Abstract
Purpose
To establish the population pharmacokinetic (PPK) model of cyclosporine (CsA) in Chinese renal transplant recipients and evaluate the influence of various indexes including CYP3A5 and MDR1 genetic polymorphism on pharmacokinetic parameters.
Methods
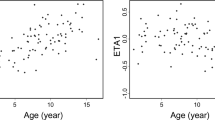
Trough (C0) and peak (C2) CsA concentration were monitored conventionally after renal transplantation. C0 and C2 were collected for 5 months in 146 patients. The CYP3A5*3 genotype and MDR1 haplotype were determined by methods based on amplification refractory mutant PCR. The data were analyzed by nonlinear mixed-effect modeling (NONMEM). The model was evaluated using goodness of fit plots and relative error measurements. Physiological and pathological factors including CYP3A5 and MDR1 genotypes were evaluated as covariates of CsA pharmacokinetic parameters.
Results
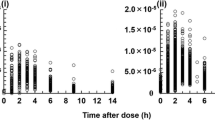
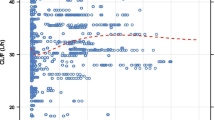
Pharmacokinetics of CsA was best described by a one-compartment disposition model followed a first-order absorption process. The estimated clearance (CL/F) was 49.5 l·h−1, the volume of distribution (Vd/F) was 226 l. Ka was fixed as 1.25 h−1. Post-transplant data, body weight, total bilirubin, and MDR1 genotype were covariates of CL/F (P < 0.005). Gender and MDR1 haplotype were covariates of Vd/F (P < 0.005). The AUC estimated based on the Bayesian method was 7,465 ± 1,708 ng·h·ml−1 (2,946 ∼13,926 ng·h·ml-1).
Conclusion
The PPK model developed in this study could be used to optimize CsA dose for Chinese renal transplant recipients by using conventional therapeutic drug monitoring (TDM) data.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
The Canadian Multicentre Transplant Study Group (1986) A randomized clinical trial of cyclosporine in cadaveric renal transplantation. Analysis at three years. N Engl J Med 314(19):1219–1225
Ponticelli C, Minetti L, Di Palo FQ, Vegeto A, Belli L, Corbetta G, Tarantino A, Civati G (1988) The Milan clinical trial with cyclosporine in cadaveric renal transplantation. A three year follow up. Transplantation 45(5):908–913
Kahan BD (2004) Therapeutic drug monitoring of cyclosporine: 20 years of progress. Transplant Proc 36(2 Suppl):378S–391S
Nankivell BJ, Hibbins M, Chapman JR (1994) Diagnostic utility of whole blood cyclosporine measurements in renal transplantation using triple therapy. Transplantation 58(9):989–996
Oellerich M, Armstrong VW, Kahan B, Shaw L, Holt DW, Yatscoff R, Lindholm A, Halloran P, Gallicano K, Wonigeit K (1995) Lake Louise Consensus Conference on cyclosporin monitoring in organ transplantation: report of the consensus panel. Ther Drug Monit 17(6):642–654
Lindholm A, Kahan BD (1993) Influence of cyclosporine pharmacokinetics, trough concentrations, and AUC monitoring on outcome after kidney transplantation. Clin Pharmacol Ther 54(2):205–218
Schroeder TJ, Hariharan S, First MR (1994) Relationship between cyclosporine bioavailability and clinical outcome in renal transplant recipients. Transplant Proc 26(5):2787–2790
Kahan BD, Grevel J (1988) Optimization of cyclosporine therapy in renal transplantation by a pharmacokinetic strategy. Transplantation 46(5):631–644
International Neoral Renal Transplantation Study Group (2002) Cyclosporine microemulsion (Neoral) absorption profiling and sparse-sample predictors during the first 3 months after renal transplantation. Am J Transplant 2(2):148–156
Lindholm A, Säwe J (1995) Pharmacokinetics and therapeutic drug monitoring of immunosuppressants. Ther Drug Monit 17(6):570–573
Cantarovich M, Barkun JS, Tchervenkov JI, Besner JG, Aspeslet L, Metrakos P (1998) Comparison of neoral dose monitoring with cyclosporine through levels versus 2-hr postdose levels in stable liver transplant patients. Transplantation 66(12):1621–1627
Morris RG, Russ GR, Cervelli MJ, Juneja R, McDonald SP, Mathew TH (2002) Comparison of trough, 2-hour, and limited AUC blood sampling for monitoring cyclosporin (Neoral) at day 7 post-renal transplantation and incidence of rejection in the first month. Ther Drug Monit 24(4):479–486
Marquet P (2005) Clinical application of population pharmacokinetic methods developed for immunosuppressive drugs. Ther Drug Monit 27(6):727–732
Awni WM (1992) Pharmacodynamic monitoring of cyclosporin. Clin Pharmacokinet 23(6):428–448
Saint-Marcoux F, Marquet P, Jacqz-Aigrain E, Bernard N, Thiry P, Le Meur Y, Rousseau A (2006) Patient characteristics influencing ciclosporin pharmacokinetics and accurate Bayesian estimation of ciclosporin exposure in heart, lung and kidney transplant patients. Clin Pharmacokinet 45(9):905–922
Dai D, Tang J, Rose R, Hodgson E, Bienstock RJ, Mohrenweiser HW, Goldstein JA (1992) Identification of variants of CYP3A4 and characterization of their abilities to metabolize testosterone and chlorpyrifos. Biochem Pharmacol 43(10):2201–2208
Hsieh KP, Lin YY, Cheng CL, Lai ML, Lin MS, Siest JP, Huang JD (2001) Novel mutations of CYP3A4 in Chinese. Drug Metab Dispos 29(3):268–273
Balram C, Zhou Q, Cheung YB, Lee EJ (2003) CYP3A5*3 and *6 single nucleotide polymorphisms in three distinct Asian populations. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 59(2):123–126
Miao LY, Huang CR, Hou JQ, Qian MY (2008) Association study of ABCB1 and CYP3A5 gene polymorphisms with sirolimus trough concentration and dose requirements in Chinese renal transplant recipients. Biopharm Drug Dispos 29(1):1–5
Ambudkar SV, Kimchi-Sarfaty C, Sauna ZE, Gottesman MM (2003) P-glycoprotein: from genomics to mechanism. Oncogene 22(47):7468–7485
Marzolini C, Paus E, Buclin T, Kim RB (2004) Polymorphisms in human MDR1 (P-glycoprotein): recent advances and clinical relevance. Clin Pharmacol Ther 75:13–33
Sakaeda T, Nakamura T, Okumura K (2002) MDR1 genotype-related pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics. Biol Pharm Bull 25:1391–1400
Chen B, Zhang W, Fang J, Jin Z, Li J, Yu Z, Cai W (2009) Influence of the MDR1 haplotype and CYP3A5 genotypes on cyclosporine blood level in Chinese renal transplant recipients. Xenobiotica 39(12):931–938
Cockcroft DW, Gault MH (1976) Prediction of creatinine clearance from serum creatinine. Nepharon 16:31–41
Traub SL, Johnson CE (1980) Comparison of methods of estimating creatinine clearance in children. Am J Hosp Pharm 37:195–201
Chen B, Fang J, Zhang W, Jin Z, Yu Z, Cai W (2009) Detection of C1236T, G2677T/A, and C3435T polymorphism of MDR1 by amplification refractory mutation system PCR. J Clin Lab Anal 23(2):110–116
Barrett JC, Fry B, Maller J, Daly MJ (2005) Haploview: analysis and visualization of LD and haplotype maps. Bioinformatics 21(2):263–265
Wu KH, Cui YM, Guo JF, Zhou Y, Zhai SD, Cui FD, Lu W (2005) Population pharmacokinetics of cyclosporine in clinical renal transplant patients. Drug Metab Dispos 33(9):1268–1275
Schädeli F, Marti HP, Frey FJ, Uehlinger DE (2002) Population pharmacokinetic model to predict steady-state exposure to once-daily cyclosporin microemulsion in renal transplant recipients. Clin Pharmacokinet 41(1):59–69
Chowbay B, Cumaraswamy S, Cheung YB, Zhou Q, Lee EJ (2003) Genetic polymorphisms in MDR1 and CYP3A4 genes in Asians and the influence of MDR1 haplotypes on cyclosporin disposition in heart transplant recipients. Pharmacogenetics 13(2):89–95
Tang K, Ngoi SM, Gwee PC, Chua JM, Lee EJ, Chong SS, Lee CG (2002) Distinct haplotype profiles and strong linkage disequilibrium at the MDR1 multidrug transporter gene locus in three ethnic Asian populations. Pharmacogenetics 12:425–427
Keown P, Landsberg D, Halloran P, Shoker A, Rush D, Jeffery J, Russell D, Stiller C, Muirhead N, Cole E, Paul L, Zaltzman J, Loertscher R, Daloze P, Dandavino R, Boucher A, Handa P, Lawen J, Belitsky P, Parfrey P (1996) A randomized, prospective multicenter pharmacoepidemiologic study of cyclosporine microemulsion in stable renal graft recipients. Report of the Canadian Neoral Renal Transplantation Study Group. Transplantation 62(12):1744–1752
David OJ, Johnston A (2001) Limited sampling strategies for estimating cyclosporin area under the concentration-time curve: review of current algorithms. Ther Drug Monit 23(2):100–114
Rosenbaum SE, Baheti G, Trull AK, Akhlaghi F (2005) Population pharmacokinetics of cyclosporine in cardiopulmonary transplant recipients. Ther Drug Monit 27(2):116–122
Fanta S, Jönsson S, Backman JT, Karlsson MO, Hoppu K (2007) Developmental pharmacokinetics of ciclosporin—a population pharmacokinetic study in paediatric renal transplant candidates. Br J Clin Pharmacol 64(6):772–784
Grevel J, Post BK, Kahan BD (1993) Michaelis-Menten kinetics determine cyclosporine steady-state concentrations: a population analysis in kidney transplant patients. Clin Pharmacol Ther 53(6):651–660
Parke J, Charles BG (2000) Factors affecting oral cyclosporin disposition after heart transplantation: bootstrap validation of a population pharmacokinetic model. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 56(6–7):481–487
Irtan S, Saint-Marcoux F, Rousseau A, Zhang D, Leroy V, Marquet P, Jacqz-Aigrain E (2007) Population pharmacokinetics and bayesian estimator of cyclosporine in pediatric renal transplant patients. Ther Drug Monit 29(1):96–102
Lampen A, Christians U, Bader A, Hackbarth I, Sewing KF (1996) Drug interactions and interindividual variability of ciclosporin metabolism in the small intestine. Pharmacology 52(3):159–168
Lown KS, Kolars JC, Thummel KE, Barnett JL, Kunze KL, Wrighton SA, Watkins PB (1994) Interpatient heterogeneity in expression of CYP3A4 and CYP3A5 in small bowel. Lack of prediction by the erythromycin breath test. Drug Metab Dispos 22(6):947–955
Hustert E, Haberl M, Burk O, Wolbold R, He YQ, Klein K, Nuessler AC, Neuhaus P, Klattig J, Eiselt R, Koch I, Zibat A, Brockmöller J, Halpert JR, Zanger UM, Wojnowski L (2001) The genetic determinants of the CYP3A5 polymorphism. Pharmacogenetics 11:773–779
Kuehl P, Zhang J, Lin Y, Lamba J, Assem M, Schuetz J, Watkins PB, Daly A, Wrighton SA, Hall SD, Maurel P, Relling M, Brimer C, Yasuda K, Venkataramanan R, Strom S, Thummel K, Boguski MS, Schuetz E (2001) Sequence diversity in CYP3A promoters and characterization of the genetic basis of polymorphic CYP3A5 expression. Nat Genet 27:383–391
Min DI, Ellingrod VL, Marsh S, McLeod H (2004) CYP3A5 polymorphism and the ethnic differences in cyclosporine pharmacokinetics in healthy subjects. Ther Drug Monit 26(5):524–528
Haufroid V, Mourad M, Van Kerckhove V, Wawrzyniak J, De Meyer M, Eddour DC, Malaise J, Lison D, Squifflet JP, Wallemacq P (2004) The effect of CYP3A5 and MDR1 (ABCB1) polymorphisms on cyclosporine and tacrolimus dose requirements and trough blood levels in stable renal transplant patients. Pharmacogenetics 14(3):147–154
Fredericks S, Jorga A, MacPhee IA, Reboux S, Shiferaw E, Moreton M, Carter ND, Holt DW, Johnston A (2007) Multi-drug resistance gene-1 (MDR1) haplotypes and the CYP3A5*1 genotype have no influence on ciclosporin dose requirements as assessed by C0 or C2 measurements. Clin Transplant 21(2):252–257
Thiebaut F, Tsuruo T, Hamada H, Gottesman MM, Pastan I, Willingham MC (1987) Cellular localization of the multidrug-resistance gene product P-glycoprotein in normal human tissues. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 84:7735–7738
Schinkel AH, Jonker JW (2003) Mammalian drug efflux transporters of the ATP binding cassette (ABC) family: an overview. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 55(1):3–29
Christians U, Sewing KF (1993) Cyclosporin metabolism in transplant patients. Pharmacol Ther 57(2–3):291–345
Lindholm A (1991) Factors influencing the pharmacokinetics of cyclosporine in man. Ther Drug Monit 13:464–477
Acknowledgement
Supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 30500626).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, B., Zhang, W., Gu, Z. et al. Population pharmacokinetic study of cyclosporine in Chinese renal transplant recipients. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 67, 601–612 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00228-010-0959-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00228-010-0959-2