experimental study of nucleate pool boiling is conducted on the GNP/Ni-Al2O3 (GNP-graphene nano particle) nano-composite coated copper surfaces at atmospheric pressure using distilled water (DI) as boiling fluid. The microporous coated surfaces are fabricated using hybrid method (electrochemical deposition of GNP and nano-composite coating of Ni-Al2O3). A modified surface structure is generated as a result of this deposition, and different surface morphological parameters of this modified structure, such as surface structure, roughness and wettability, are investigated. Results show the enhancement in boiling heat transfer coefficient (BHTC) and critical heat flux (CHF) in nano-composite coated surfaces compared to the bare Cu surface. The improvement in boiling performance is mostly attributable to the enhancement of roughness and wettability as well as the higher thermal conductivity of the GNP/Ni-Al2O3 nano-coating. The highest CHF of 2217 (kW/m2) and BHTC of 112.83 (kW/m2K) is found in case of composite nano-coated superhydrophilic (CNCS) surfaces, which are 104% and 123% more than the bare Cu surface. High-speed visualization is used to conduct a quantitative investigation of the dynamics of bubble, including active bubble site density, emission frequency of the bubble, bubble departure diameter and their impact on the performance of pool boiling heat transfer.
Graphical Abstract
















Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Data may be available on request.
Abbreviations
- BHTC [kW/m2k]:
-
Boiling heat transfer coefficient
- CHF [kW/m2]:
-
Critical heat flux
- kcu [W/mK]:
-
Copper thermal conductivity
- Ra [mm]:
-
Value of average surface roughness
- H [kW/m2k]:
-
Coefficient of heat transfer
- q// [kW/m2]:
-
Heat flux
- dT/dx [K/m]:
-
Temperature gradient
- T1 [K]:
-
Thermocouple 1 temperature
- T2 [K]:
-
Thermocouple 2 temperature
- T3 [K]:
-
Thermocouple 3 temperature
- ΔT [K]:
-
Wall superheat
- Tf [K]:
-
Saturation temperature of boiling fluid
- Ts [K]:
-
Temperature of surface
- x [m]:
-
Distance between thermocouple
- y [m]:
-
Distance between thermocouple 1 and testing sample
- Dd [m]:
-
Departure diameter of bubble
- Na [cm− 2]:
-
Active nucleation site density
- CA [θ]:
-
Contact angle
- λ [J/kg]:
-
Latent heat of vaporization
- μ [(N s)/m2]:
-
Dynamic viscosity
- \(\uprho\) [kg/m3]:
-
Density
- σ [N/m]:
-
Surface tension
- Cp [J/(kg K)]:
-
Specific heat at constant pressure
References
Moita AS, Teodori E, Moreira ALN (2015) Influence of surface topography in the boiling mechanisms. Int J Heat and Fluid Flow 52:50–63. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijheatfluidflow.2014.11.003
Kim JS, Girard A, Jun S, Lee J, You SM (2018) Effect of surface roughness on pool boiling heat transfer of water on hydrophobic surfaces. Int J Heat Mass Transf 118:802–811. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijheatmasstransfer.2017.10.124
Arenales MRM, Kumar S, Kuo LS, Chen PH (2020) Surface roughness variation effects on copper tubes in pool boiling of water. Int J Heat Mass Transf 151:119399. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijheatmasstransfer.2020.119399
Phan HT, Caney N, Marty P, Colasson S, Gavillet J (2009) Surface wettability control by nano-coating: The effects on pool boiling heat transfer and nucleation mechanism. Int J Heat Mass Transf 52:5459–5471. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijheatmasstransfer.2009.06.032
Wang YQ, Luo JL, Heng Y, Mo DC, Lyu SS (2018) Wettability modification to further enhance the pool boiling performance of the micro nano bi-porous copper surface structure. Int J Heat Mass Transf 119:333–342. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijheatmasstransfer.2017.11.080
Mohammadi N, Fadda D, Choi CK, Lee J, You SM (2018) Effects of surface wettability on pool boiling of water using super-polished silicon surfaces. Int J Heat Mass Transf 127:1128–1137. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijheatmasstransfer.2018.07.122
Mogra A, Pandey PK, Gupta KK (2021) Influence of surface wettability and selection of coating material for enhancement of heat transfer performance. Materials Today: Proc 44:4433–4438. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2020.10.595
Jun S, Kim J, You SM, Kim HY (2016) Effect of heater orientation on pool boiling heat transfer from sintered copper microporous coating in saturated water. Int J Heat Mass Transf 103:277–284. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijheatmasstransfer.2016.07.030
Chuang TJ, Chang YH, Ferng YM (2019) Investigating effects of heating orientations on nucleate boiling heat transfer, bubble dynamics, and wall heat flux partition boiling model for pool boiling. Appl Therm Eng 163:114358. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.applthermaleng.2019.114358
Kim J, Jun S, Laksnarain R, You SM (2016) Effect of surface roughness on pool boiling heat transfer at a heated surface having moderate wettability. Int J Heat Mass Transf 101:992–1002. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijheatmasstransfer.2016.05.067
Alvariño PF, Simón MLS, Guzella MS, Paz JMA, Jabardo JMS, Gómez LC (2019) Experimental investigation of the CHF of HFE-7100 under pool boiling conditions on differently roughened surfaces. Int J Heat Mass Transf 139:269–279. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijheatmasstransfer.2019.04.142
Yim K, Lee J, Naccarato B, Kim KJ (2019) Surface wettability effect on nucleate pool boiling heat transfer with titanium oxide (TiO2) coated heating surface. Int J Heat Mass Transf 133:352–358. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijheatmasstransfer.2018.12.075
Shi J, Jia X, Feng D, Chen Z, Dang C (2020) Wettability effect on pool boiling heat transfer using a multiscale copper foam surface. Int J Heat Mass Transf 146:118726. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijheatmasstransfer.2019.118726
Ahn HS, Sinha N, Zhang M, Banerjee D, Baughman SFRH (2006) Pool boiling experiments on multiwalled carbon nanotube (MWCNT) forests. J Heat Transf 128:1335–1342. https://doi.org/10.1115/1.2349511
Ji X, Xu J, Zhao Z, Yang W (2013) Pool boiling heat transfer on uniform and non-uniform porous coating surfaces. Exp Therm Fluid Sci 48:198–212. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.expthermflusci.2013.03.002
Lu MC, Chen R, Srinivasan V, Carey VP, Majumdar A (2011) Critical heat flux of pool boiling on Si nanowire array-coated surfaces. Int J Heat Mass Transf 54:5359–5367. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijheatmasstransfer.2011.08.007
Cao Z, Liu B, Preger C, Wu Z, Zhang Y, Wang X, Messing ME, Deppert K, Wei J, Sundén B (2018) Pool boiling heat transfer of FC-72 on pin-fin silicon surfaces with nanoparticle deposition. Int J Heat Mass Transf 126:1019–1033. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijheatmasstransfer.2018.05.033
Saelim N, Magaraphan R, Sreethawong T (2011) Preparation of sol–gel TiO2/purified Na-bentonite composites and their photovoltaic application for natural dye-sensitised solar cells. Energy Convers Manage 52:2815–2818. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enconman.2011.02.016
Das S, Kumar DS, BhaumikS, (2016) Experimental study of nucleate pool boiling heat transfer of water on silicon oxide nanoparticle coated copper heating surface. Appl Therm Eng 96:555–567. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.applthermaleng.2015.11.117
Tang Y, Tang B, Li Q, Qing J, Lu L, Chen K (2013) Pool-boiling enhancement by novel metallic nanoporous surface. Exp Therm Fluid Sci 44:194–198. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.expthermflusci.2012.06.008
Sen P, Kalita S, Sen D, Das S, Das AK (2022) Pool boiling heat transfer on a micro-structured copper oxide surface with varying wettability. Chem Eng Technol 45:808–816. https://doi.org/10.1002/ceat.202100558
Jo HS, An S, Park HG, Kim MW, Al-Deyab SS, James SC, Choi J, Yoon SS (2017) Enhancement of critical heat flux and superheat through controlled wettability of cuprous-oxide fractal-like nanotextured surfaces in pool boiling. Int J Heat Mass Transf 107:105–111. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijheatmasstransfer.2016.11.029
Das S, Saha B, Bhaumik S (2017) Experimental study of nucleate pool boiling heat transfer of water by surface functionalization with SiO2 nanostructure. Exp Therm Fluid Sci 81:454–465. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.expthermflusci.2016.09.009
Huang CK, Lee CW, Wang CK (2011) Boiling enhancement by TiO2 nanoparticle deposition. Int J Heat Mass Transf 54:4895–4903. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijheatmasstransfer.2011.07.001
Kim SJ, Bang IC, Buongiorno J, Hu LW (2007) Surface wettability change during pool boiling of nanofluids and its effect on critical heat flux. Int J Heat Mass Transf 50:4105–4116. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijheatmasstransfer.2007.02.002
Gupta SK, Misra RD (2018) Experimental study of pool boiling heat transfer on copper surfaces with Cu-Al2O3 nanocomposite coatings. Int J Heat Mass Transf 97:47–55. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.icheatmasstransfer.2018.07.004
Jun S, Ray SS, Yarin AL (2013) Pool boiling on nano-textured surfaces. Int J Heat Mass Transf 62:99–111. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijheatmasstransfer.2013.02.046
CilogluD BA (2015) A comprehensive review on pool boiling of nanofluids. Appl Therm Engg 84:45–63. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.applthermaleng.2015.03.063
Ciloglu D (2017) An experimental investigation of nucleate pool boiling heat transfer of nanofluids from a hemispherical surface. Heat Transf Engg 38(10):919–930. https://doi.org/10.1080/01457632.2016.1212571
Bolukbasi A, Ciloglu D (2011) Pool boiling heat transfer characteristics of vertical cylinder quenched by SiO2-waternanofluids. Int J Therm Sci 50(6):1013–1021. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijthermalsci.2011.01.011
MaoL, Zhou W, Hu X, He Y, Zhang G, Zhang L, Fu R (2020) Pool boiling performance and bubble dynamics on graphene oxide nano-coating surface. Int J Therm Sci 147:106154. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijthermalsci.2019.106154
Seo H, Chu JH, KwonbSY BIC (2015) Pool boiling CHF of reduced graphene oxide, graphene, and SiC-coated surfaces under highly wettable FC-72. Int J Heat Mass Transf 82:490–502. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijheatmasstransfer.2014.11.019
Zhou W, Mao L, Hu X, He Y (2019) An optimised graphene oxide self-assembly surface for significantly enhanced boiling heat transfer. Carbon 150:168–178. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbon.2019.04.119
Rishi AM, Kandlikar SG, Gupta A (2019) Improved wettability of graphene nanoplatelets (GNP)/copper porous coatings for dramatic improvements in pool boiling heat transfer. Int J Heat Mass Transf 132:462–472. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijheatmasstransfer.2018.11.169
Gupta SK, Misra RD (2019) Effect of two-step electrodeposited Cu–TiO2 nanocomposite coating on pool boiling heat transfer performance. J Therm Anal Calorim 136:1781–1793. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-018-7805-7
Rishi AM, Gupta A, Kandlikar SG (2018) Improving Aging Performance of Electrodeposited Copper Coatings during Pool Boiling. Appl Therm Eng 140:406–414. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.applthermaleng.2018.05.061
Gheitaghy AM, Saffari H, Mohebbi M (2016) Investigation pool boiling heat transfer in U-shaped mesochannel with electrodeposited porous coating. Exp Therm Fluid Sci 76:87–97. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.expthermflusci.2016.03.011
Patil CM, Santhanam KSV, Kandlikar SG (2014) Development of a two-step electrodeposition process for enhancing pool boiling. Int J Heat Mass Transf 79:989–1001. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijheatmasstransfer.2014.08.062
Rohsenow WM (1952) A method of correlating heat transfer data for surface boiling of liquids. Trans ASME 74:969–975. https://doi.org/10.1115/1.4015984
Fang X, Dong A (2016) A comparative study of correlations of critical heat flux of pool boiling. J Nucl Sci Tech 54:1–12. https://doi.org/10.1080/00223131.2016.1209138
O'Hanley H, Coyle C, Buongiorno J, McKrell T, Hu LW (2013) Separate effects of surface roughness, wettability, and porosity on the boiling critical heat flux. Appl Phys Lett 103:024102. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.4813450
Phan HT, Caney N, Marty P, Colasson S, Gavillet J (2009) Surface wettability control by nanocoating: The effects on pool boiling heat transfer and nucleation mechanism. Int J Heat Mass Transf 52:5459–5471. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijheatmasstransfer.2009.06.032
Chu KH, Enright R, Wang EN (2012) Structured surfaces for enhanced pool boiling heat transfer. Appl Phys Lett 100:241603. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.4724190
Wang CH, Dhir VK (1993) Effect of surface wettability on active nucleation site density during pool boiling of water on a vertical surface. J Heat Transf 115:659–669. https://doi.org/10.1115/1.2910737
Hsu CC, Chen PH (2012) Surface wettability effects on critical heat flux of boiling heat transfer using nanoparticle coatings. Int J Heat Mass Transf 55:3713–3719. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijheatmasstransfer.2012.03.003
Mao L, Zhou W, Hu X, Yu H, Zhang G, Zhang L, Fu R (2020) Pool boiling performance and bubble dynamics on graphene oxide nanocoating surface. Int J Therm Sci 147:106154. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijthermalsci.2019.106154
Kwark SM, Kumar R, Moreno G, Yoo J, You SM (2010) Pool boiling characteristics of low concentration nanofluids. Int J Heat Mass Transf 53:972–981. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijheatmasstransfer.2009.11.018
Betz AR, Xu J, Qiu H, Attinger D (2010) Do surfaces with mixed hydrophilic and hydrophobic areas enhance pool boiling?. Appl Phys Lett 97:141909. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.3485057
Shi B, Wang YB, Chen K (2015) Pool boiling heat transfer enhancement with copper nanowire arrays. Appl Therm Eng 75:115–121. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.applthermaleng.2014.09.040
Dharmendra M, Suresh S, C.S. Kumar S, Yang Q, (2016) Pool boiling heat transfer enhancement using vertically aligned carbon nanotube coatings on a copper substrate. Appl Therm Eng 99:61–71. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.applthermaleng.2015.12.081
Das AK, Das PK, Saha P (2007) Nucleate boiling of water from plain and structured surfaces. Exp Therm Fluid Sci 31:967–977. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.expthermflusci.2006.10.006
Cook D, Kandlikar SG (2012) Effect of open microchannel geometry on pool boiling enhancement. Int J Heat Mass Transf 55:1004–1013. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijheatmasstransfer.2011.10.010
Mori S, Okuyama K (2009) Enhancement of the critical heat flux in saturated pool boiling using honeycomb porous media. Int J Multiph Flow 35:946–951. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijmultiphaseflow.2009.05.003
Cole R (1967) Bubble frequencies and departure volumes at sub atmospheric pressures. AIChE J 13:779–783. https://doi.org/10.1002/aic.690130434
Zuber N (1959) Hydrodynamic aspects of boiling heat transfer. United States Atomic Energy Commission, Technical Information Service. https://doi.org/10.2172/4175511
Fritz W (1935) Berechnung des maximale volume von dampfblasen. Phys Z 36:379–384
Zuber N (1963) Nucleate boiling. The region of isolated bubbles and the similarity with natural convection. Int J Heat Mass Transf 6:53–78. https://doi.org/10.1016/0017-9310(63)90029-2
Kocamustafaogullari G, Ishii M (1983) Aireinterfacialeetdensite de sites de nucleation dans les systemes en ebullition. Int J Heat Mass Transf 26:1377–1387. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0017-9310(83)80069-6
Benjamin RJ, Balakrishnan AR (1997) Nucleation Site Density in Pool Boiling of Saturated Pure Liquids: Effect of Surface Microroughness and Surface and Liquid Physical Properties. Exp Therm Fluid Sci 15:32–42. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0894-1777(96)00168-9
Saeidi D, Alemrajabi AA (2013) Experimental investigation of pool boiling heat transfer and critical heat flux of nanostructured surfaces. Int J Heat Mass Transf 60:440–449. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijheatmasstransfer.2013.01.016
Yeom H, Sridharan K, Corradini M (2015) Bubble dynamics in pool boiling on nanoparticle-coated surfaces. Heat Transf Eng 36:1013–1027. https://doi.org/10.1080/01457632.2015.979116
Tey E, Hashim M, Ismail I (2015) Characterization of Cu-Al2O3 and Ni-Al2O3 nanocomposites electrodeposited on copper substrate. Materials Sci Forum 846:471–478. https://doi.org/10.4028/www.scientific.net/MSF.846.471
MacNamaraa RJ, Luptona TL, Lupoia R, Robinson AJ (2019) Enhanced nucleate pool boiling on copper-diamond textured surfaces. Appl Therm Eng 162:114145. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.applthermaleng.2019.114145
Nikolic ND (2010) Fundamental aspects of copper electrodeposition in the hydrogen co-deposition range, Zaštita Materijala 51:197–203. https://cer.ihtm.bg.ac.rs/handle/123456789/725
Acknowledgements
The authors gratefully acknowledge the CIC Tripura University for providing FESEM pictures and NIT Arunachal Pradesh for financial assistance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Shil, B., Sen, D., Das, A.K. et al. Pool boiling performance enhancement of micro/nanoporous coated surfaces fabricated through novel hybrid method. Heat Mass Transfer 60, 47–66 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00231-023-03420-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00231-023-03420-5