Abstract
Aim
To compare the time course of morphine and metabolite concentrations in serum and cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) after intravenous and intramuscular administration after surgery.
Methods
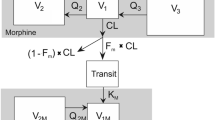
This was a randomized double-blind, double-dummy study in patients who had undergone hip replacement surgery. Morphine (M, 10 mg) was administered intravenously (IV) or intramuscularly (IM). Arterial blood and CSF samples (from a spinal catheter) were drawn simultaneously at 10, 30, 60, and 120 min after administration. Morphine and metabolites [morphine-3-glucuronide (M-3-G), morphine-6-glucuronide (M-6-G), and normorphine (NM)] were determined by a validated liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry method.
Results
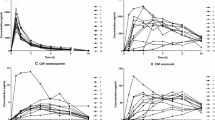
Thirty-eight patients were included: 13 men and 25 women, 20 in the IV, 18 in the IM group. Serum concentrations of M after 10 min were consistently higher after IM than IV, concentrations of M-3-G and M-6-G after IM surpassed those of IV after 45 min. NM was not found. None of the metabolites was found in CSF. CSF morphine concentrations and CSF/serum concentration ratios were consistently higher after IV compared to IM. The mean AUCCSF/AUCserum (0–120 min) concentration ratios were 0.18 and 0.09 after IV and IM, respectively.
Conclusions
The uptake of morphine to the CSF was consistently higher after IV administration than after IM already after 10 min. The higher CSF concentration may be caused by an initially higher morphine blood/CSF gradient following IV morphine injection. The pharmacokinetic findings are compatible with a more rapid and extensive initial effect of IV morphine compared with IM.



Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- AUC:
-
area under the time-concentration curve
- CSF:
-
cerebrospinal fluid
- IV:
-
intravenous
- IM:
-
intramuscular
- LCMSMS:
-
liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry
- LOQ:
-
limit of quantification
- M:
-
morphine
- M-3-G:
-
morphine-3-glucuronide
- M-6-G:
-
morphine-6-glucuronide
- NM:
-
normorphine
- t max :
-
time to maximum concentration
References
Kuhn S, Cooke K, Collins M, Jones JM, Mucklow JC (1990) Perceptions of pain relief after surgery. BMJ 300(6741):1687–1690
Moote CA (1994) The prevention of postoperative pain. Can J Anaesth 41(6):527–533
Ready LB (1992) The acute pain service. Acta Anaesthesiol Belg 43(1):21–27
Dahlstrom B, Tamsen A, Paalzow L, Hartvig P (1982) Patient-controlled analgesic therapy. Part IV: pharmacokinetics and analgesic plasma concentrations of morphine. Clin Pharmacokinet 7(3):266–279
Kirkpatrick T, Henderson PD, Nimmo WS (1988) Plasma morphine concentrations after intramuscular injection into the deltoid or gluteal muscles. Anaesthesia 43(4):293–295
Stanski DR, Greenblatt DJ, Lowenstein E (1978) Kinetics of intravenous and intramuscular morphine. Clin Pharmacol Ther 24(1):52–59
Nordberg G, Borg L, Hedner T, Mellstrand T (1985) CSF and plasma pharmacokinetics of intramuscular morphine. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 27(6):677–681
Laizure SC, Miller JH, Stevens RC, Donahue DJ, Laster RE, Brown D (1993) The disposition and cerebrospinal fluid penetration of morphine and its two major glucuronidated metabolites in adults undergoing lumbar myelogram. Pharmacotherapy 13(5):471–475
Meineke I, Freudenthaler S, Hofmann U, Schaeffeler E, Mikus G, Schwab M, Prange HW, Gleiter CH, Brockmoller J (2002) Pharmacokinetic modelling of morphine, morphine-3-glucuronide and morphine-6-glucuronide in plasma and cerebrospinal fluid of neurosurgical patients after short-term infusion of morphine. Br J Clin Pharmacol 54(6):592–603
D’Honneur G, Gilton A, Sandouk P, Scherrmann JM, Duvaldestin P (1994) Plasma and cerebrospinal fluid concentrations of morphine and morphine glucuronides after oral morphine. The influence of renal failure. Anesthesiology 81(1):87–93
Klepstad P, Kaasa S, Skauge M, Borchgrevink PC (2000) Pain intensity and side effects during titration of morphine to cancer patients using a fixed schedule dose escalation. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand 44(6):656–664
Tyrefors N, Hyllbrant B, Ekman L, Johansson M, Langstrom B (1996) Determination of morphine, morphine-3-glucuronide and morphine-6-glucuronide in human serum by solid-phase extraction and liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry with electrospray ionisation. J Chromatogr A 729(1–2):279–285
Kvalsvik O, Borchgrevink PC, Hagen L, Dale O (2003) Randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study of the effect of rectal paracetamol on morphine consumption after abdominal hysterectomy. Acta Anaesth Scand 47(4):451–456
Nau R, Zysk G, Thiel A, Prange HW (1993) Pharmacokinetic quantification of the exchange of drugs between blood and cerebrospinal fluid in man. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 45(5):469–475
Hain RD, Hardcastle A, Pinkerton CR, Aherne GW (1999) Morphine and morphine-6-glucuronide in the plasma and cerebrospinal fluid of children. Br J Clin Pharmacol 48(1):37–42
Upton RN, Semple TJ, Macintyre PE (1997) Pharmacokinetic optimisation of opioid treatment in acute pain therapy. Clin Pharmacokinet 33(3):225–244
Bjorkman S, Akeson J, Helfer M, Fyge A, Gustafsson LL (1995) Cerebral uptake of morphine in the pig calculated from arterio-venous plasma concentration gradients: an alternative to tissue microdialysis. Life Sci 57(25):2335–2345
Hand CW, Moore RA, McQuay HJ, Allen MC, Sear JW (1987) Analysis of morphine and its major metabolites by differential radioimmunoassay. Ann Clin Biochem 24(Pt 2):153–160
Wolff T, Samuelsson H, Hedner T (1996) Concentrations of morphine and morphine metabolites in CSF and plasma during continuous subcutaneous morphine administration in cancer pain patients. Pain 68(2–3):209–216
Wolff T, Samuelsson H, Hedner T (1995) Morphine and morphine metabolite concentrations in cerebrospinal fluid and plasma in cancer pain patients after slow-release oral morphine administration. Pain 62(2):147–154
Lotsch J, Weiss M, Ahne G, Kobal G, Geisslinger G (1999) Pharmacokinetic modeling of M6G formation after oral administration of morphine in healthy volunteers. Anesthesiology 90(4):1026–1038
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful to Trine N Andreassen, M.Sc., for analysing the biological samples. We are also grateful to Dr. Ingolf Meineke, Ph.D., University of Göttingen, Germany, for placing his data to our disposal for analysis of his 90- and 120-min samples. This study complied with Norwegian legislation.
Conflict of interest
None
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dale, O., Thoner, J., Nilsen, T. et al. Serum and cerebrospinal fluid morphine pharmacokinetics after single doses of intravenous and intramuscular morphine after hip replacement surgery. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 63, 837–842 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00228-007-0329-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00228-007-0329-x