Abstract
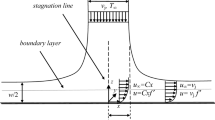
Jet impingement boiling is very efficient in cooling of hot surfaces as a part of the impinging liquid evaporates. Several studies have been carried out to measure and correlate the heat transfer to impinging jets as a function of global parameters such as jet subcooling, jet velocity, nozzle size and distance to the surface, etc. If physically based mechanistic models are to be developed, studies on the fundamentals of two-phase dynamics near the hot surface are required. In the present study the vapor–liquid structures underneath a subcooled (20 K) planar (1 mm × 9 mm) water jet, impinging the heated plate vertically with a velocity of 0.4 m/s, were analyzed by means of a miniaturized optical probe. It has a tip diameter of app. 1.5 μm and is moved toward the plate by a micrometer device. The temperature controlled experimental technique enabled steady-state experiments in all boiling regimes. The optical probe data provides information about the void fraction, the contact frequencies and the distribution of the vapor and liquid contact times as a function of the distance to the surface. The measured contact frequencies range from 40 Hz at the onset of nucleate boiling to nearly 20,000 Hz at the end of the transition boiling regime. Due to condensation in the subcooled jet vapor disappears at a distance to the surface of app. 1.2 mm in nucleate boiling. This vapor layer becomes smaller with increasing wall superheat. In film boiling a vapor film thickness of 8 ± 2 μm was found.











Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- CHF:
-
critical heat flux (W/m2)
- d d :
-
bubble departure diameter (μm)
- PIF:
-
phase indicator function (Eq. 1)
- N min :
-
minimum number of data points
- t meas :
-
measurement period (s)
- x max :
-
distance of maximum void fraction (μm)
- ε :
-
Void fraction
References
Auracher H (1987) Partielles Filmsieden in Zweiphasenströmungen, Fortschritt-Berichte VDI. VDI Verlag, Düsseldorf
Buchholz M (2005) Lokale Mechanismen des Wärmeübergangs beim Behältersieden in allen Bereichen der Siedekennlinie, Fortschritt-Berichte VDI. VDI Verlag, Düsseldorf
Buchholz M, Auracher H (2003) Improved optical probes and their validation for local measurements in two-phase flows. Proc. German-Japanese Workshop on Multi-Phase Flow Wiss Ber FZKA 6759:B1–B10
Buchholz M, Lüttich T, Auracher H, Marquardt W (2004) Experimental investigation of local processes in pool boiling along the entire boiling curve. Int J Heat Fluid Flow 25:243–261
Buchholz M, Auracher H, Lüttich T, Marquardt W (2006) A study of local heat transfer mechanisms along the entire boiling curve by means of microsensors. Int J Therm Sci 45:269–283
Liu ZH, Wang J (2001) Study on film boiling heat transfer for water jet impinging on high temperature fat plate. Int J Heat Mass Transf 44:2475–2481
Mitrovic J (1985) Wärmetransport in der Umgebung einer wachsenden Dampfblase. Wärme- Stoffübertrag 19:47–52
Miyasaka Y, Inada S, Owase Y (1980) Critical heat flux and subcooled nucleate boiling in transient region between a two-dimensional water jet and a heated surface. J Chem Eng Japan 13:29–35
Robidou H, Auracher H, Gardin P, Lebouche M (2002) Controlled cooling of a hot plate with a water jet. Exp Therm Fluid Sci 26:123–129
Robidou H, Auracher H, Gardin P, Lebouche M, Bogdanic L (2003) Local heat transfer from a hot plate to a water jet. Heat Mass Transf 39:861–867
Seiler N, Simonin O, Mimouni S, Gardin P, Seiler J (2003) Modelling and computation of heat exchanges in the configuration of an impinging jet on a hot plate. Proceedings of international conference on supercomputing in nuclear applications, SNA 2003, Paris, France
Suzuki K, Saito K, Sawada T, Torikai K (2000) An experimental study on microbubble emission boiling of water. Proceedings of the 11th international heat transfer conference, Heidelberg, Germany, pp 383–388
Timm W, Weinzierl K, Leipertz A (2003) Heat transfer in subcooled jet impingement boiling at high wall temperatures. Int J Heat Mass Transf 46:1385–1393
Torikai K, Suzuki K, Suzuki A, Watanabe T (1994) Micro-bubbles emission in subcooled transition boiling by use of multi-water-jet. Proceedings of 3rd international symposium on multiphase flow and heat transfer, Xi’an, China, pp 70–77
Vader DT (1988) Convective boiling heat transfer from a heated surface to an impinging, planar jet of water. Ph.D. thesis, Pudrue University, West Lafayette
Wolf DH (1993) Turbulent development in a free surface jet and impingement boiling heat transfer. Ph.D. thesis, Purdue University, West Lafayette
Acknowledgment
The author L. Bogdanic highly appreciates financial support of the “Berliner Programm zur Förderung der Chancengleichheit in Forschung und Lehre”.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bogdanic, L., Auracher, H. & Ziegler, F. Two-phase structure above hot surfaces in jet impingement boiling. Heat Mass Transfer 45, 1019–1028 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00231-007-0272-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00231-007-0272-5