Abstract
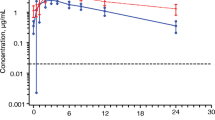
Objective: To assess the pharmacokinetics, safety and tolerability of escalating oral doses of GW420867X, a non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor, was investigated in healthy male volunteers in a randomized, double-blind placebo-controlled study. Methods: Study subjects were divided into four groups of 12 subjects (10, 50, 100 and 200-mg dose groups) with eight subjects from each group receiving active treatment and the remaining four matched placebo. Subjects were initially administered a single dose of GW420867X or placebo, and following a 24- to 28-day washout period, re-exposed to the same treatment for 14 consecutive days. Safety measurements including clinical laboratory evaluations, ECG and vital signs were performed before, during and after dosing. Results: Geometric mean GW420867X peak plasma concentrations (Cmax) following single oral doses of 10, 50, 100 and 200 mg were 160, 608, 1000 and 1662 ng/ml, respectively. Time to Cmax (t max) increased from a median value of 1 h following the 10-mg dose, to 3 h after the 200-mg dose. Geometric mean plasma areas under the curves (AUC) were 4325 (10 mg), 17,862 (50 mg), 35,295 (100 mg) and 62,338 ng/ml per hour (200 mg) and were proportionally less than the increase in the administered dose. Apparent terminal elimination half-life (t 1/2) was approximately 50 h. Following repeat dosing, accumulation ratios based on plasma AUC were: 3.0±1.0 (10 mg), 2.6±0.9 (50 mg), 1.8±0.3 (100 mg) and 1.9±0.8 (200 mg) after 14 days of dosing compared to the corresponding single dose. In general, oral clearance (CL/F) was greater after 14 days and greater with higher doses except for the 10-mg dose group. Steady-state CL/F was 2.2, 3.4, 4.2, and 5.1 l/h for 10, 50, 100, and 200 mg, respectively. Steady-state was generally achieved within 7–10 days. Comparison of single and repeat dosing with GW420867X showed that Cmax increased by a factor of between 1.4 to 1.8, after 14 days of daily dosing to 288 (10 mg), 1006 (50 mg), 1401 (100 mg) and 2613 (200 mg) ng/ml. These increases were proportionally less than the increase in the administered dose. GW420867X was well tolerated by subjects both after single and repeated dosing. Adverse effects reported by subjects on the active drug were similar to those receiving placebo. All episodes were rated as mild to moderate in severity and resolved spontaneously without further intervention. Conclusion: The pharmacokinetic findings of this study imply that systemic exposure to GW420867X decreases with increasing dose and displays time-variant pharmacokinetics, which suggests decreased absorption and/or increased clearance of GW420867X. The relatively long plasma half-life, of approximately 50 h, makes it suitable for once-daily dosing.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Accepted in revised form: 28 September 2000
Electronic Publication
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Moore, K., Cass, L., Dallow, N. et al. Pharmacokinetics and safety of escalating single and repeat oral doses of GW420867X, a novel non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 56, 805–811 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1007/s002280000224
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s002280000224