Abstract
Objective: The present study was conducted with the aim of investigating the absolute bioavailability of fluphenazine in healthy volunteers after administration of immediate and slow release oral formulations.
Methods:
The oral dose was 12 mg fluphenazine hydrochloride. The intravenous bolus dose was 2.5 mg. Fourteen healthy volunteers of both sexes were enrolled in this randomised, crossover trial. Twelve volunteers completed the trial according to protocol.
Results:
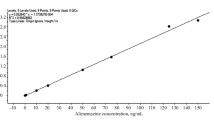
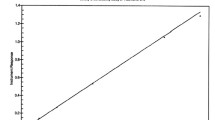
The concentration maxima after administration of the slow release formulation were approximately half those measured after the immediate release formulation and were recorded later by a factor of 2 (immediate release: Cmax = 2.3 ng⋅ml−1, tmax = 2.8 h; slow release: Cmax = 1.2 ng⋅ml−1, tmax = 4.6 h). The concentrations measured 10 min after intravenous bolus administration of 2.5 mg fluphenazine hydrochloride were approximately 100 times higher (261 ng⋅ml−1). The geometric means for the absolute bioavailability of fluphenazine were 2.7% for the immediate release formulation and 3.4% for the slow release formulation. The absolute bioavailability of fluphenazine is thus much lower than previously generally accepted.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 14 December 1995/Accepted in revised form: 26 March 1996
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Koytchev, R., Alken, RG., McKay, G. et al. Absolute bioavailability of oral immediate and slow release fluphenazine in healthy volunteers. E J Clin Pharmacol 51, 183–187 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/s002280050182
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s002280050182